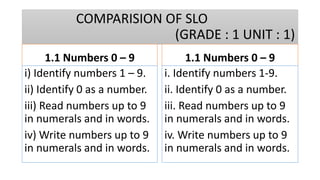
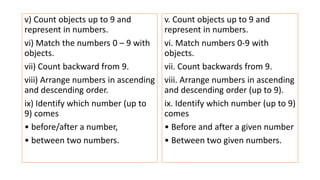
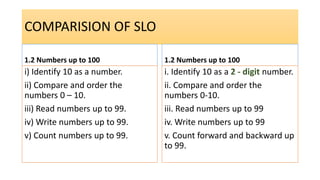
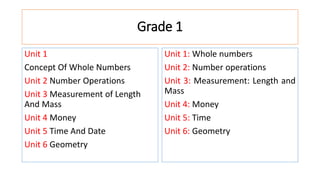
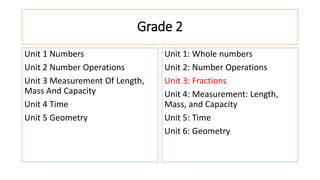
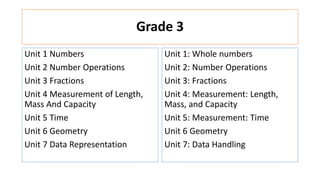
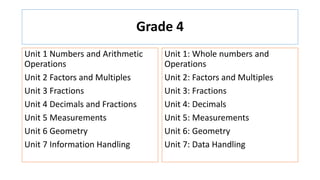
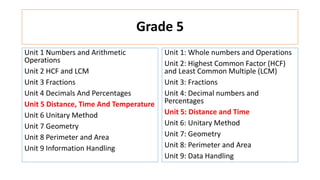
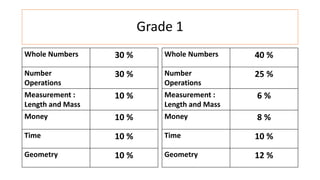
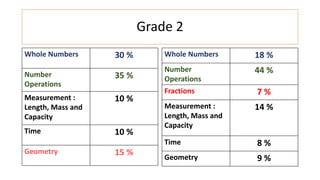
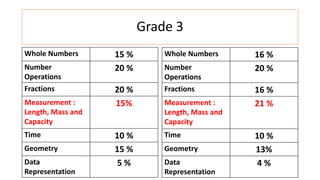
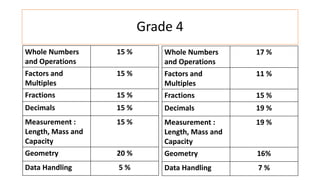
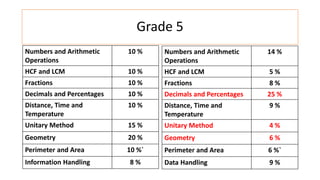
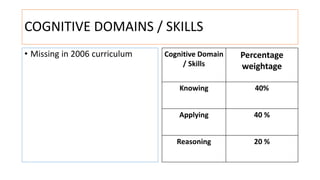
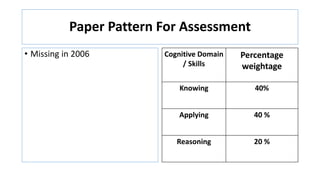
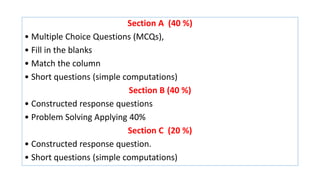
The document compares the mathematics curriculum and standards between the 2006 National Curriculum and the 2020 Single National Curriculum (SNC) in Pakistan. It shows that the core strands and standards of Numbers and Operations, Algebra, Geometry and Measurement, and Data Handling remain the same, but Reasoning and Logical Thinking is now underpinned across all strands in the SNC. The SNC also re-groups grades, updates benchmarks, standards, and student learning outcomes to emphasize application, problem-solving, and mathematical thinking over rote learning. Unit structures, weightages, and cognitive domains are also adjusted in the SNC.