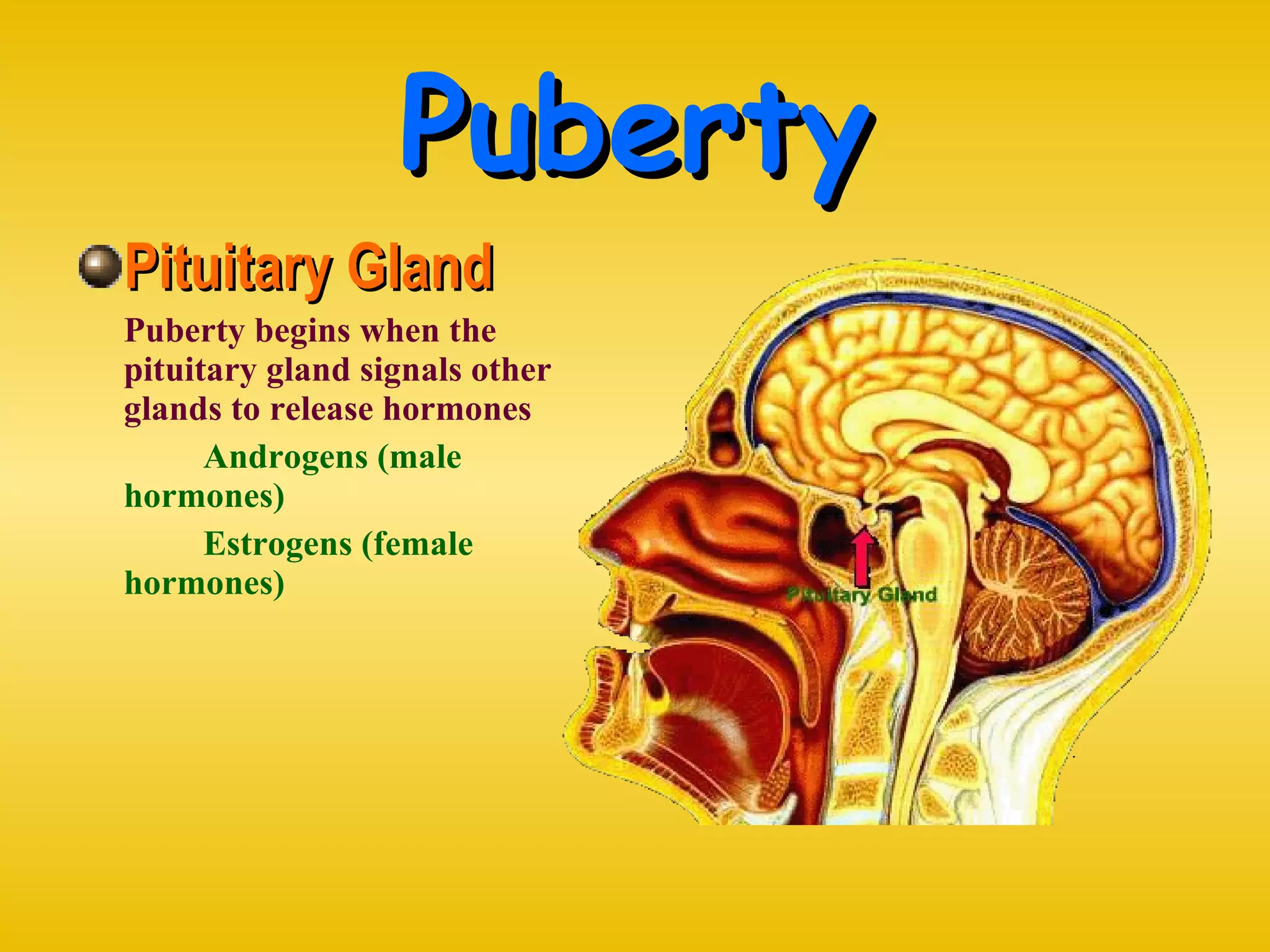
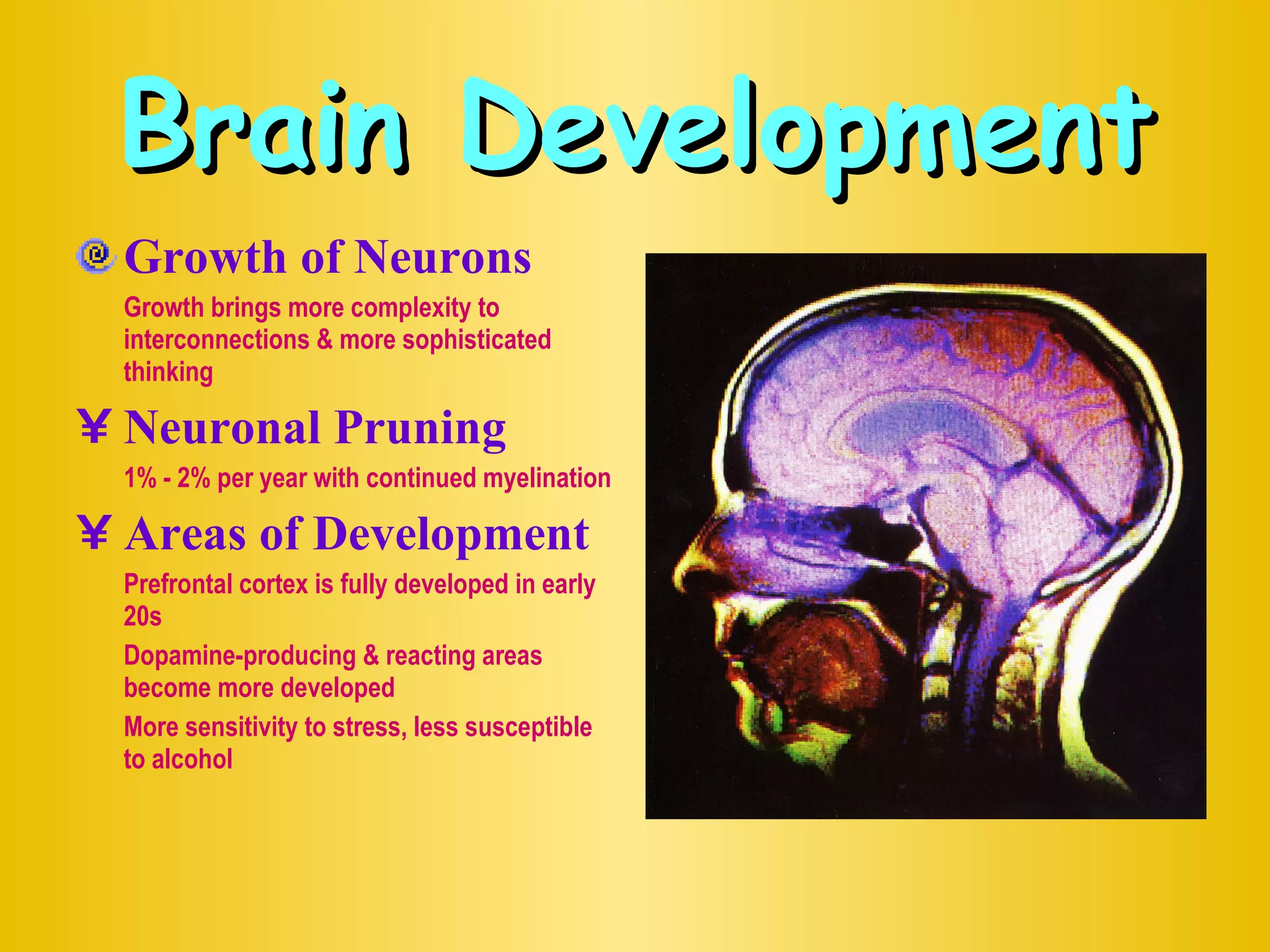
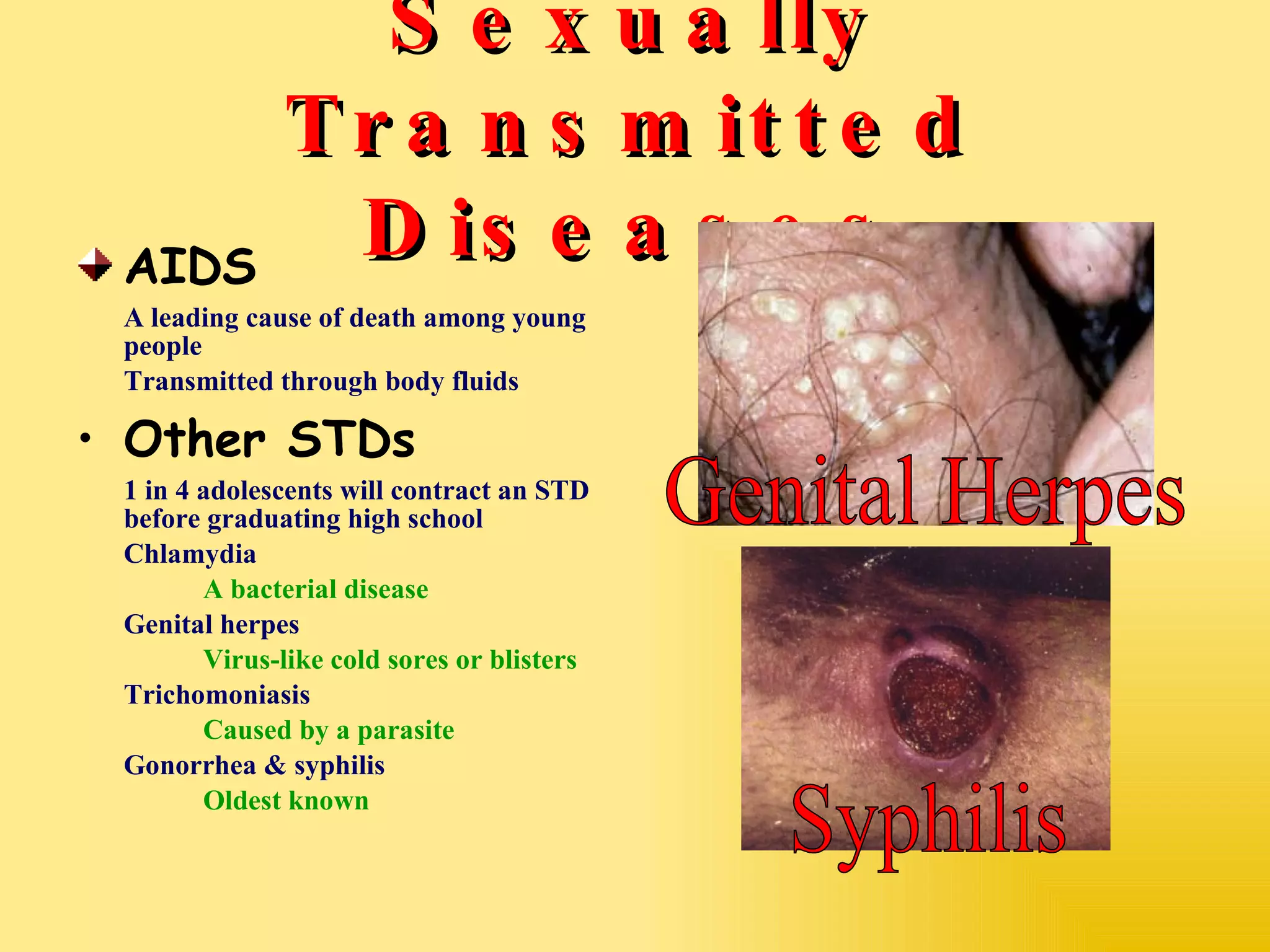
This document defines adolescence and describes some key physical, psychological, and social changes that occur during this developmental period. It discusses the onset of puberty through the maturation of sex organs and secondary sex characteristics. It also outlines factors like nutrition, stress, brain development, substance use, and sexual health risks that can impact adolescents' well-being.