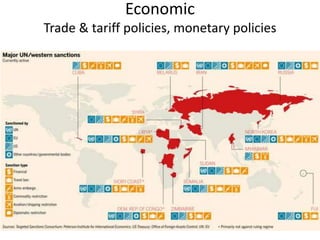
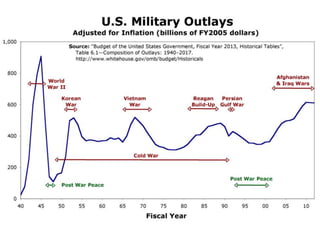
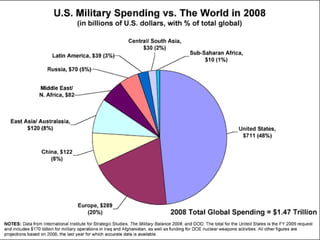
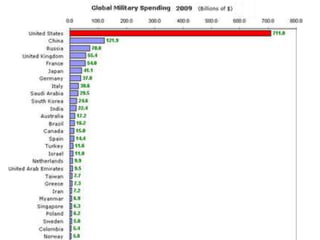
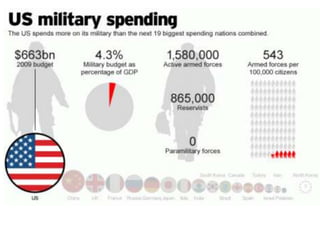
The document summarizes key aspects of US national security policymaking, including foreign policy instruments like the military, economics, and diplomacy. It outlines actors involved in foreign relations such as international organizations, regional groups, companies, NGOs, and individuals. It describes policymakers like the President, diplomats, national security establishment, and Congress. It provides an overview of periods in US foreign policy history from isolationism to the present War on Terror. It also briefly mentions military policy areas.