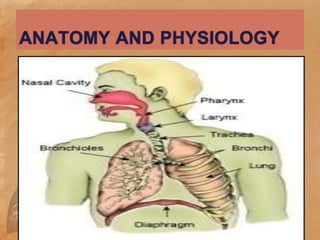
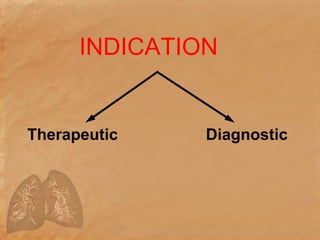
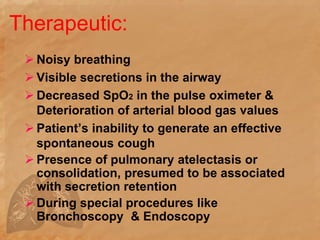
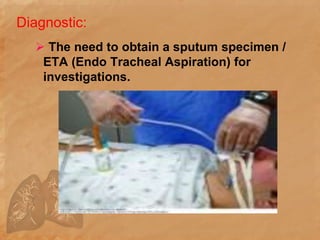
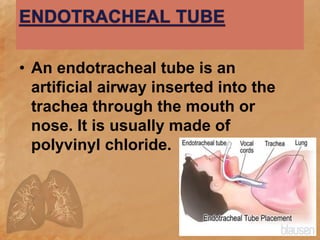
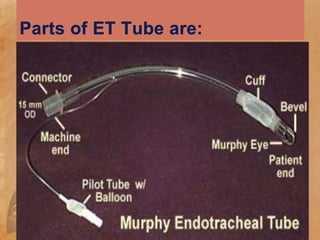
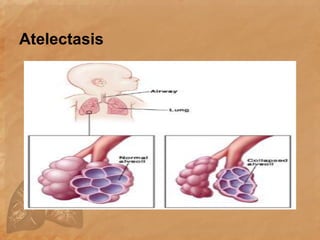
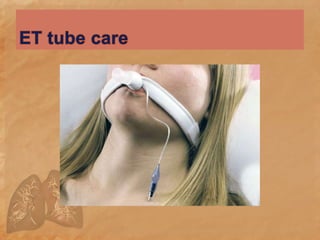
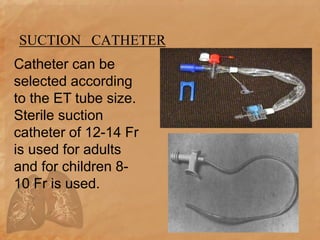
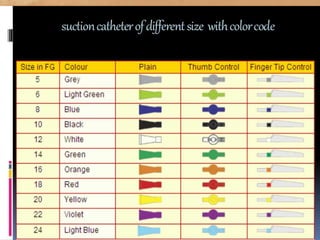
Endotracheal suctioning involves removing secretions from a patient's airway using a suction catheter inserted through an endotracheal tube. It is done to clear the airway and improve breathing. The nurse must properly assess the patient, prepare equipment, gently insert and withdraw the catheter while suction is applied, and monitor the patient after. Endotracheal suctioning requires sterile technique and care to avoid complications like infection, bleeding, or damage to the airway.