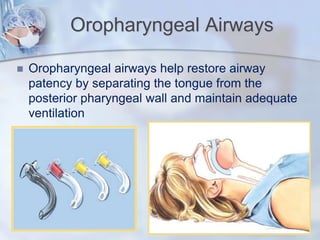
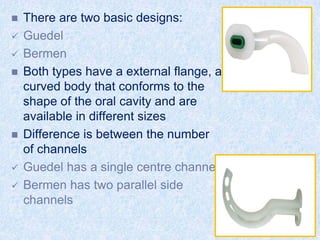
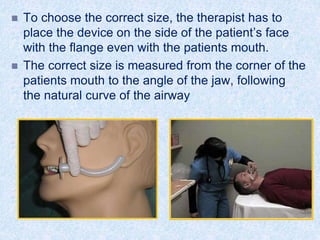
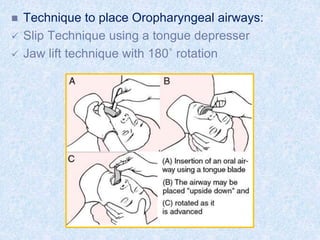
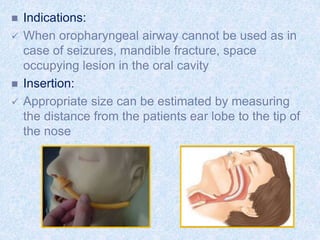
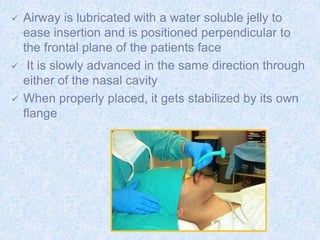
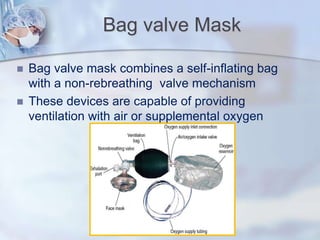
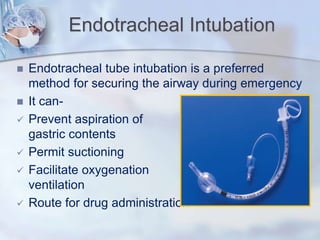
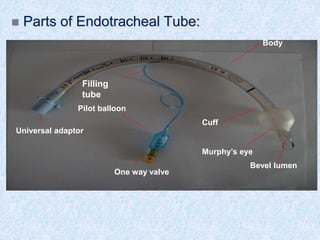
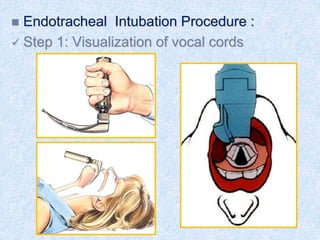
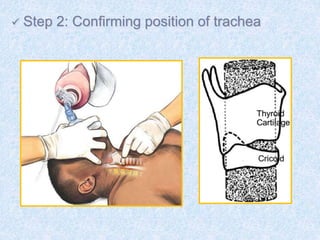
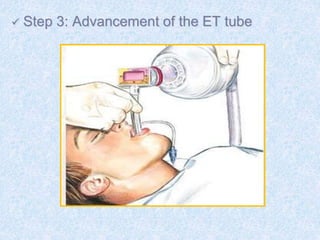
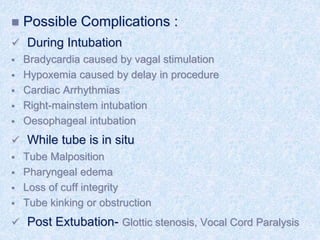
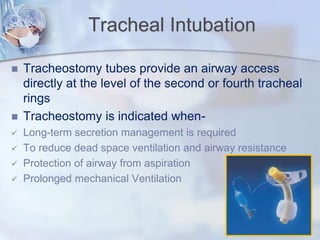
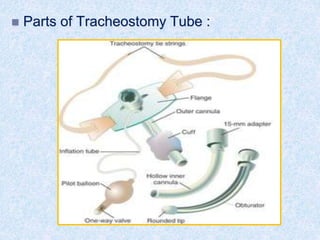
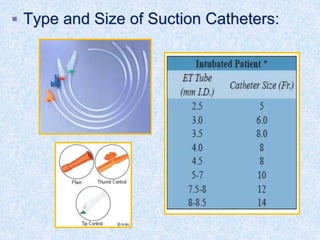
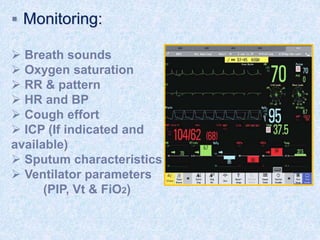
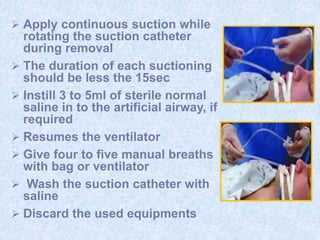
The document discusses advanced airway care techniques including oropharyngeal, nasopharyngeal, and endotracheal airways, detailing their insertion methods, indications, and potential complications. It emphasizes the importance of suctioning and manual hyperinflation for patients with artificial airways, outlining procedure steps and necessary precautions. Moreover, it addresses the risks associated with these procedures and the need for careful monitoring during airway management.