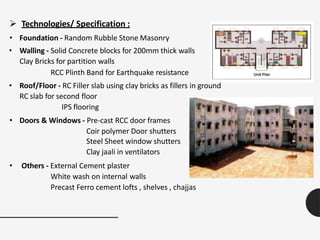
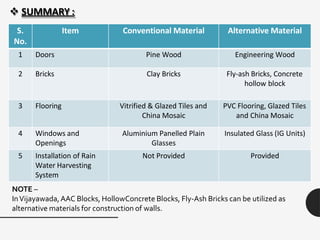
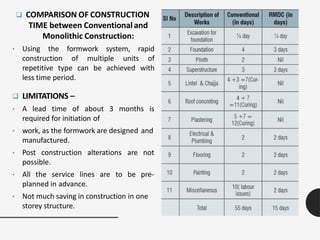
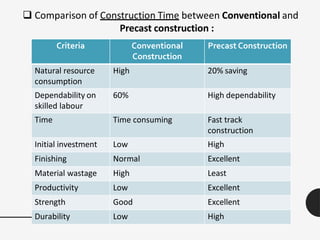
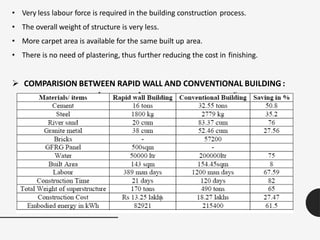
The document discusses the rapid growth of the construction industry and the challenges posed by traditional building materials, highlighting the need for sustainable alternatives. It details various eco-friendly building materials and innovative construction technologies that can reduce costs and construction time while remaining durable and energy-efficient. Case studies illustrate the successful implementation of alternative materials and modern techniques for low-cost housing solutions.