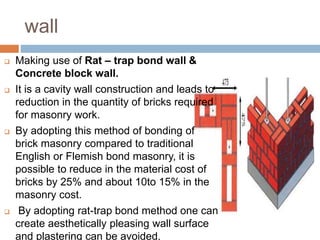
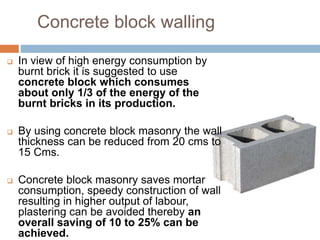
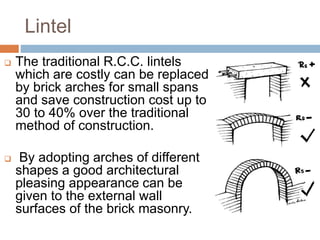
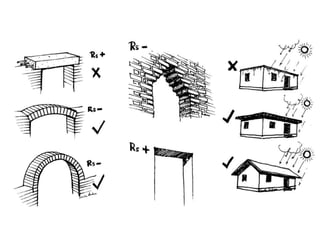
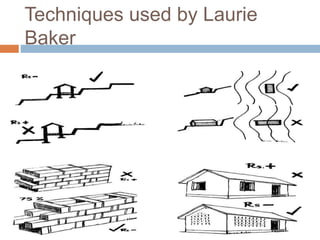
The document discusses low-cost housing solutions in India, emphasizing the need for affordable and efficient construction techniques to meet the growing demand for shelter. It outlines various modern building methods, including modular planning, recycling materials, and innovative construction practices that can reduce costs and environmental impact. Additionally, it highlights initiatives like IIT Madras's use of glass fiber reinforced gypsum panels for quick and cost-effective housing construction.