The document discusses different perspectives and models of curriculum. It begins by defining curriculum as a plan for learning that organizes teacher-student interactions and content. It then outlines traditional and progressive views of curriculum. Traditional views see curriculum as a body of subjects prepared by teachers, while progressives emphasize learner needs and experiences.
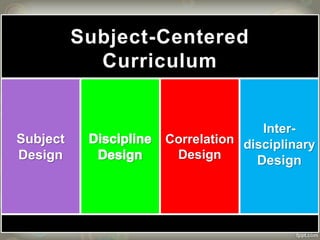
The document also describes three curriculum design models: subject-centered focuses on content divided into subjects; learner-centered considers student interests; and problem-centered integrates related content across subjects. Finally, it notes the Philippines uses a subject-centered structure in schools and discusses strengths and weaknesses of different approaches.