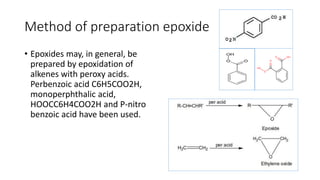
Epoxides are cyclic ethers characterized by a three-membered oxirane ring and can be prepared through the epoxidation of alkenes with peroxy acids or by reactions involving chlorohydrins. They are generally reactive due to ring strain and can yield various products through hydrolysis and reactions with Grignard reagents. Epoxides have practical applications in the production of adhesives and surface coatings, notably in the formation of epoxy resins from epichlorohydrin and bisphenol A.