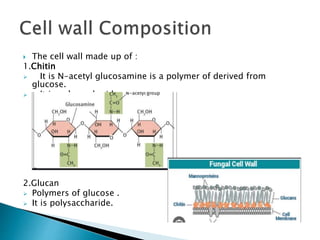
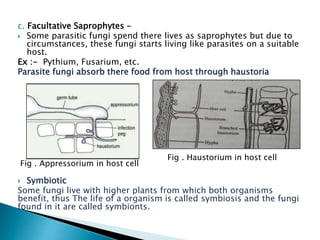
The document discusses the cell wall composition and nutrition of fungi. It states that fungi cell walls are composed of chitin and glucan, which are polysaccharides. It also describes the different types of fungi based on their nutrition - saprophytes, which feed on dead organic matter; parasites, which feed on living hosts; and symbiotic fungi, which have a mutually beneficial relationship with their hosts. Finally, it outlines some of the economic importance of fungi in areas like food, medicine, nitrogen fixation, and various industries.