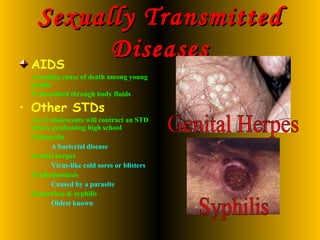
The document discusses physical, cognitive, and social development during adolescence. It covers changes in puberty like growth spurts and sexual maturation. It also discusses relationships, sexuality, health issues like STDs and obesity, cognitive changes, school performance, and risks like substance abuse.