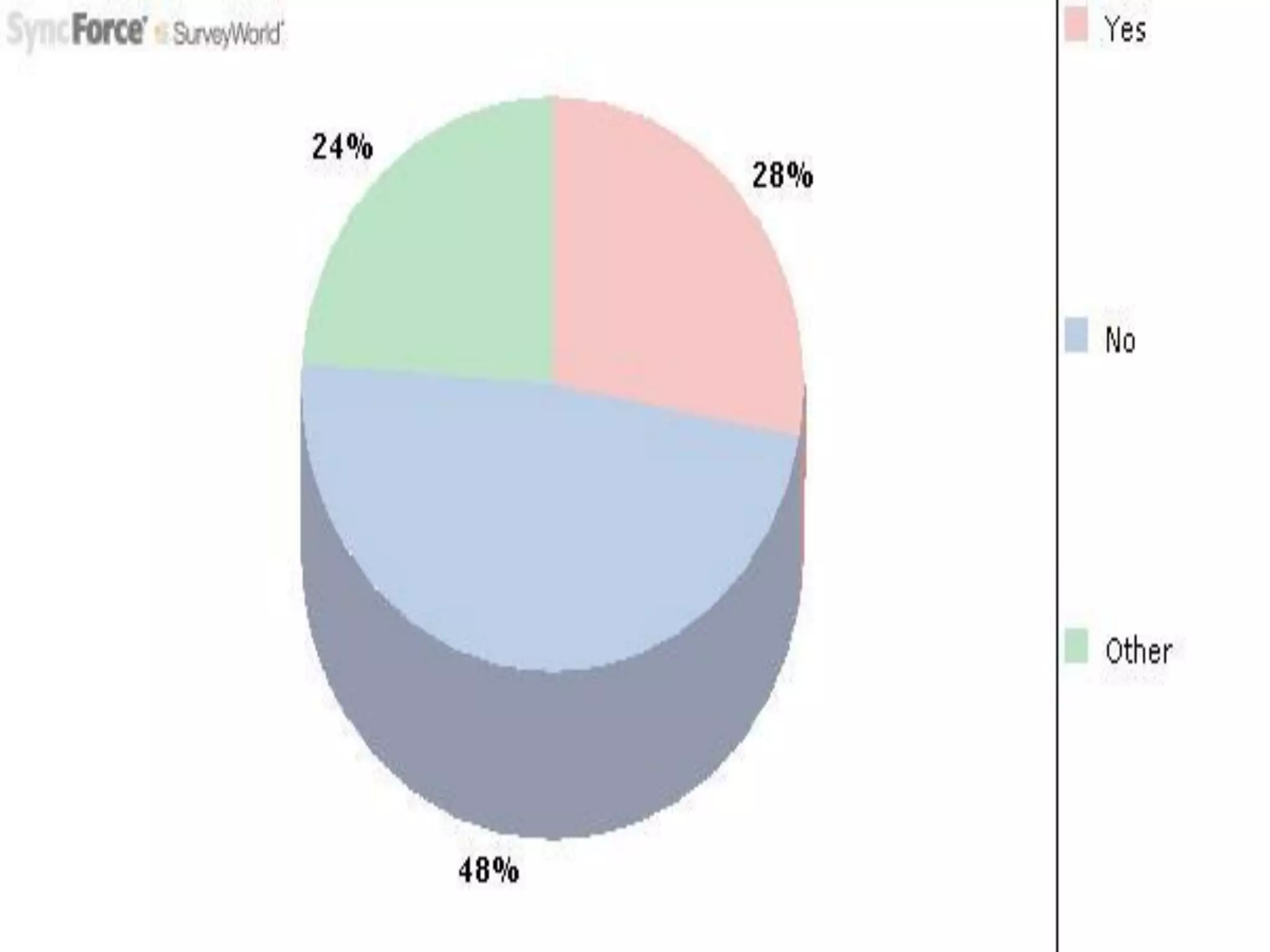
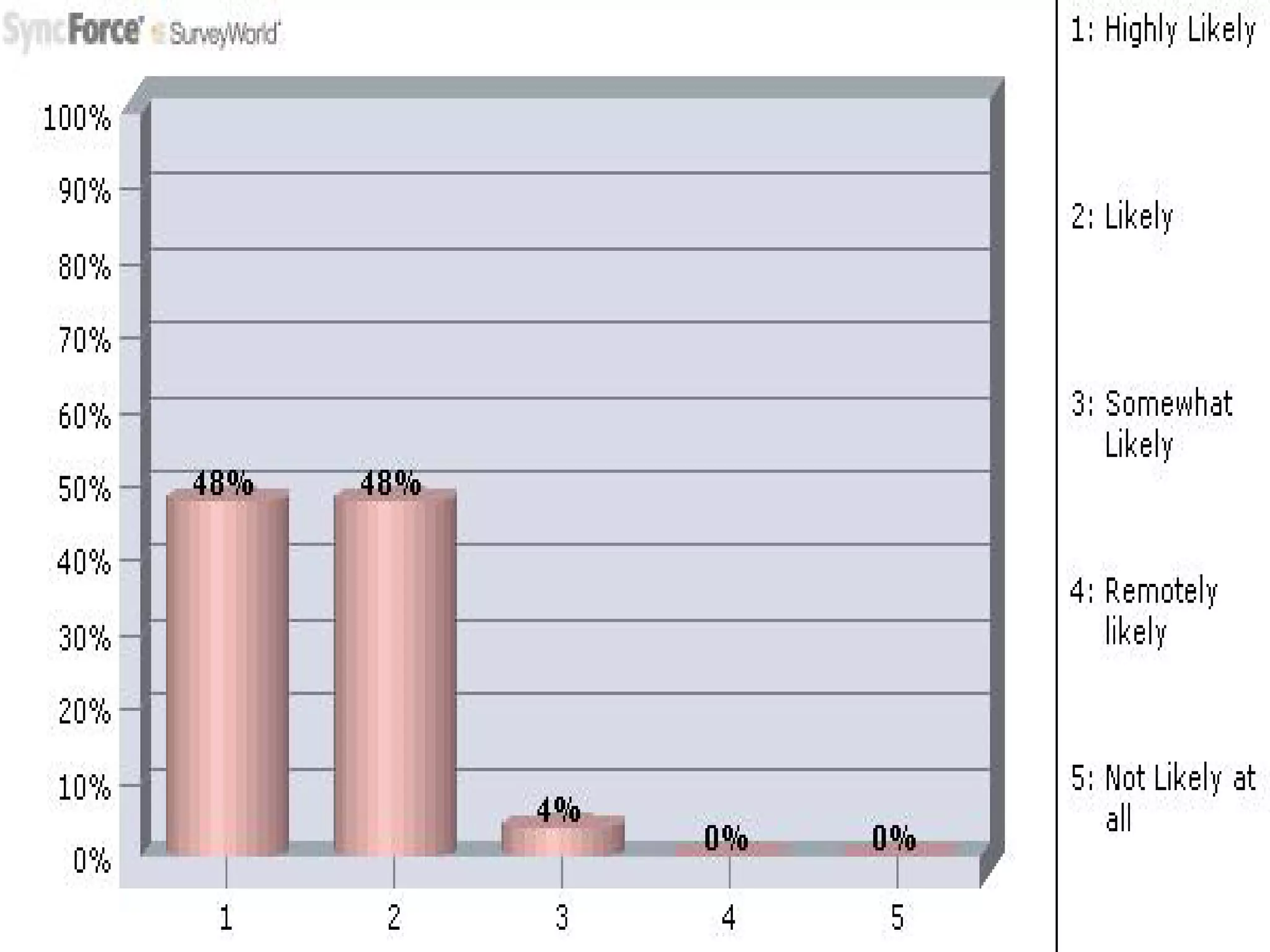
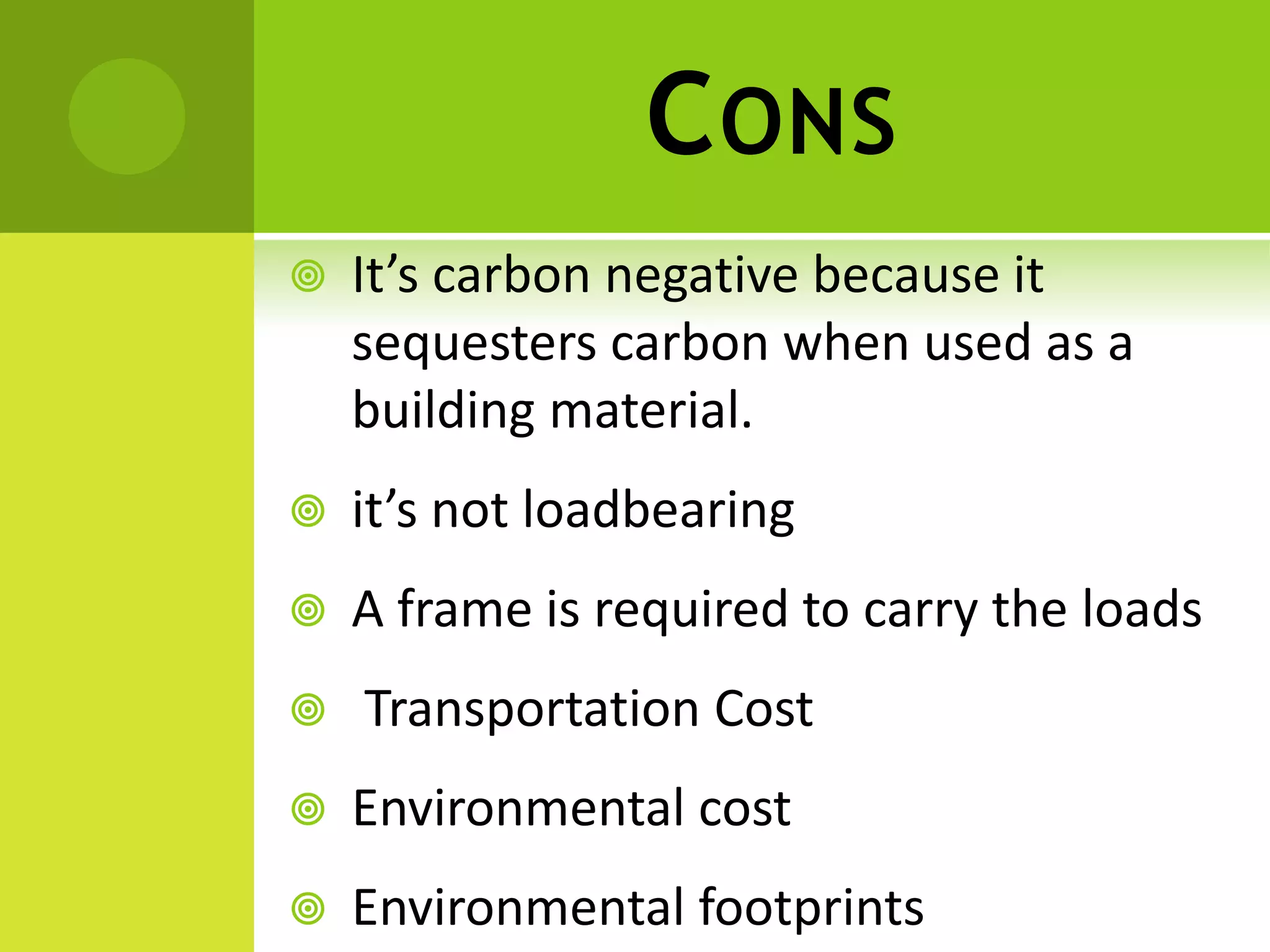
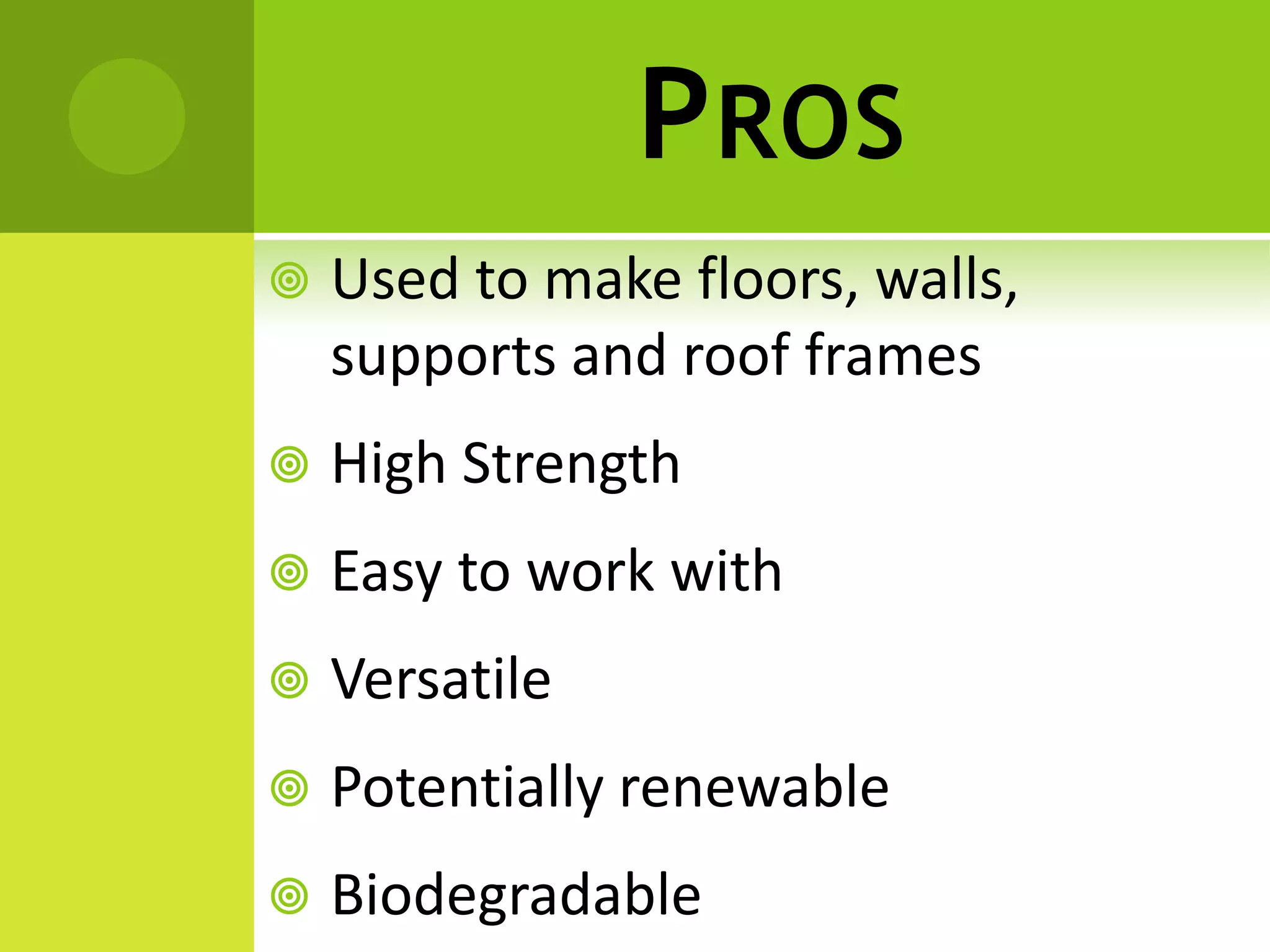
The document discusses decision making for selecting materials for green building construction. It describes green buildings as structures that reduce natural resource consumption and meet certain sustainability standards. The document outlines various green building materials like compressed earth block, hemp block, timber, and their pros and cons. It also details the decision making process, which involves problem recognition, information gathering, establishing evaluation principles, brainstorming alternatives, analyzing alternatives based on principles, and selecting the optimal material. For the given problem of green building construction, compressed earth block is selected as the best material due to its economic feasibility, high strength, and environmental benefits.