Embed presentation
Downloaded 156 times






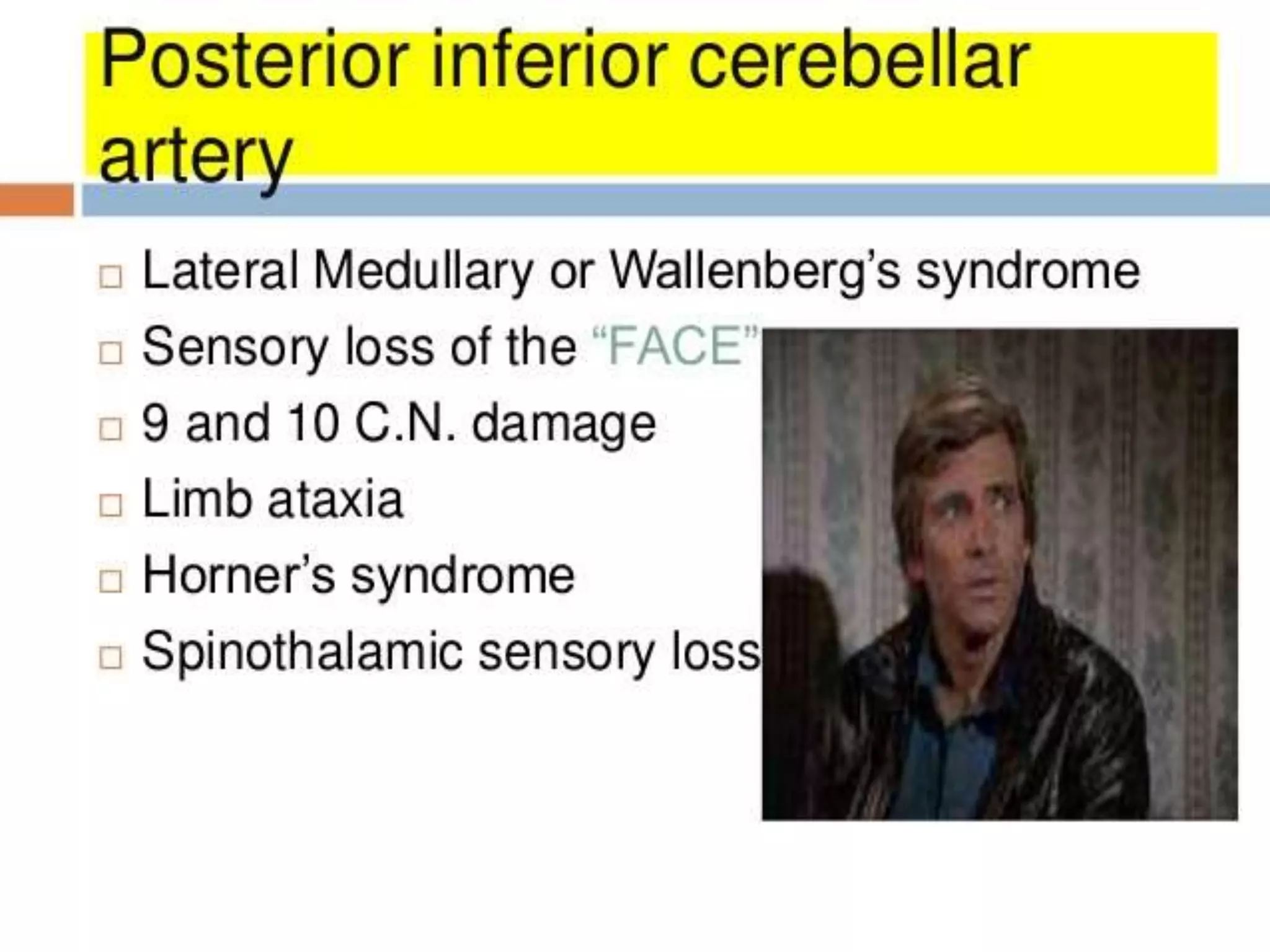
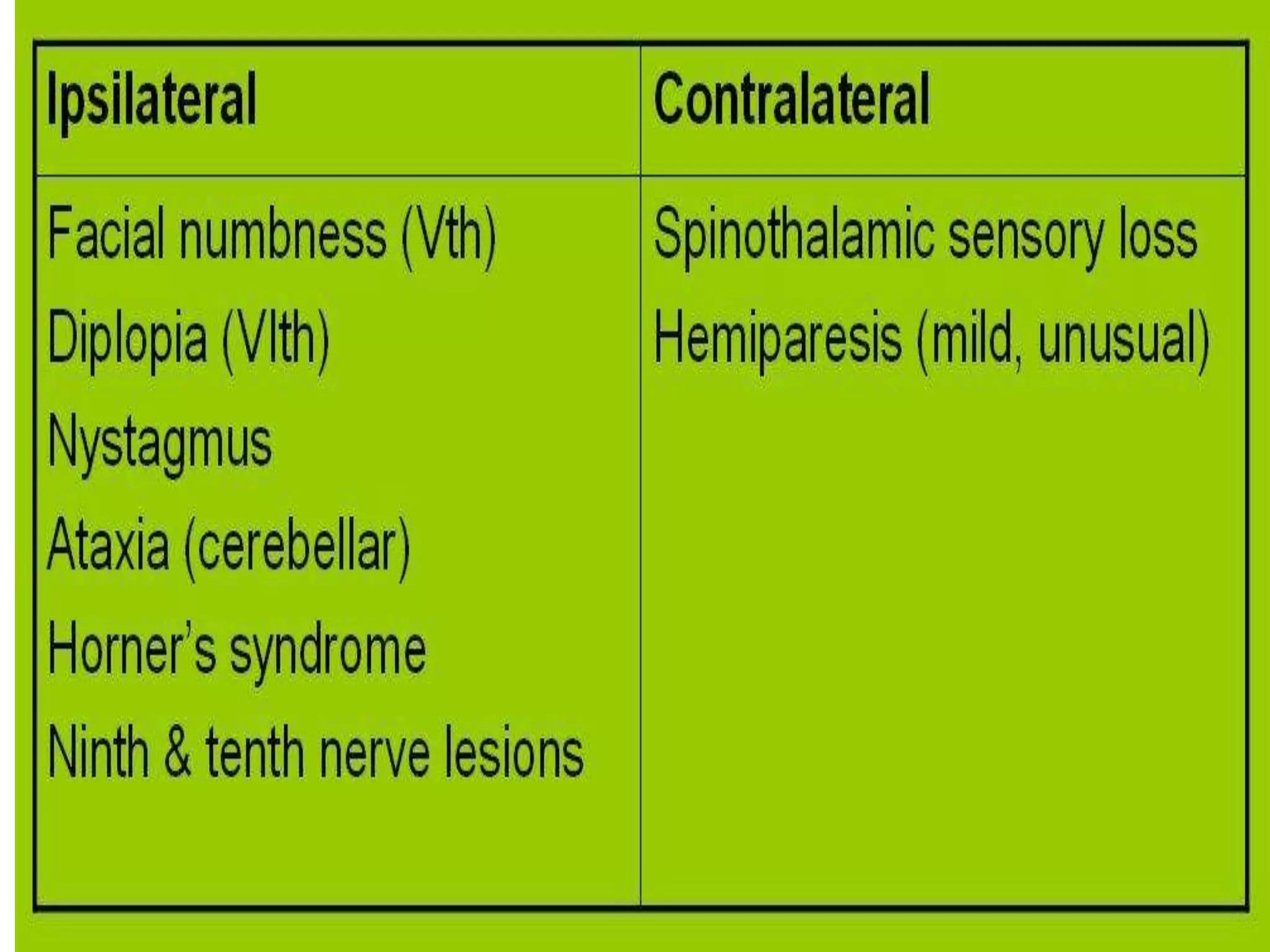

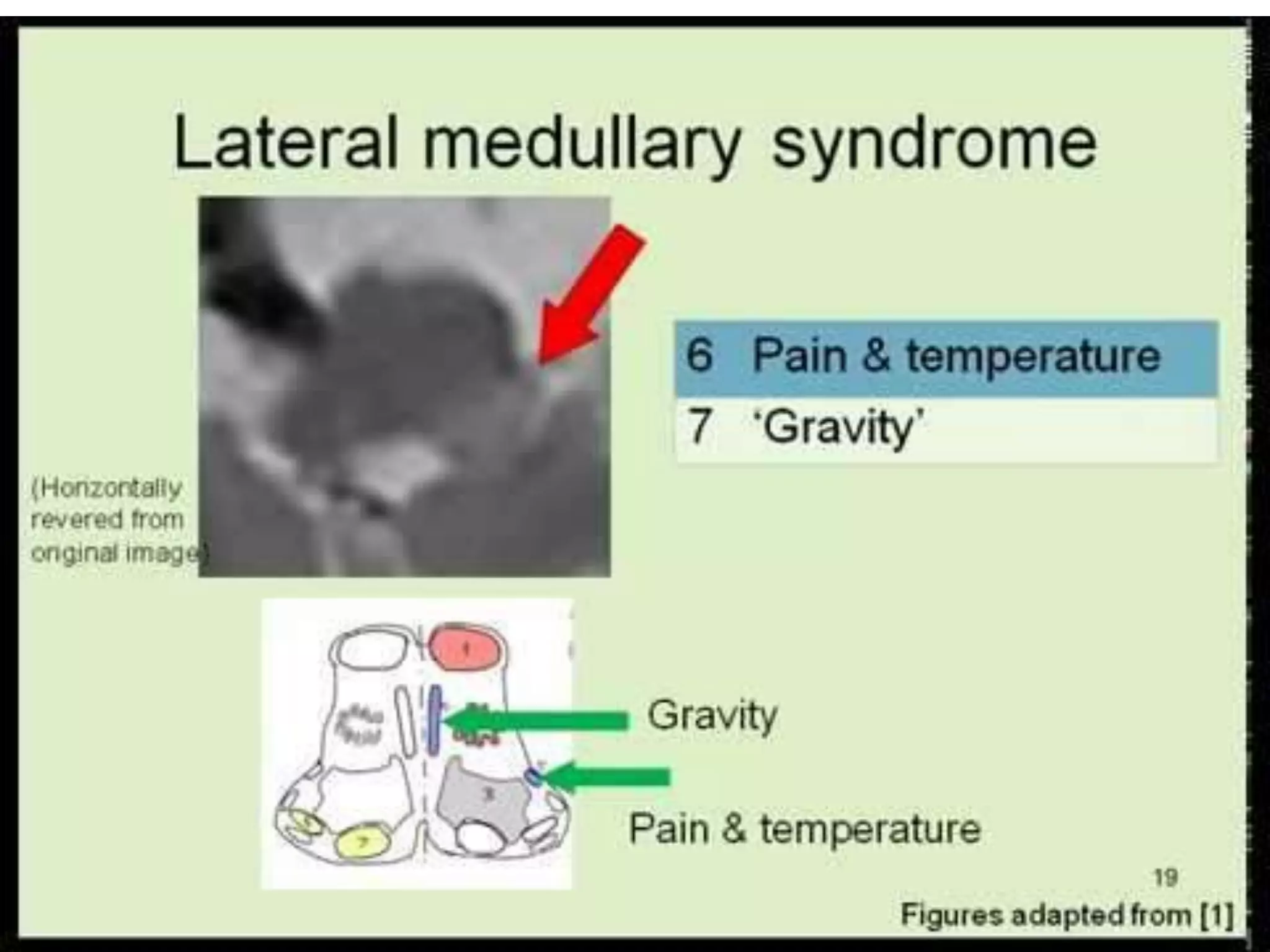

Wallenberg syndrome, also known as lateral medullary infarction, is caused by occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery, which supplies blood to the lateral medulla. This leads to vertigo, abnormal eye movements, Horner's syndrome on one side, ataxia of the limb on the same side, and dissociated sensory loss. The condition is usually due to atherosclerosis but can also result from traumatic vertebral artery dissection. MRI and MRA are used to diagnose the infraction and rule out arterial dissection.









