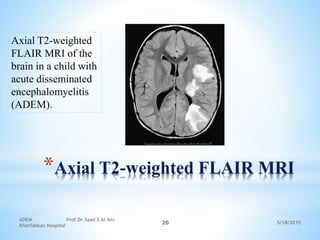
The document discusses acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), a rare inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. ADEM is typically triggered by an environmental stimulus in genetically susceptible individuals. It most commonly affects children between 5-8 years old, with symptoms developing within 2 weeks of a viral or bacterial infection in approximately 50-75% of cases. Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation and MRI findings showing multifocal brain inflammation. Treatment involves high-dose corticosteroids, with plasma exchange or IVIG recommended for non-responders. Most children recover fully, but some have residual symptoms like headaches or behavioral issues.