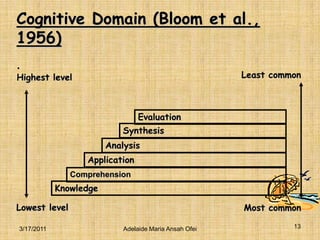
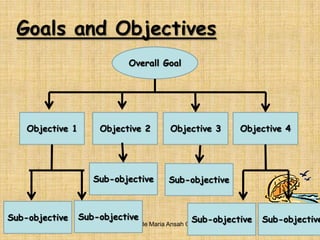
The document discusses curriculum goals, learning objectives, and their importance in education. It defines goals as broad statements about what students should know or be able to do upon graduating. Objectives are more specific and measurable statements about the intended behavioral changes and skills students will exhibit after a learning experience. The document also outlines different types of objectives, such as general vs specific, and taxonomies for classifying objectives, including Bloom's Taxonomy for cognitive objectives, Krathwohl's Taxonomy for affective objectives, and Harrow's Taxonomy for psychomotor objectives. Goals are more general while objectives should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-bound to guide lesson planning and evaluation.