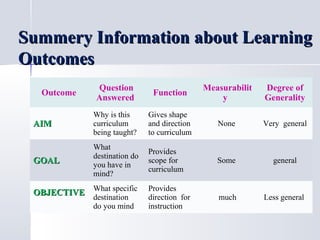
The document discusses curriculum design and the development of learning outcomes and experiences. It defines key terms like intended learning outcomes, aims, goals, and objectives. Intended learning outcomes represent what learners are expected to be able to do with curriculum content. Aims are general statements of purpose, goals are more measurable but still broad, and objectives are narrow and specific. Objectives provide direction for instruction and assessment. Effective learning experiences are determined by outlining the purpose, outcomes, assessment, content, and resources. The document also discusses alternative approaches to local curriculum decision making, with examples of school-based and district-level processes.