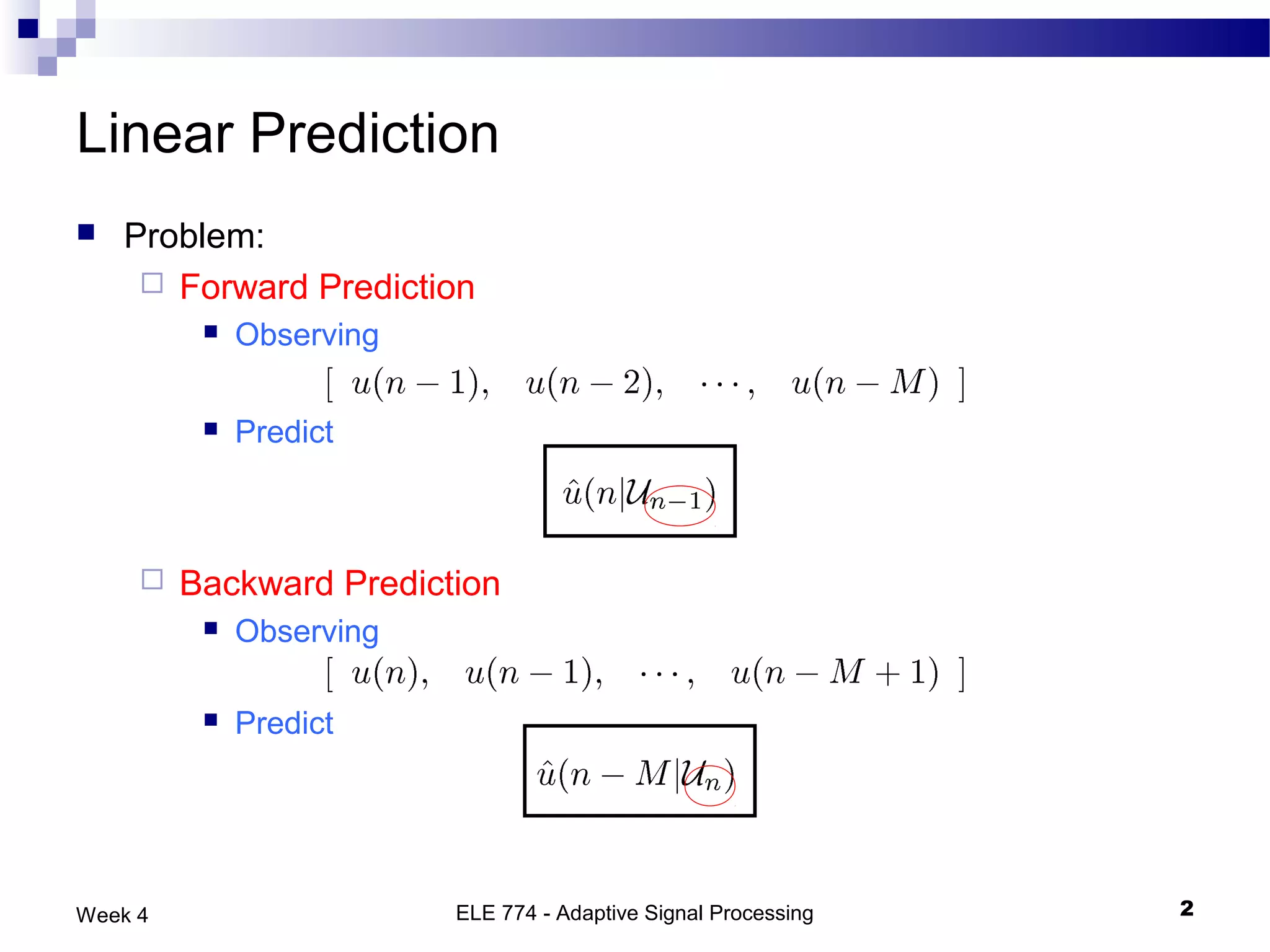
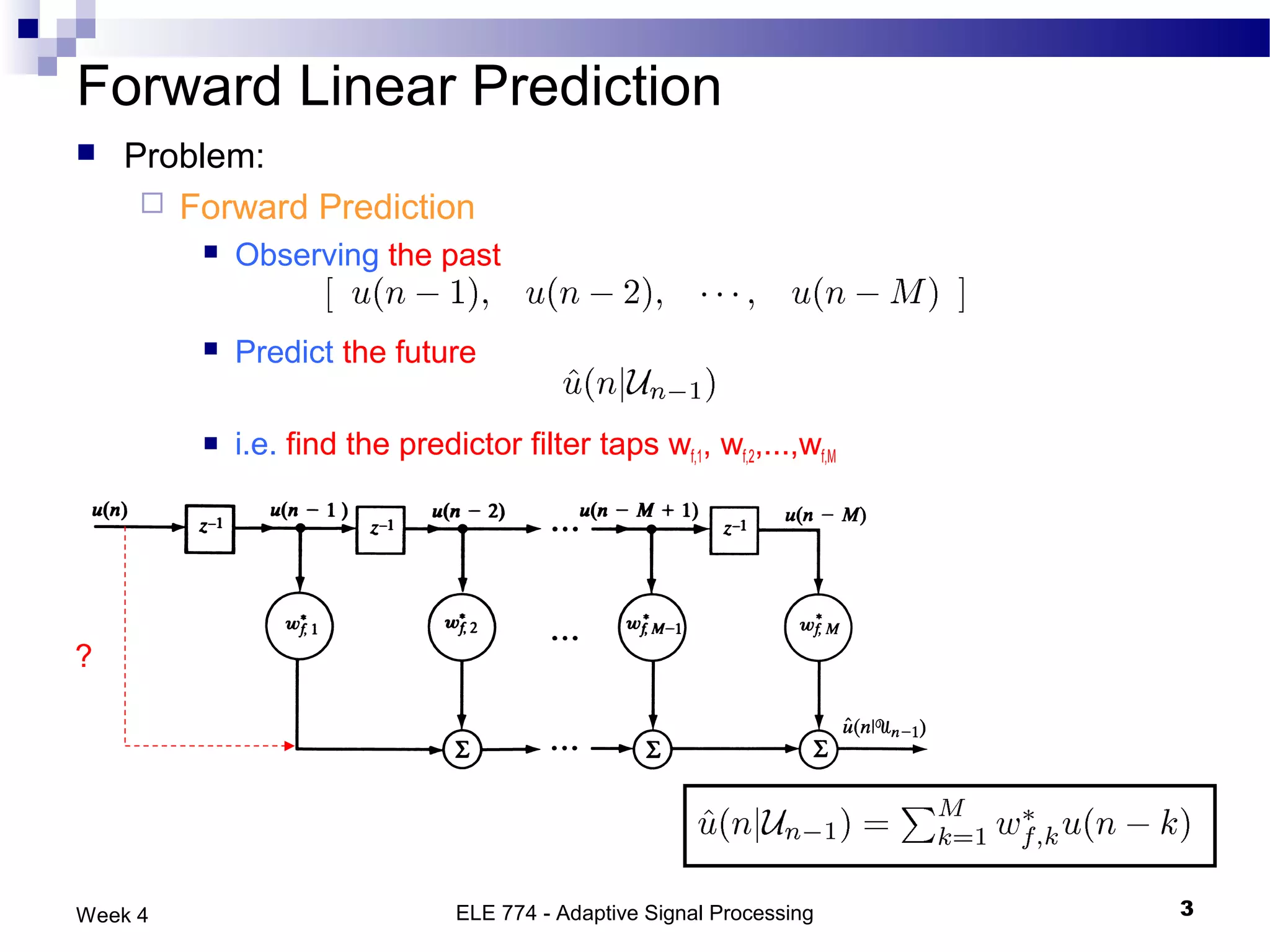
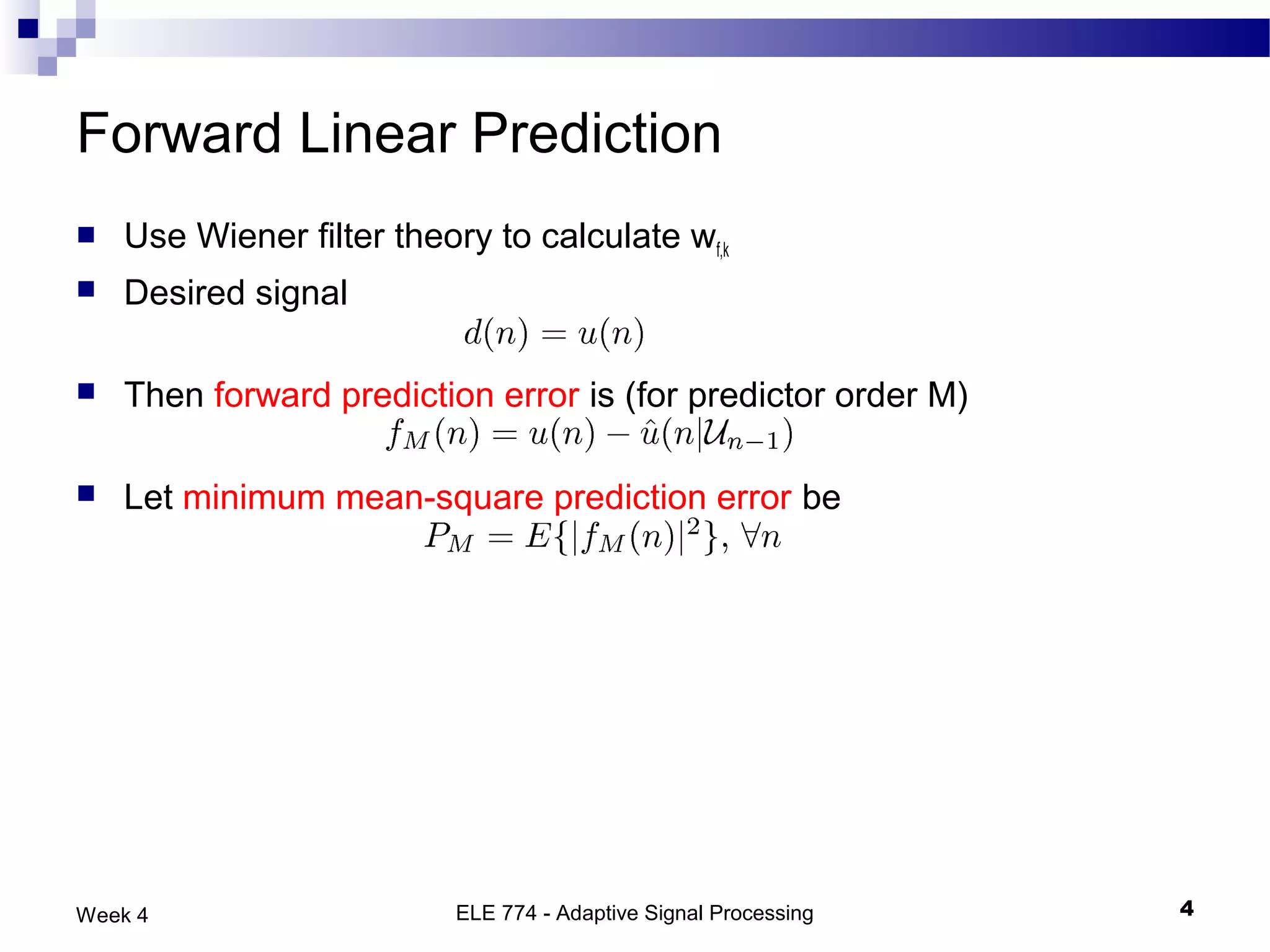
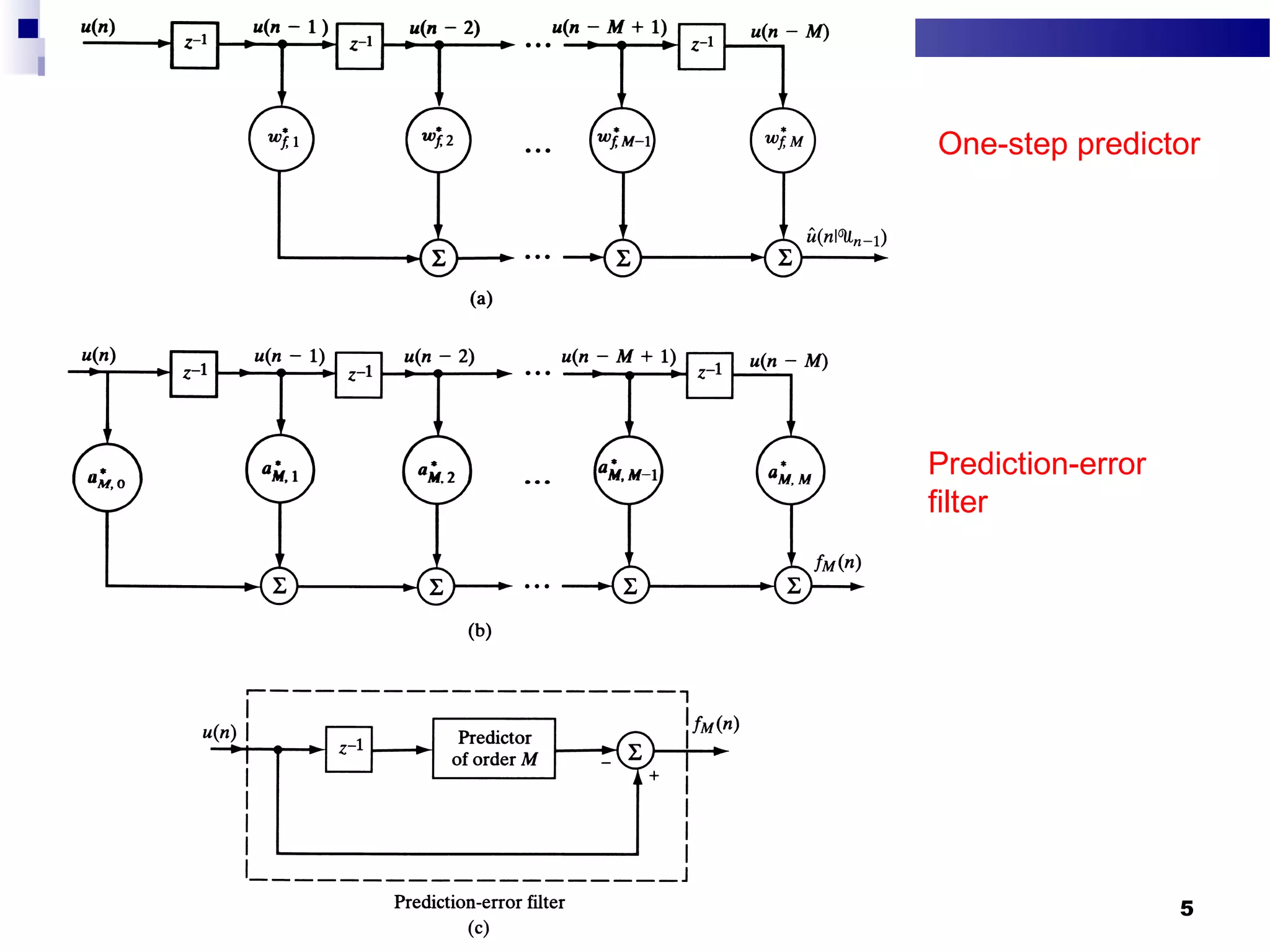
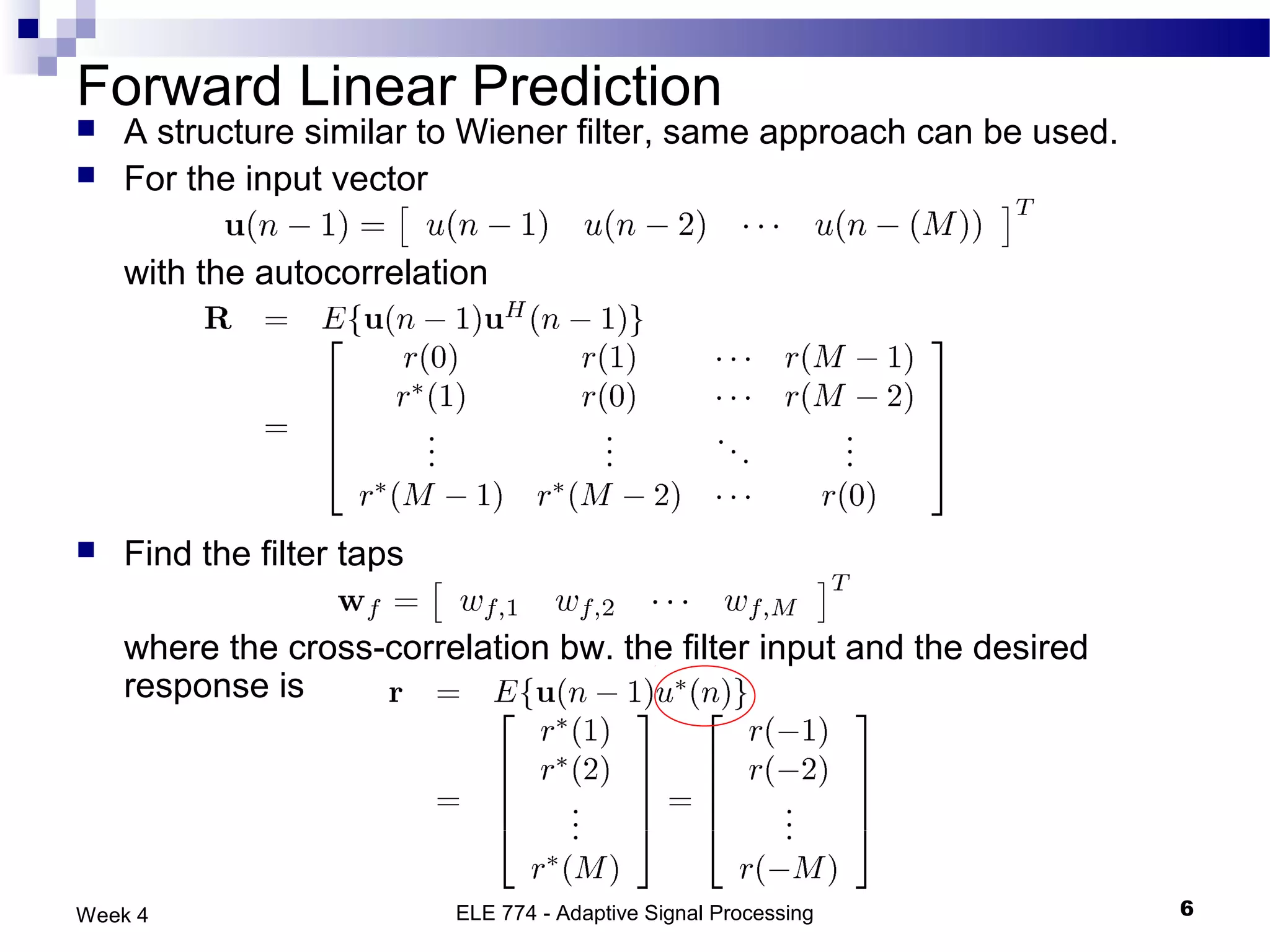
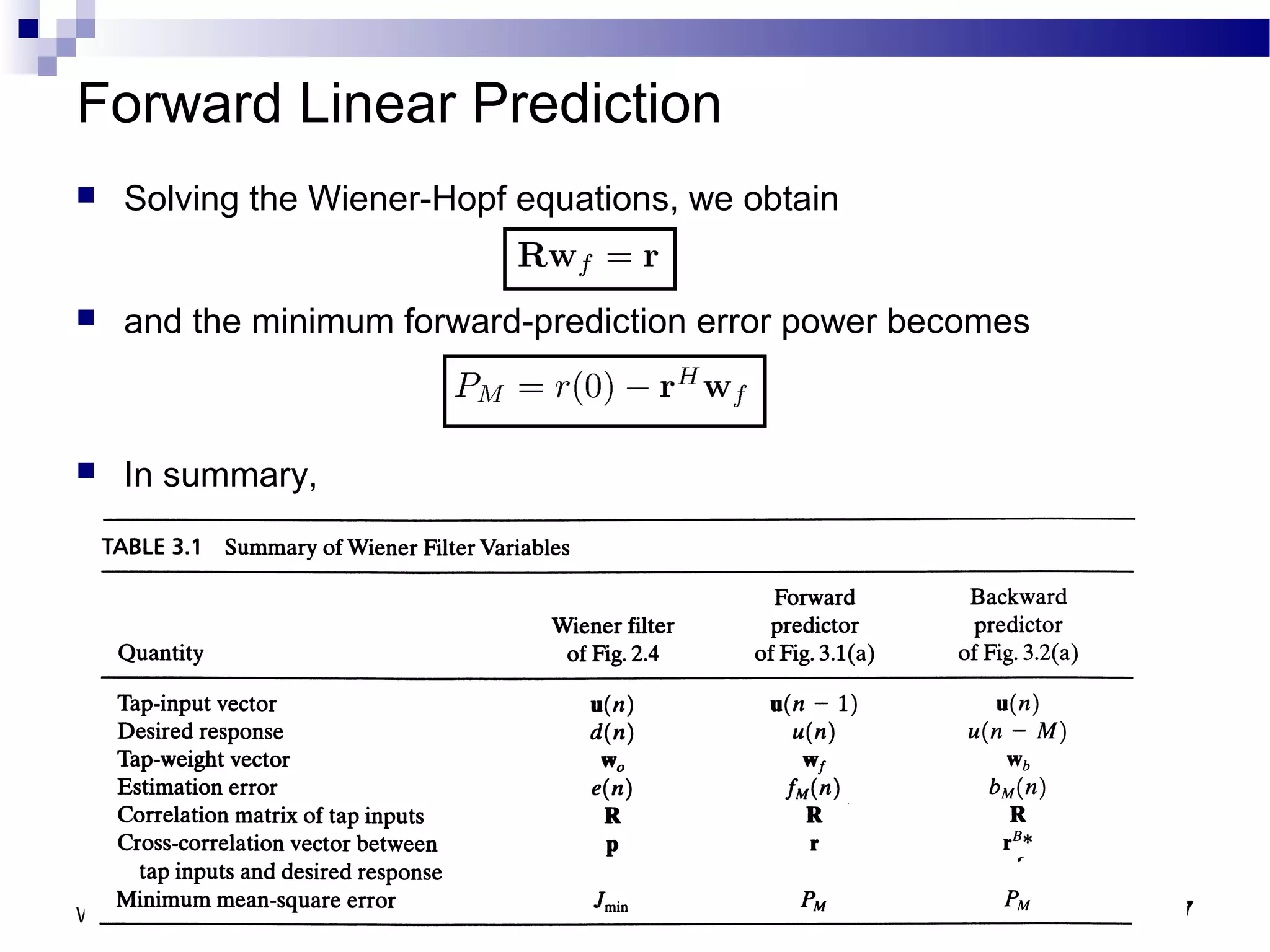
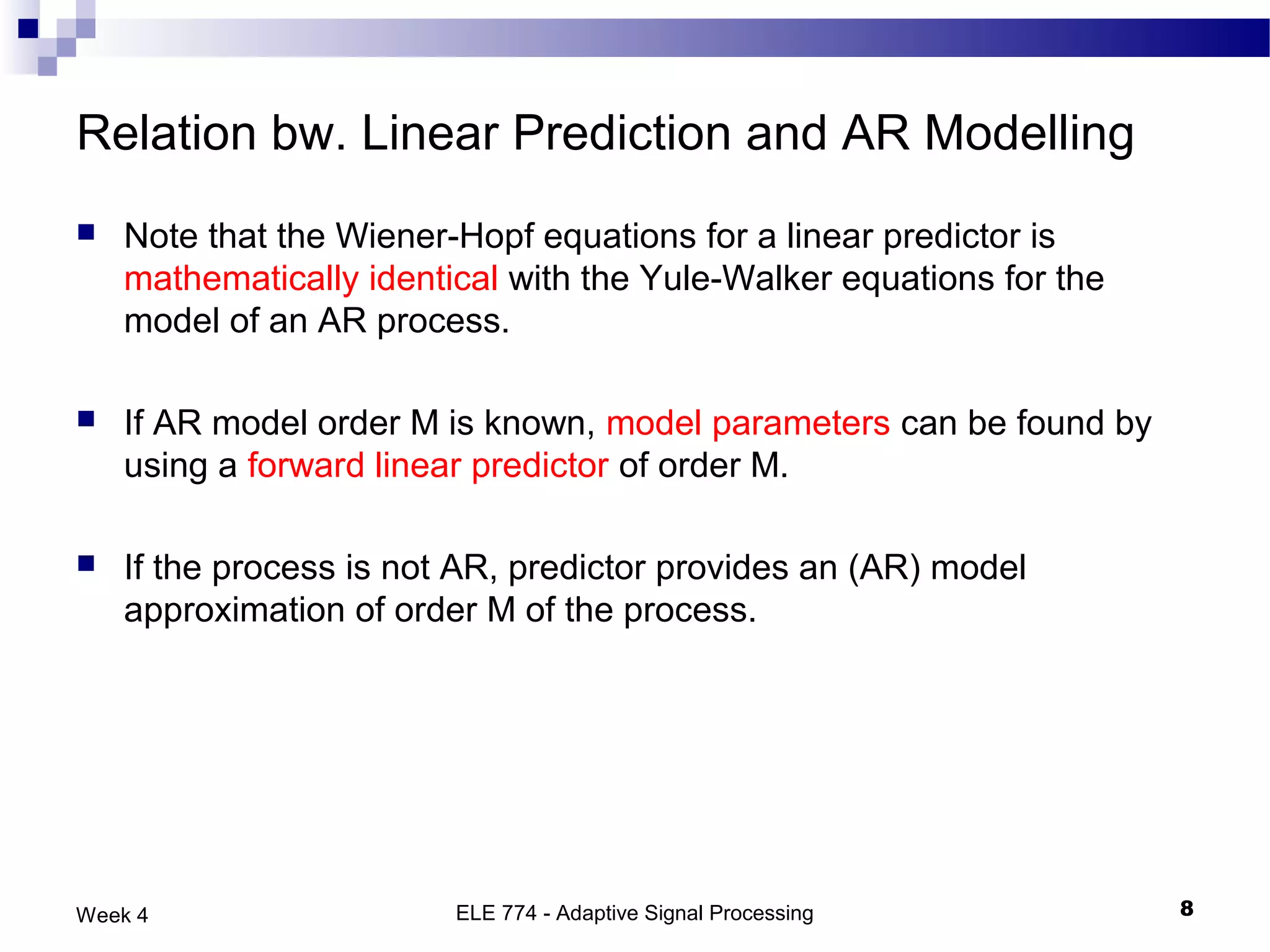
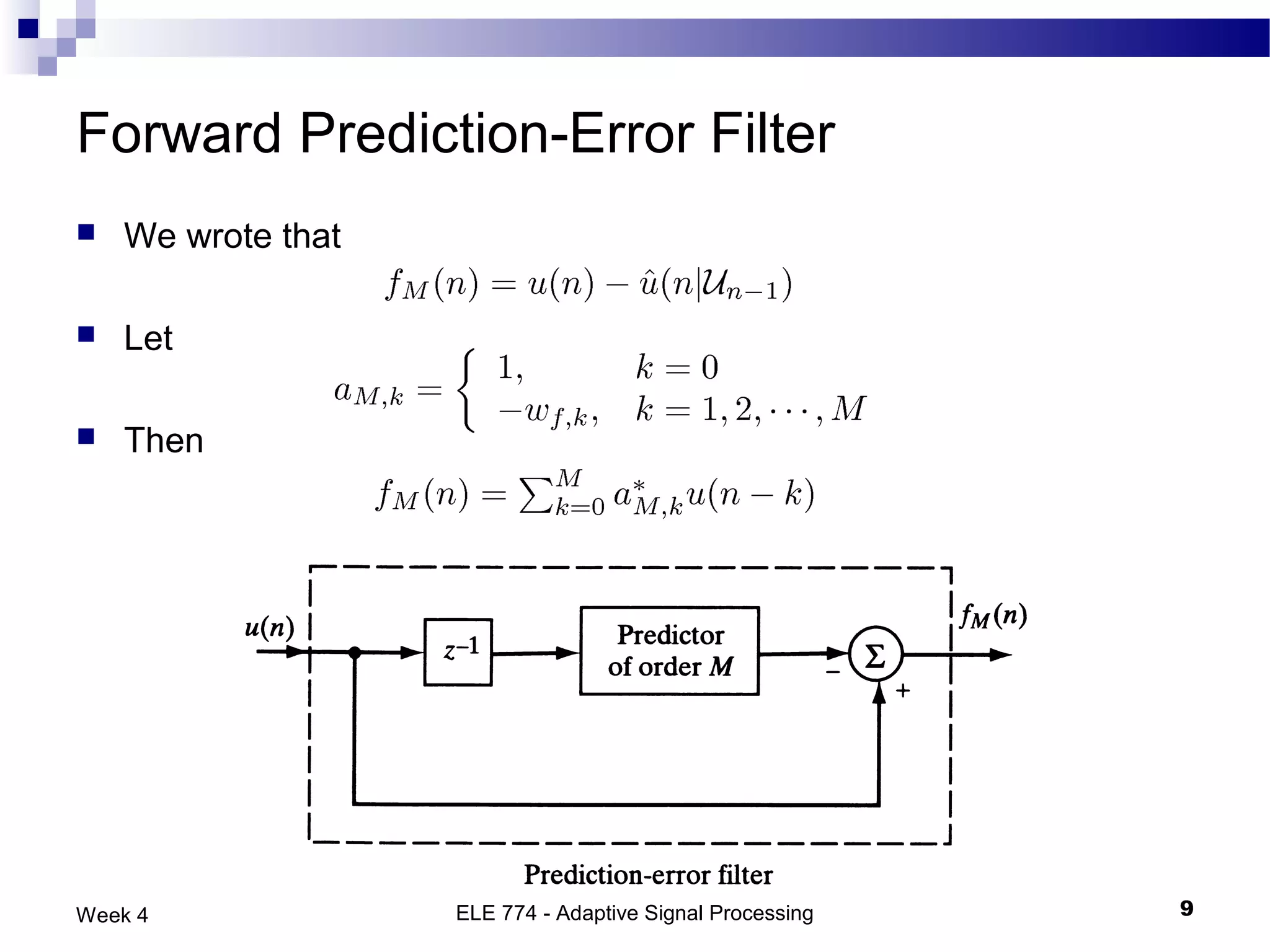
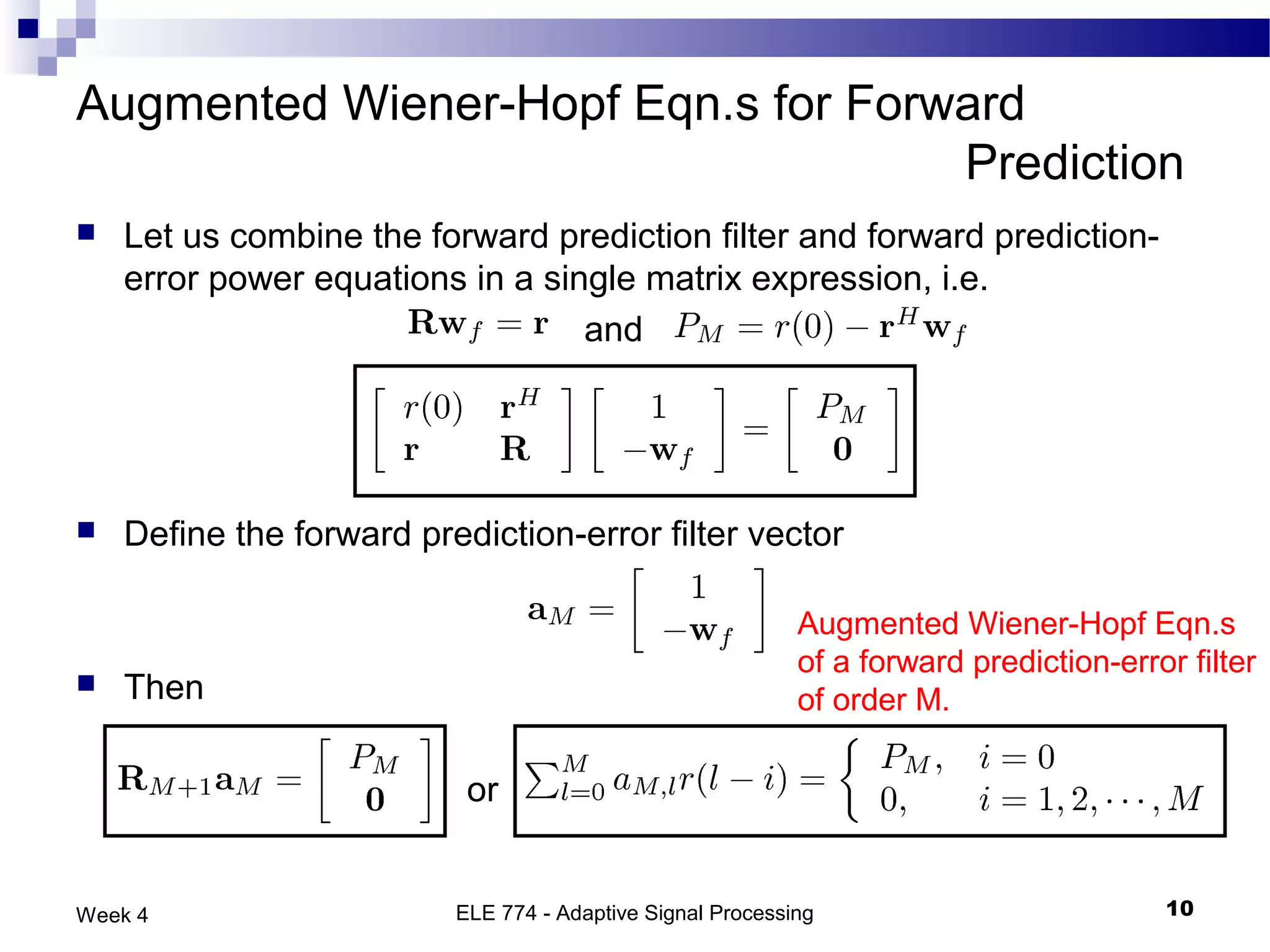
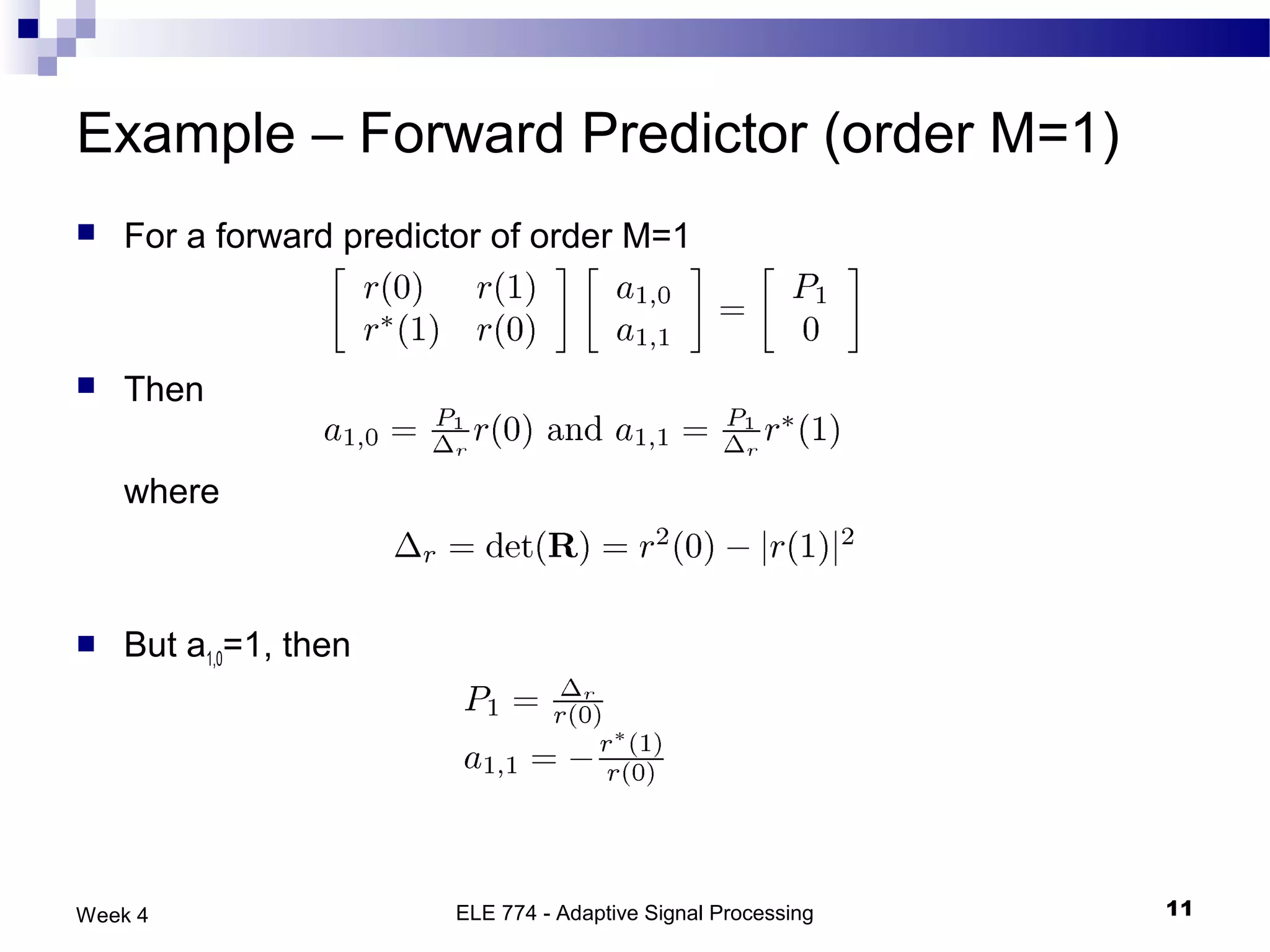
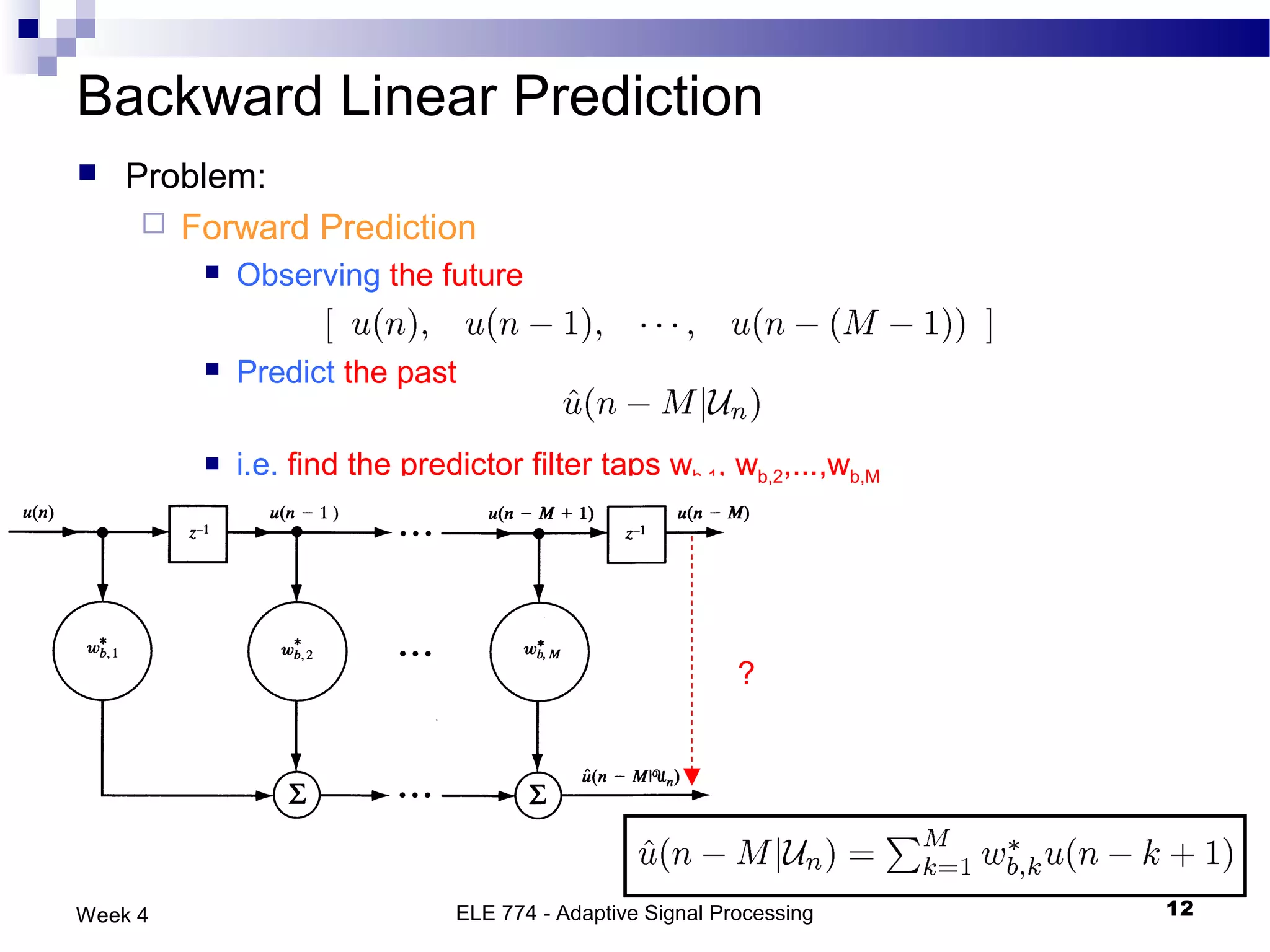
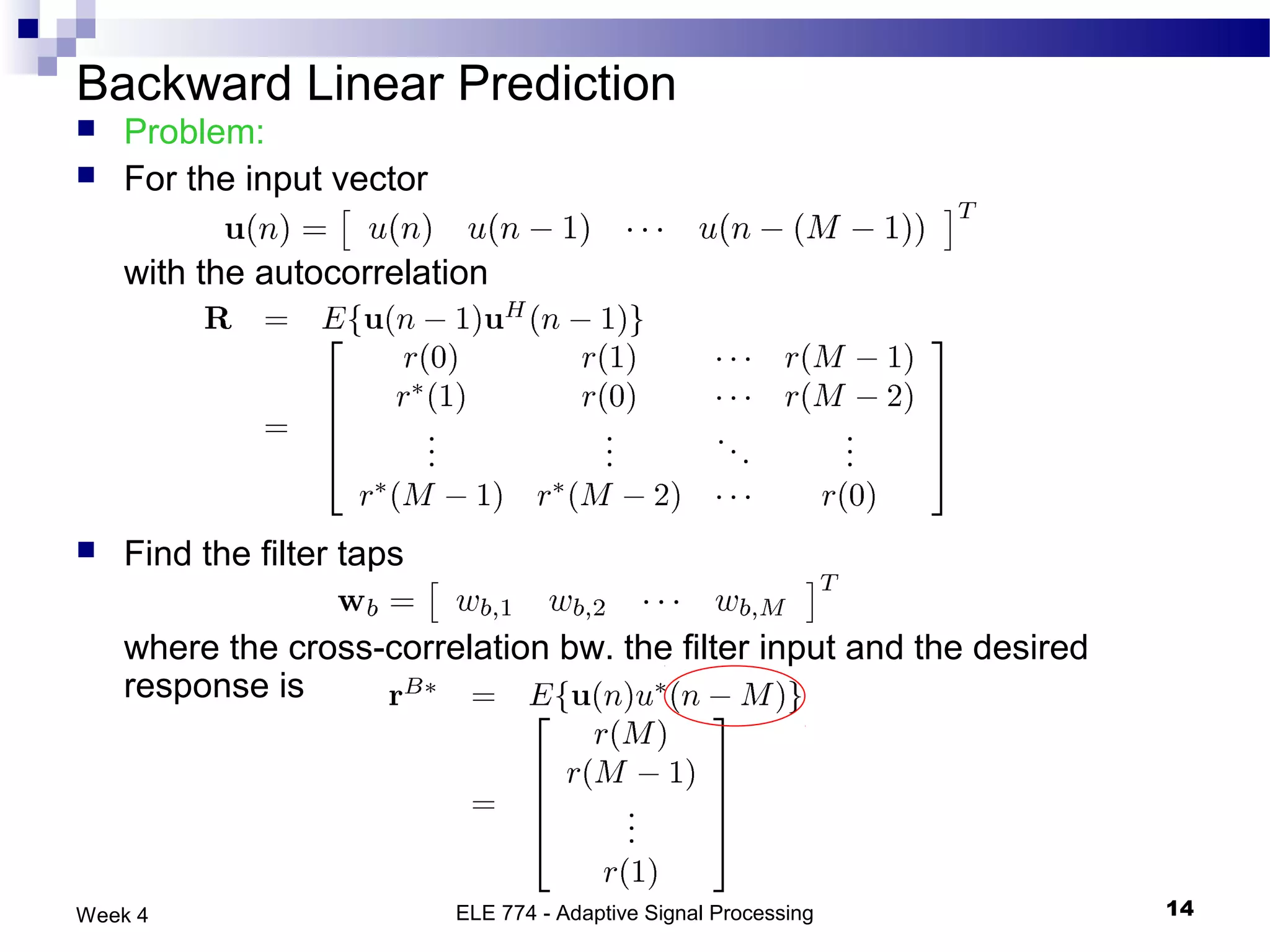
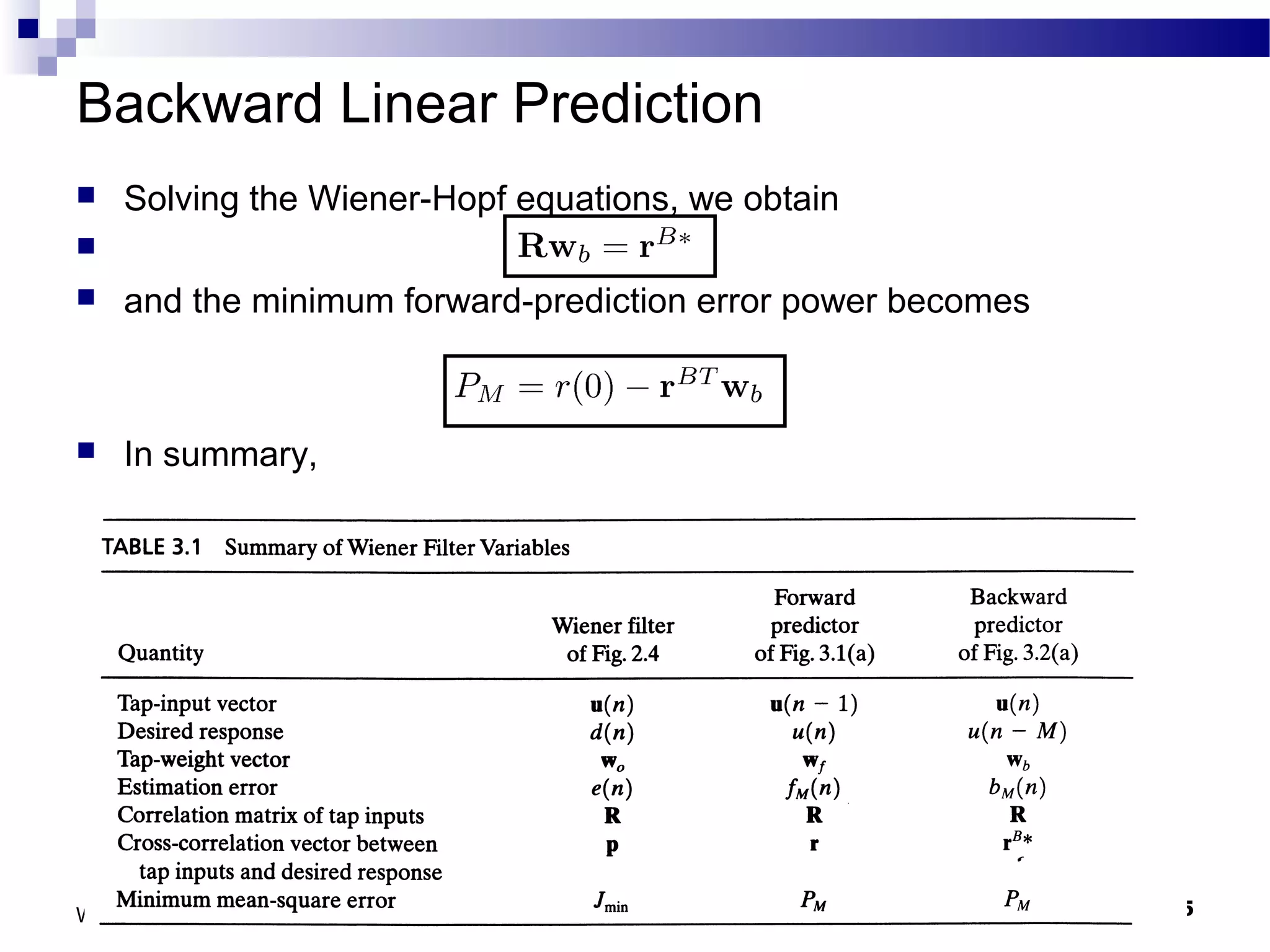
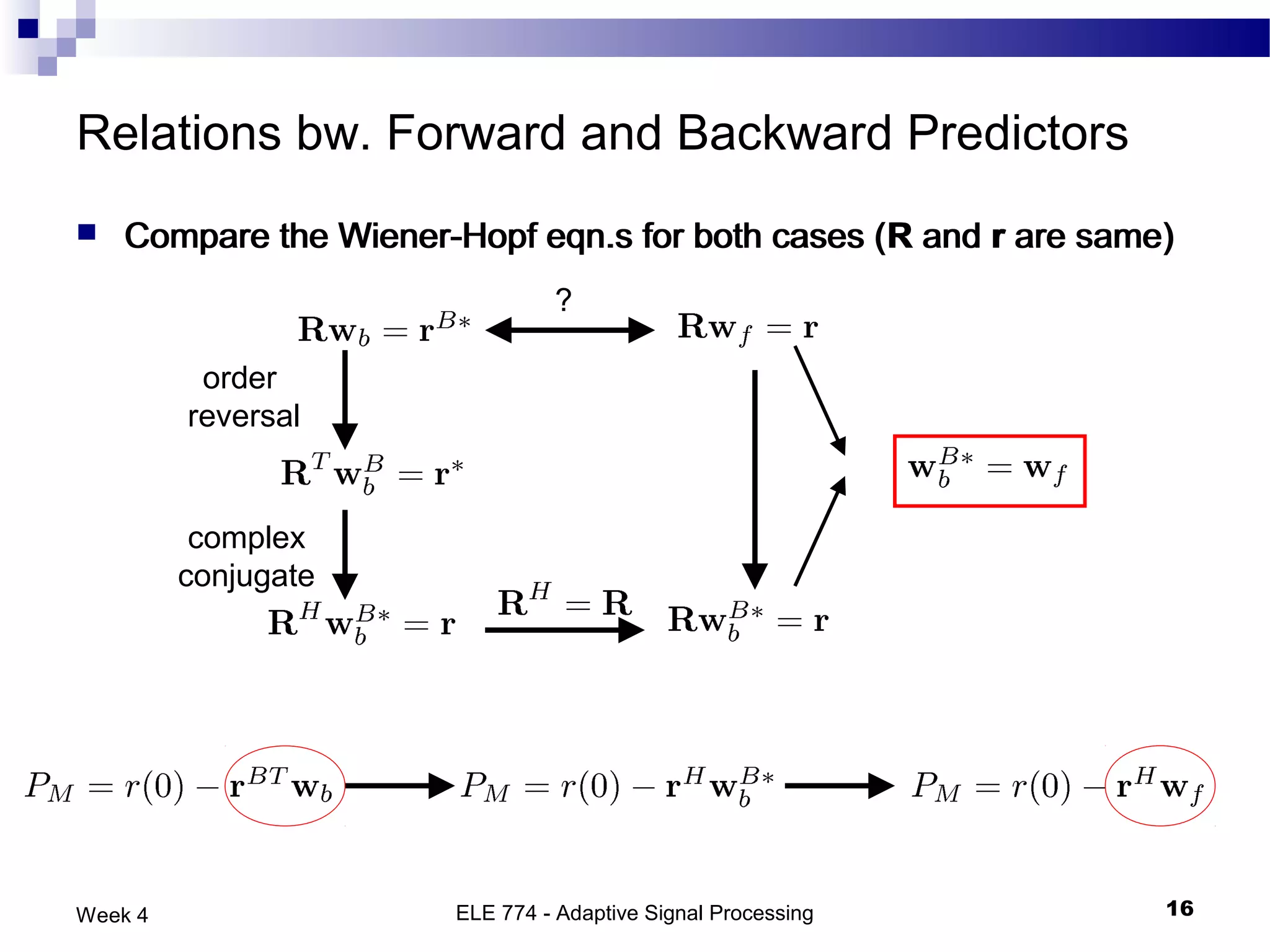
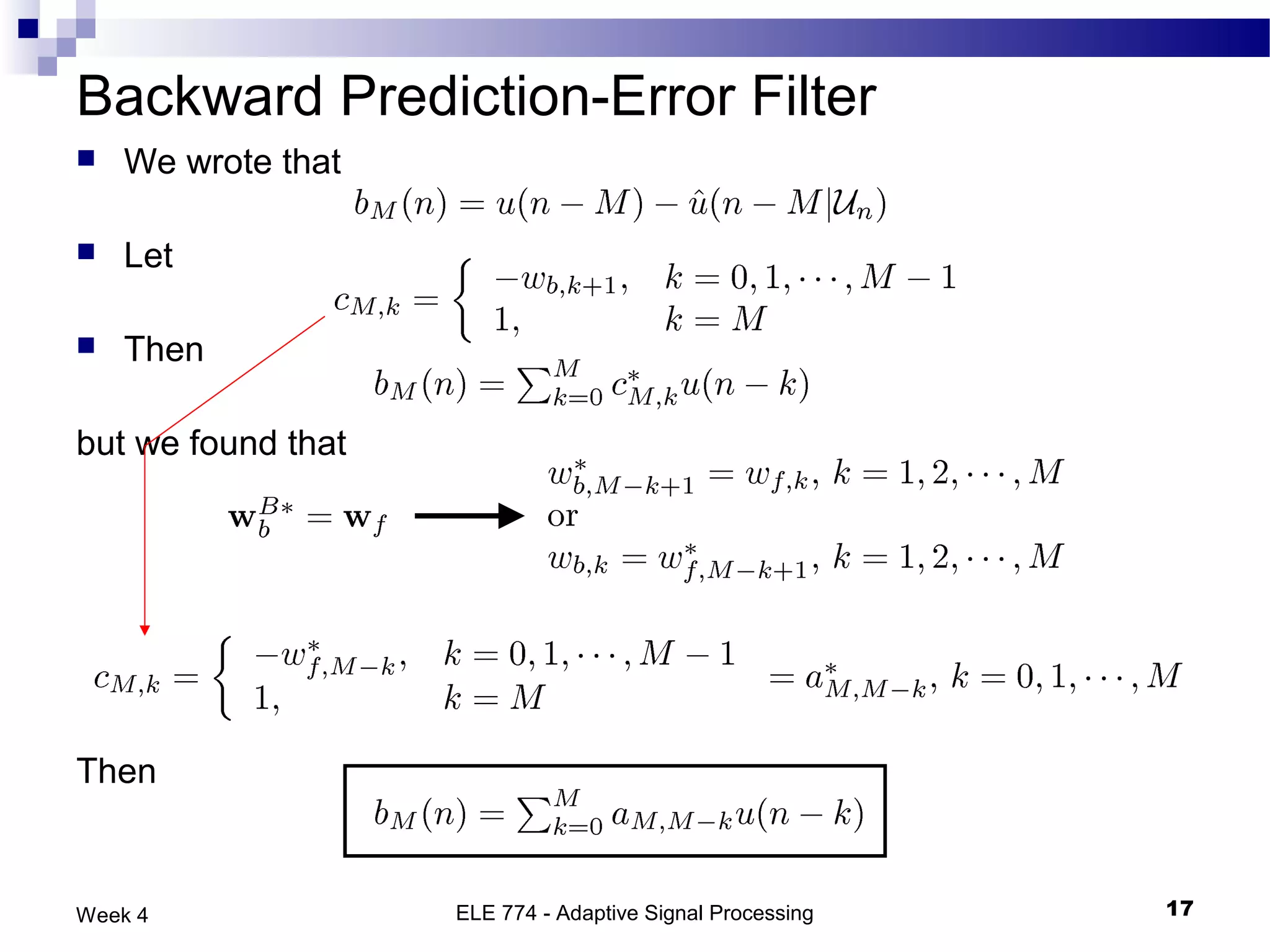
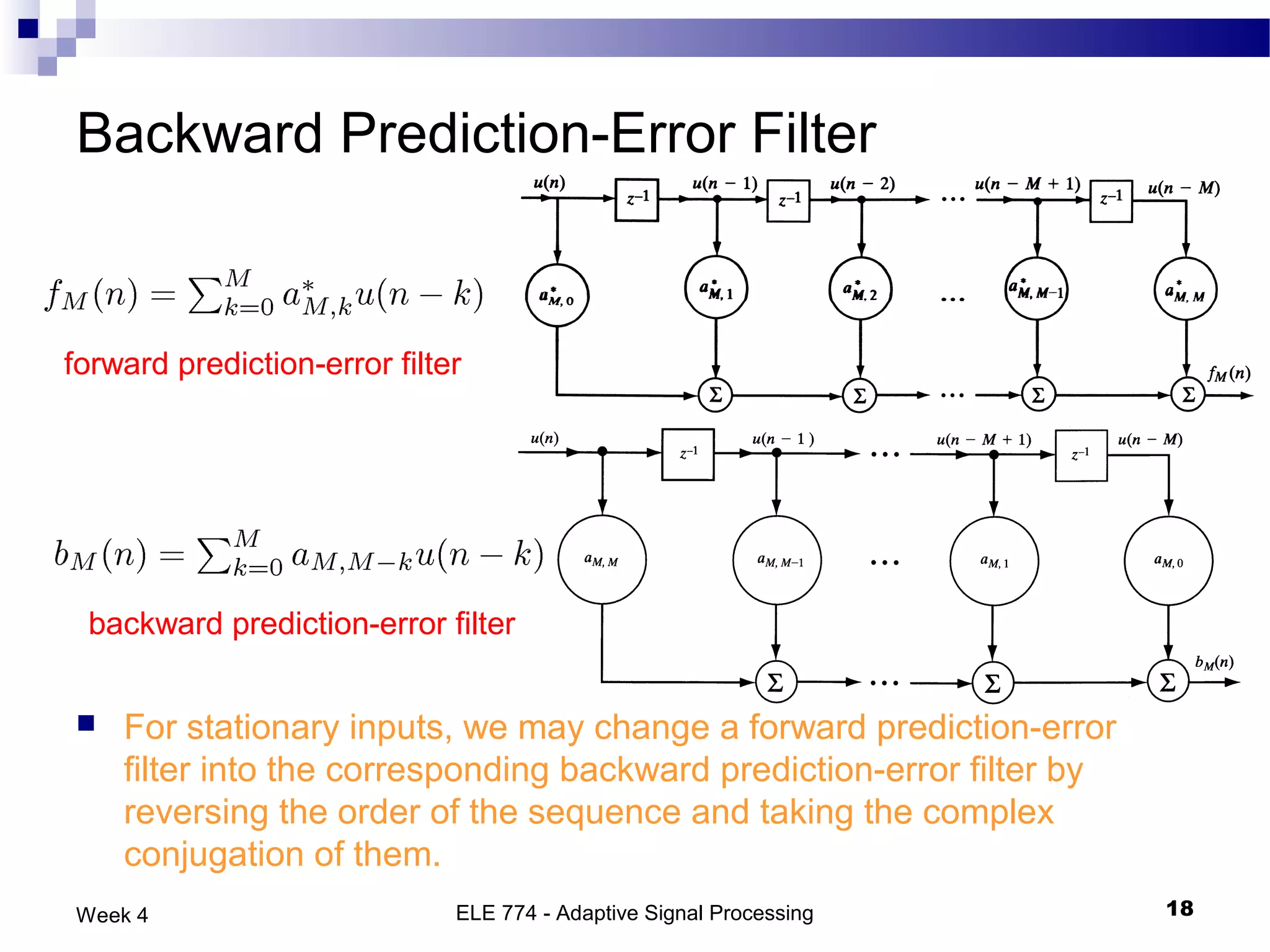
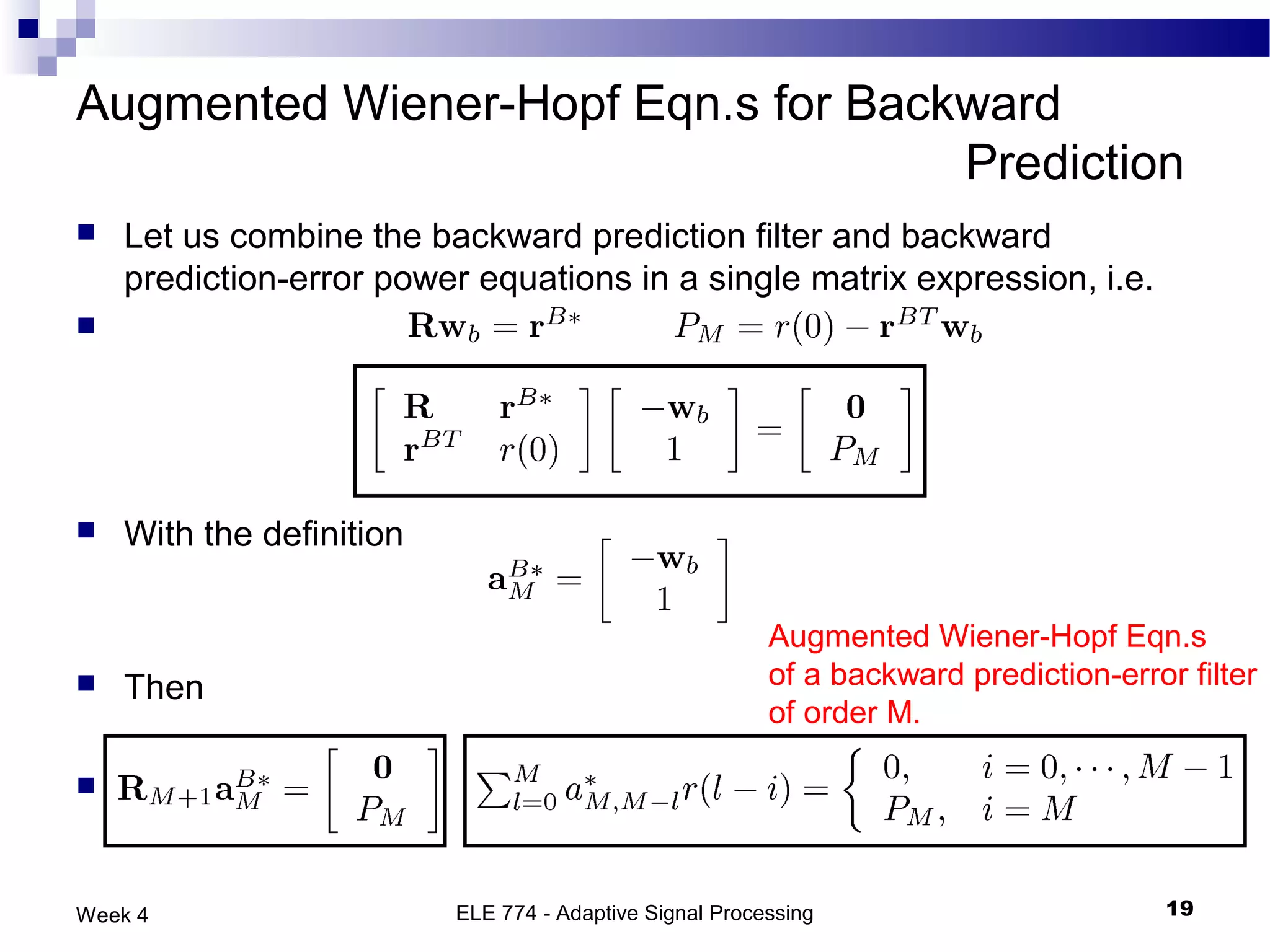
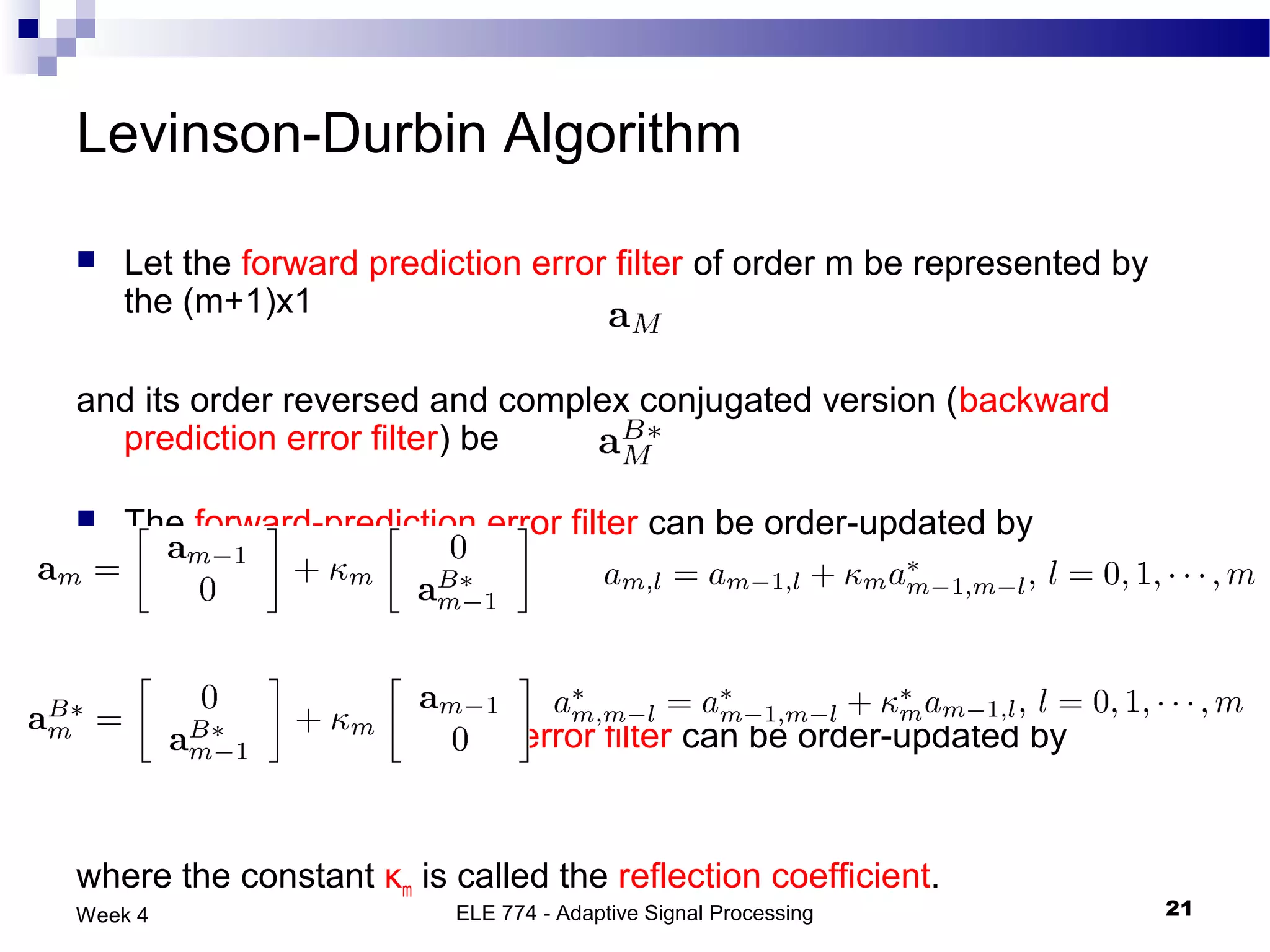
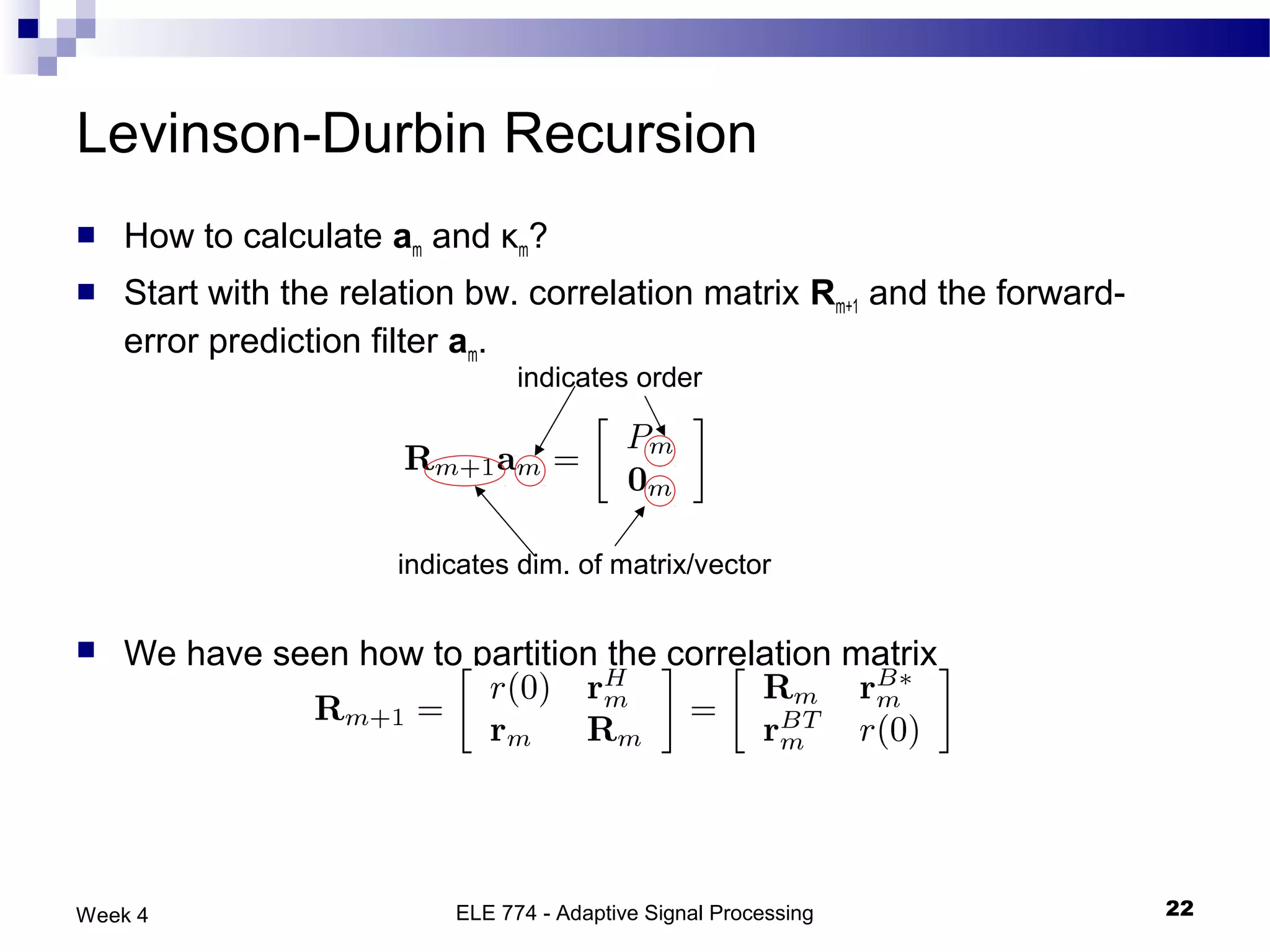
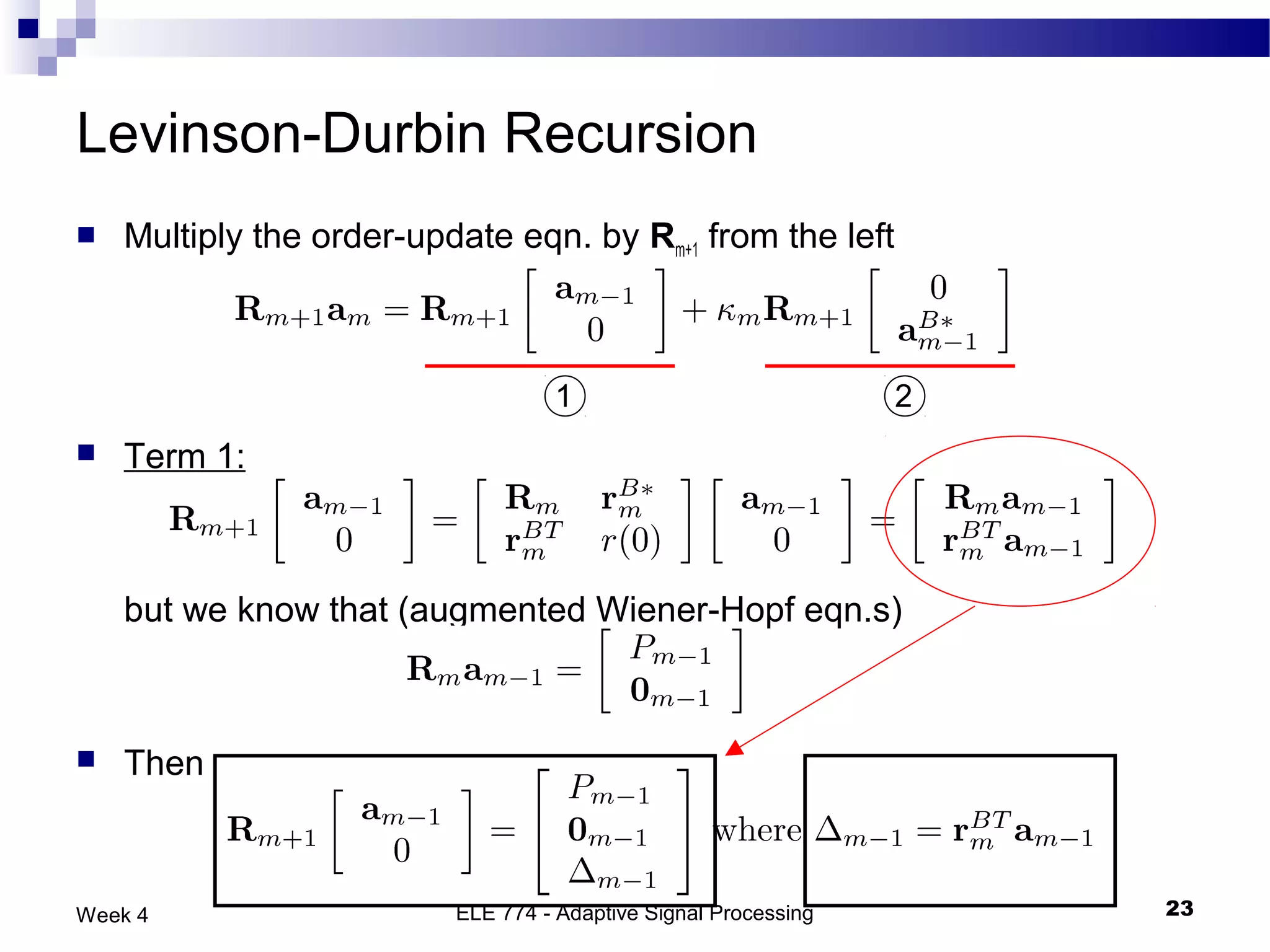
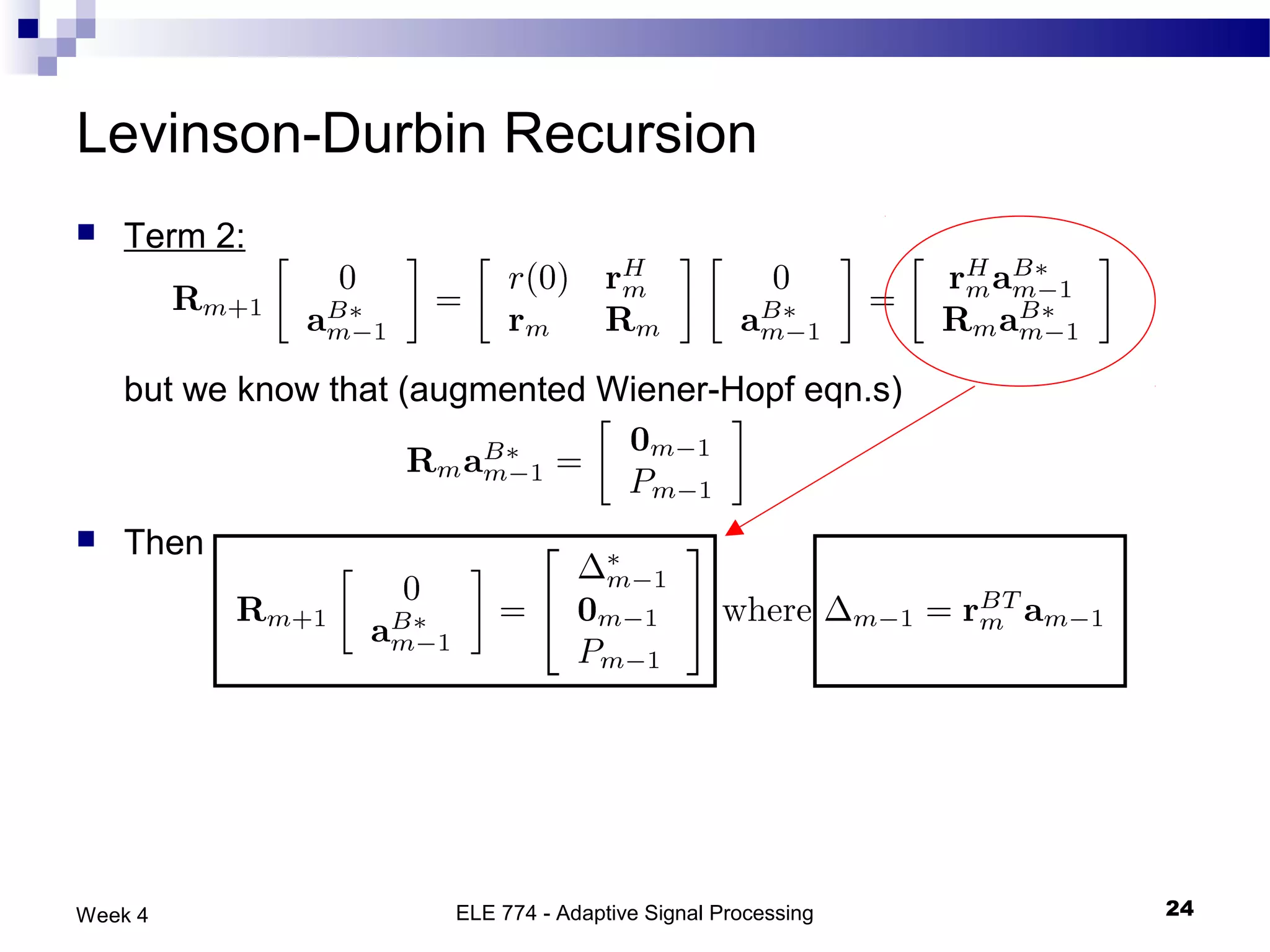
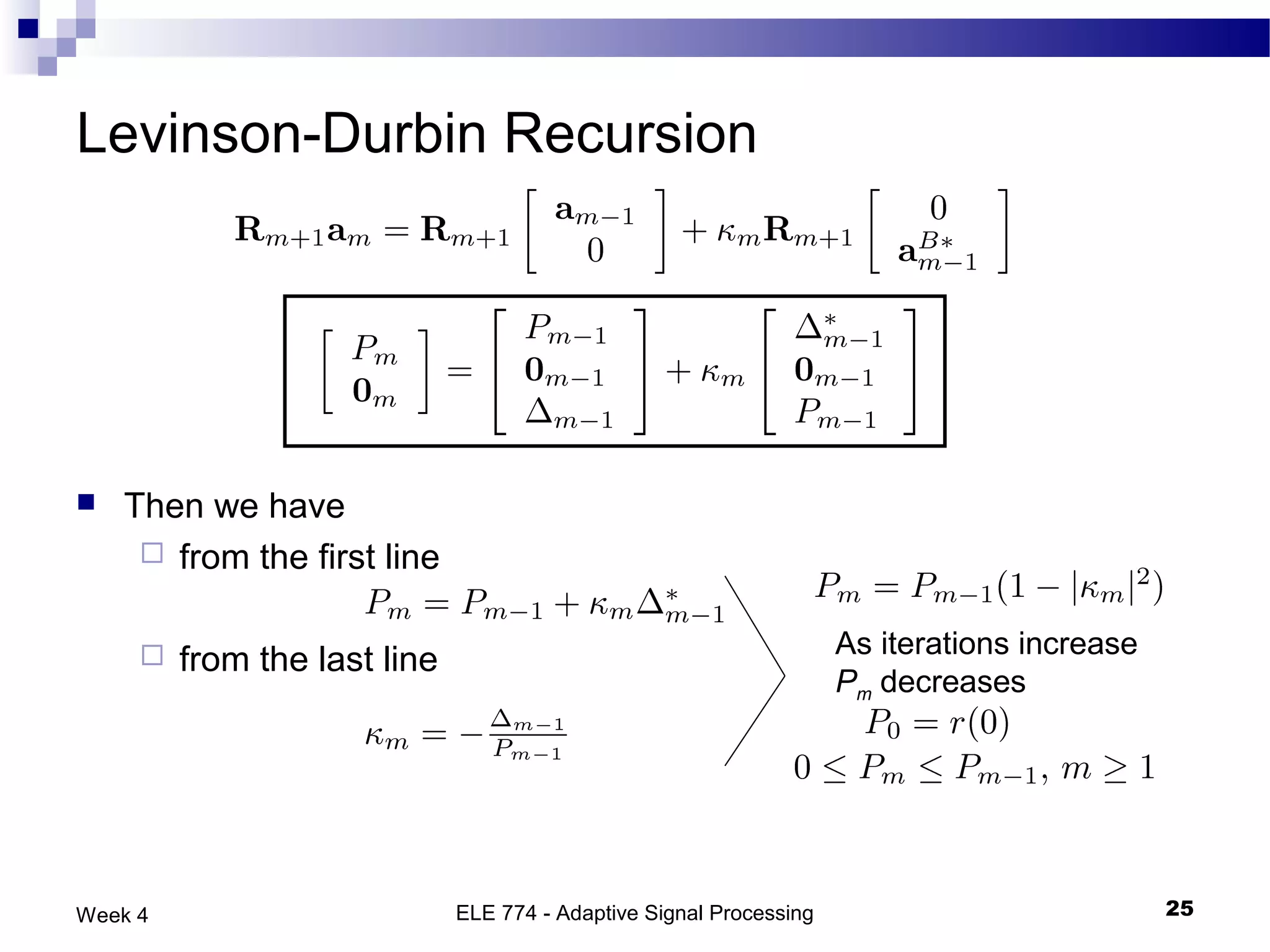
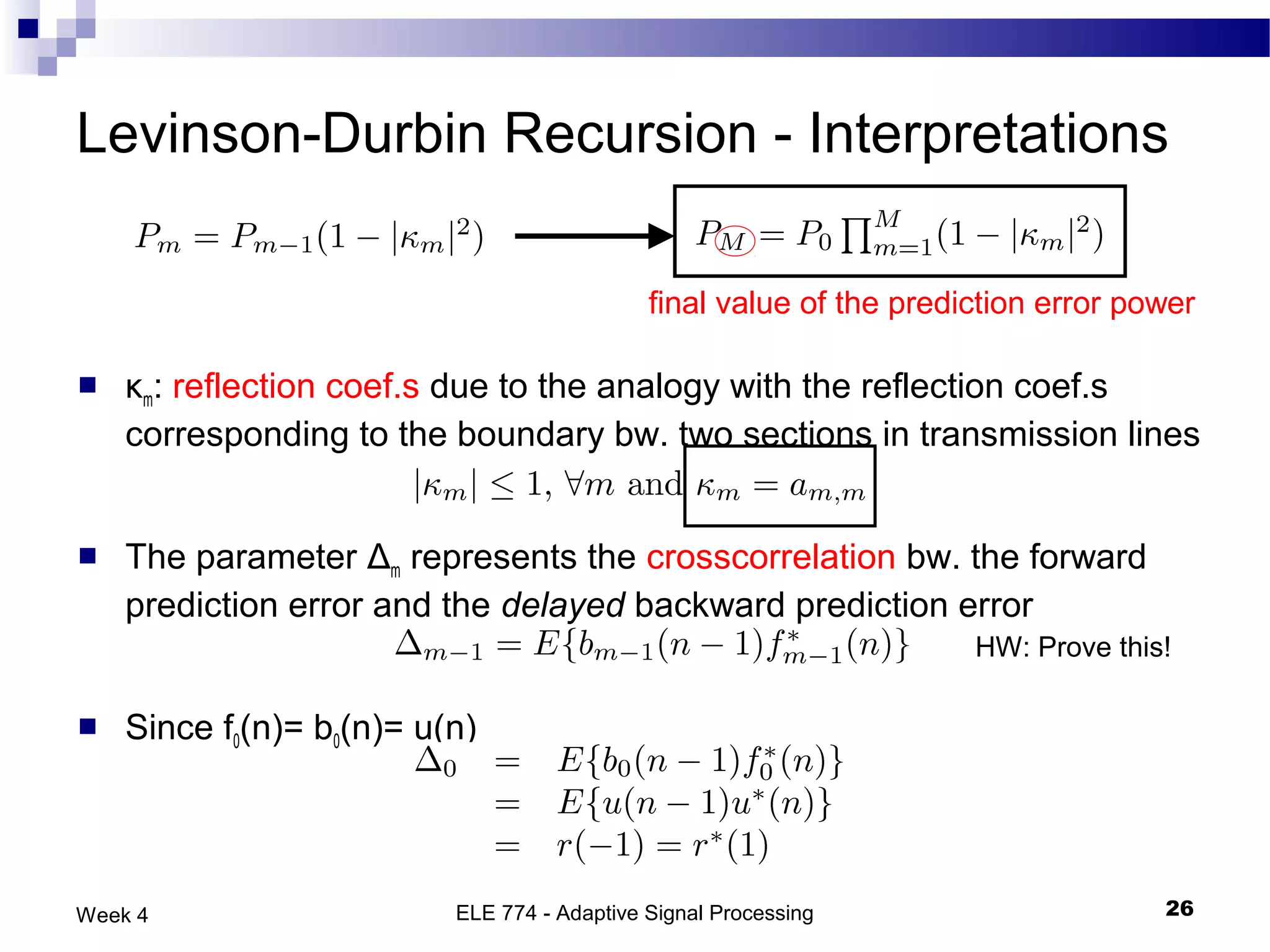
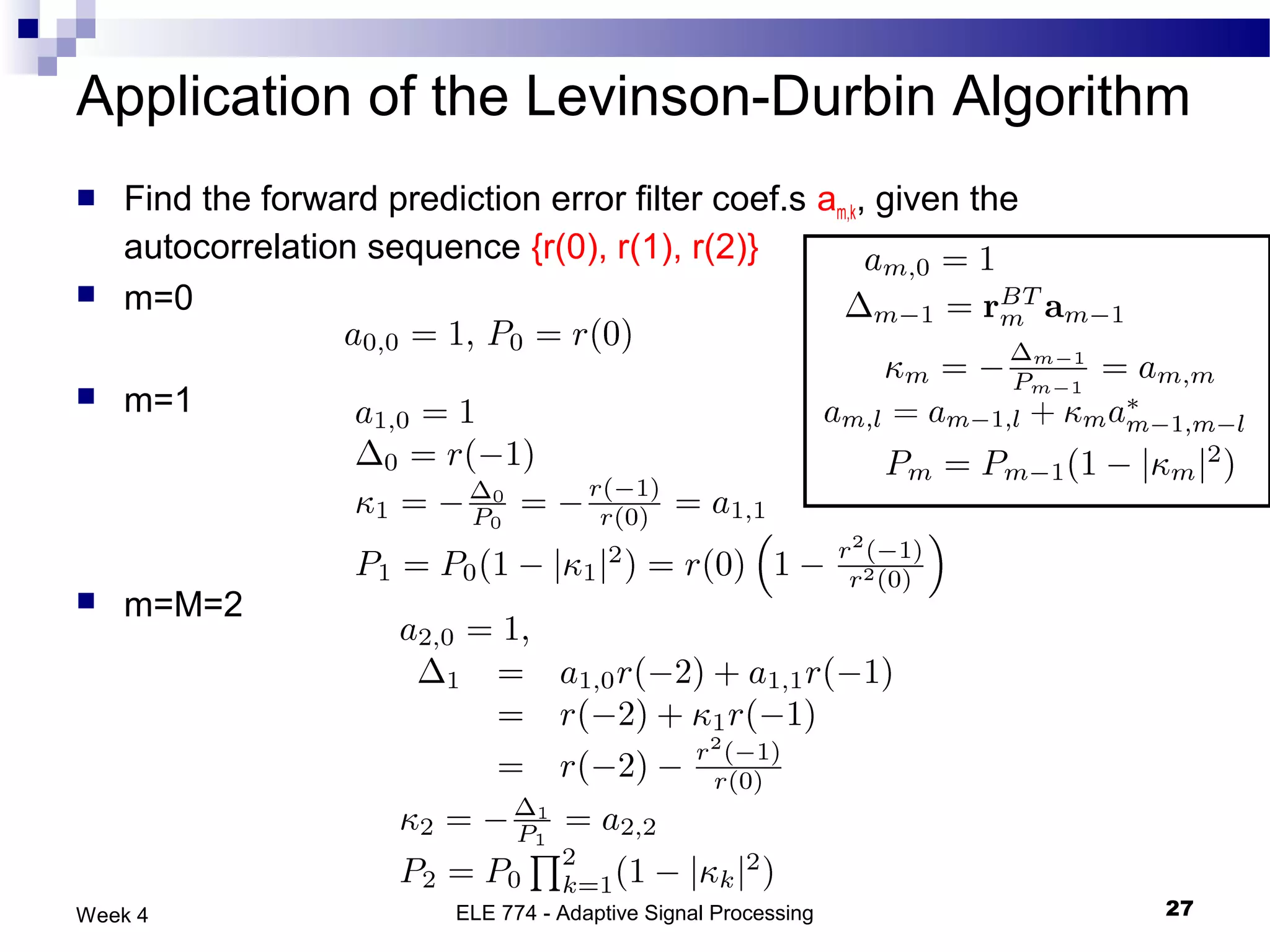
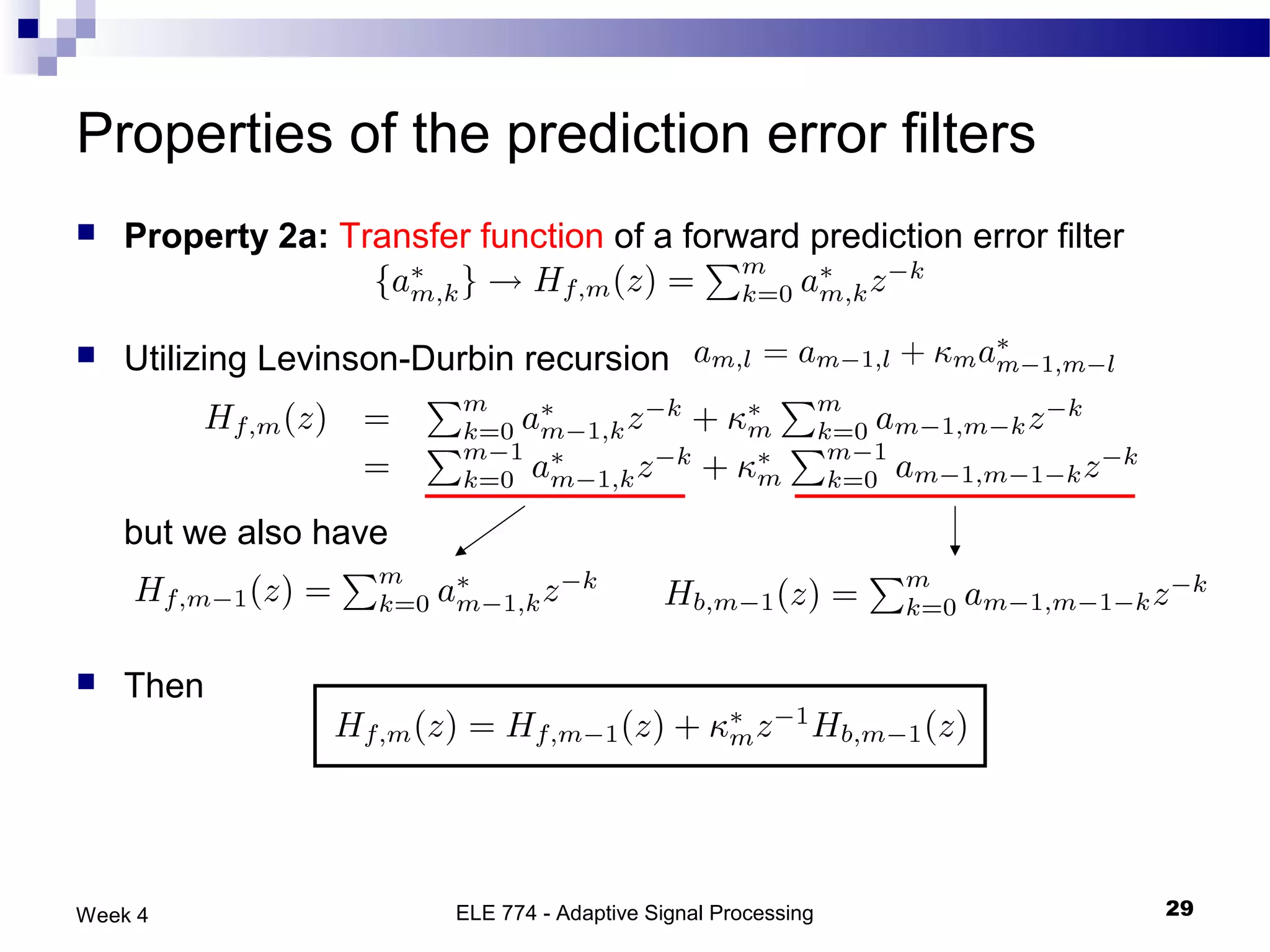
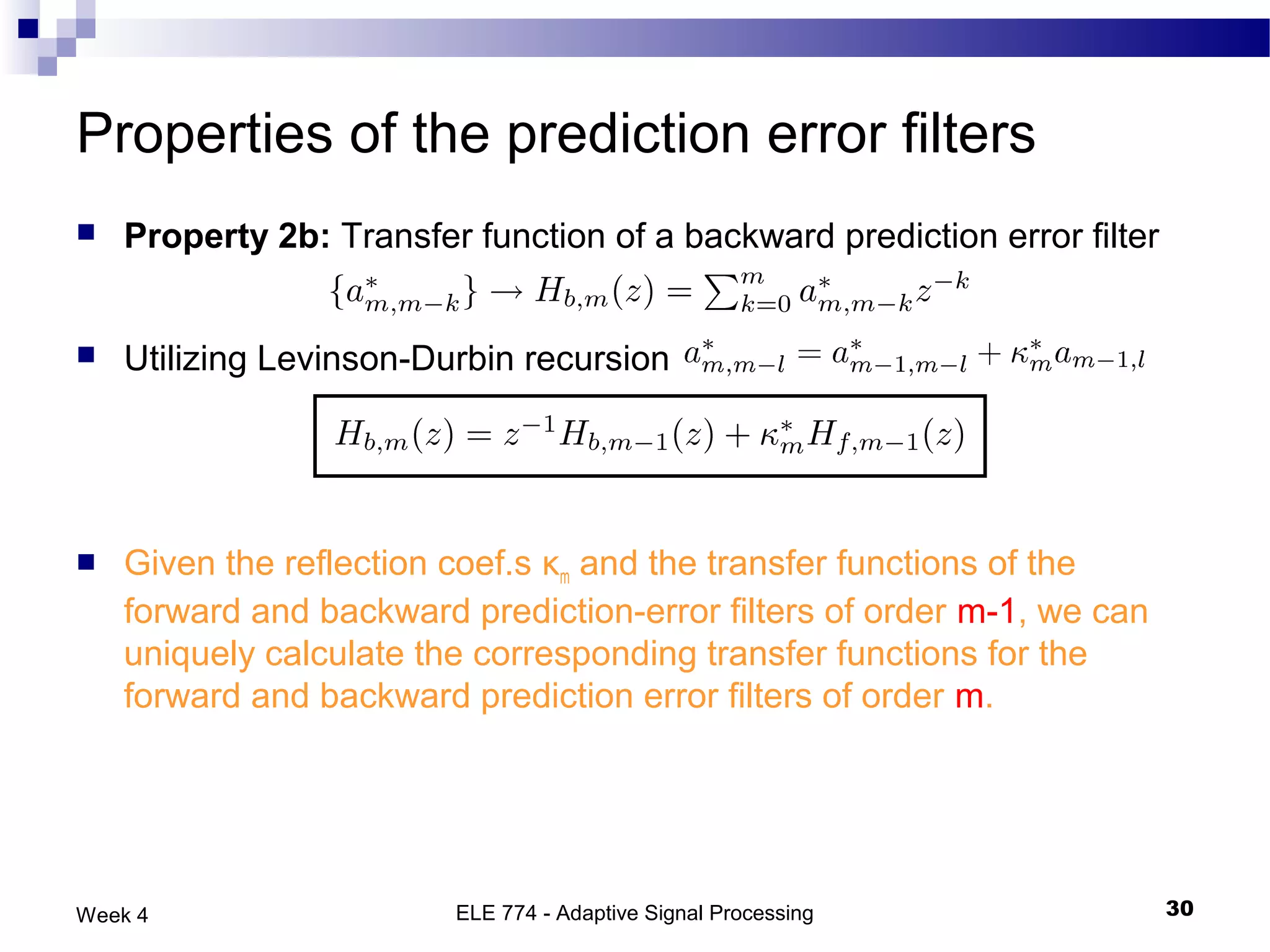
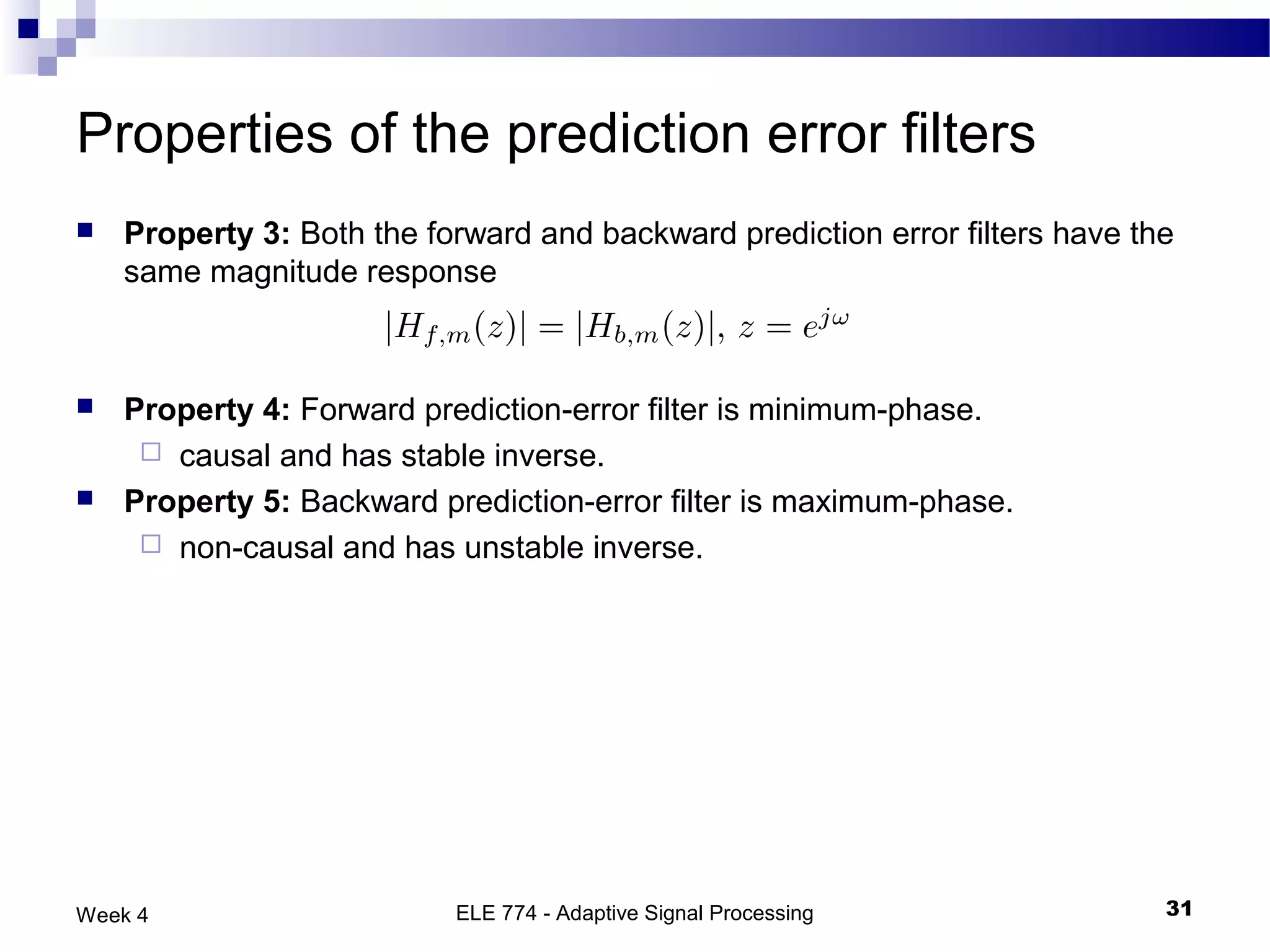
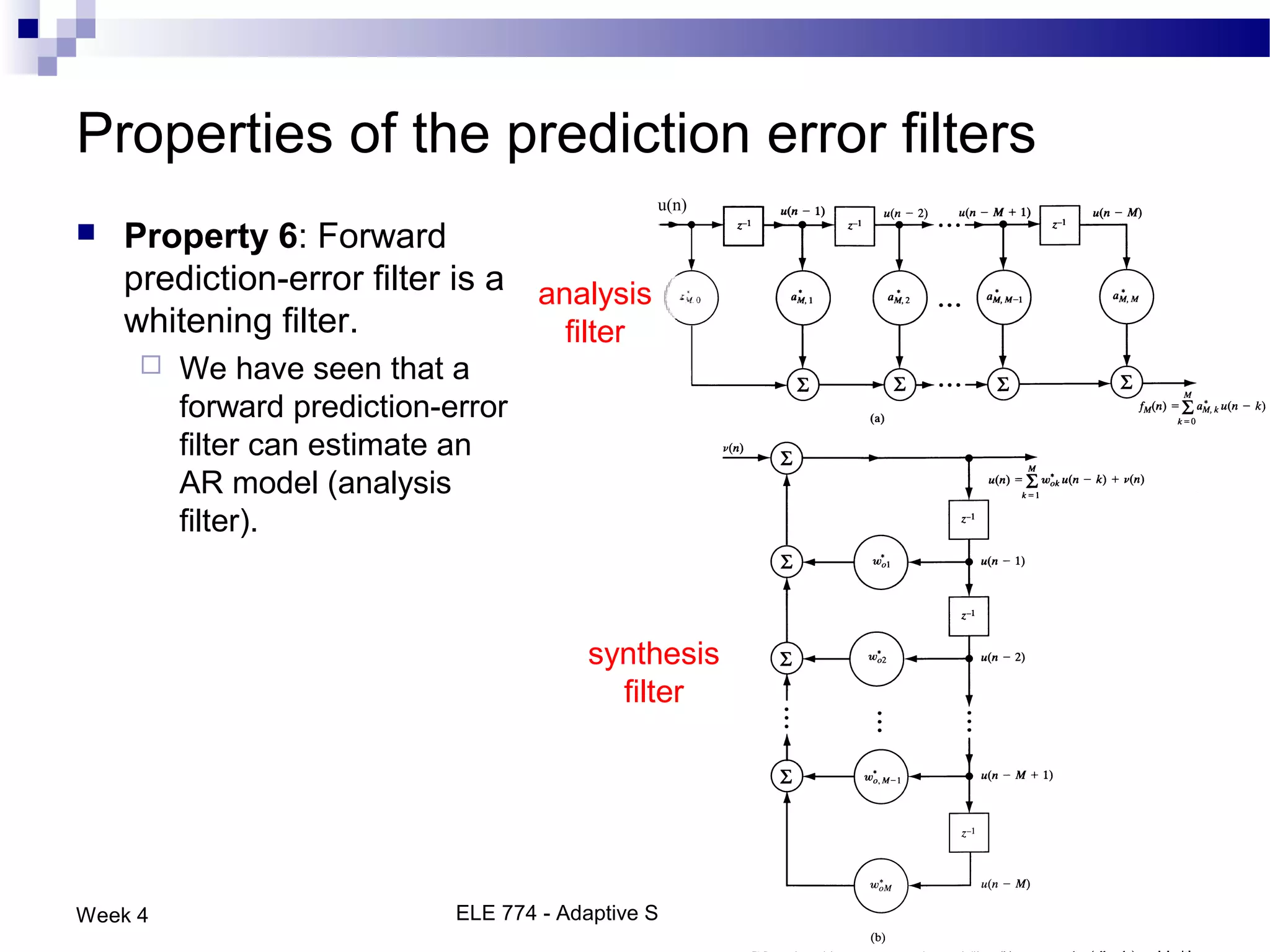
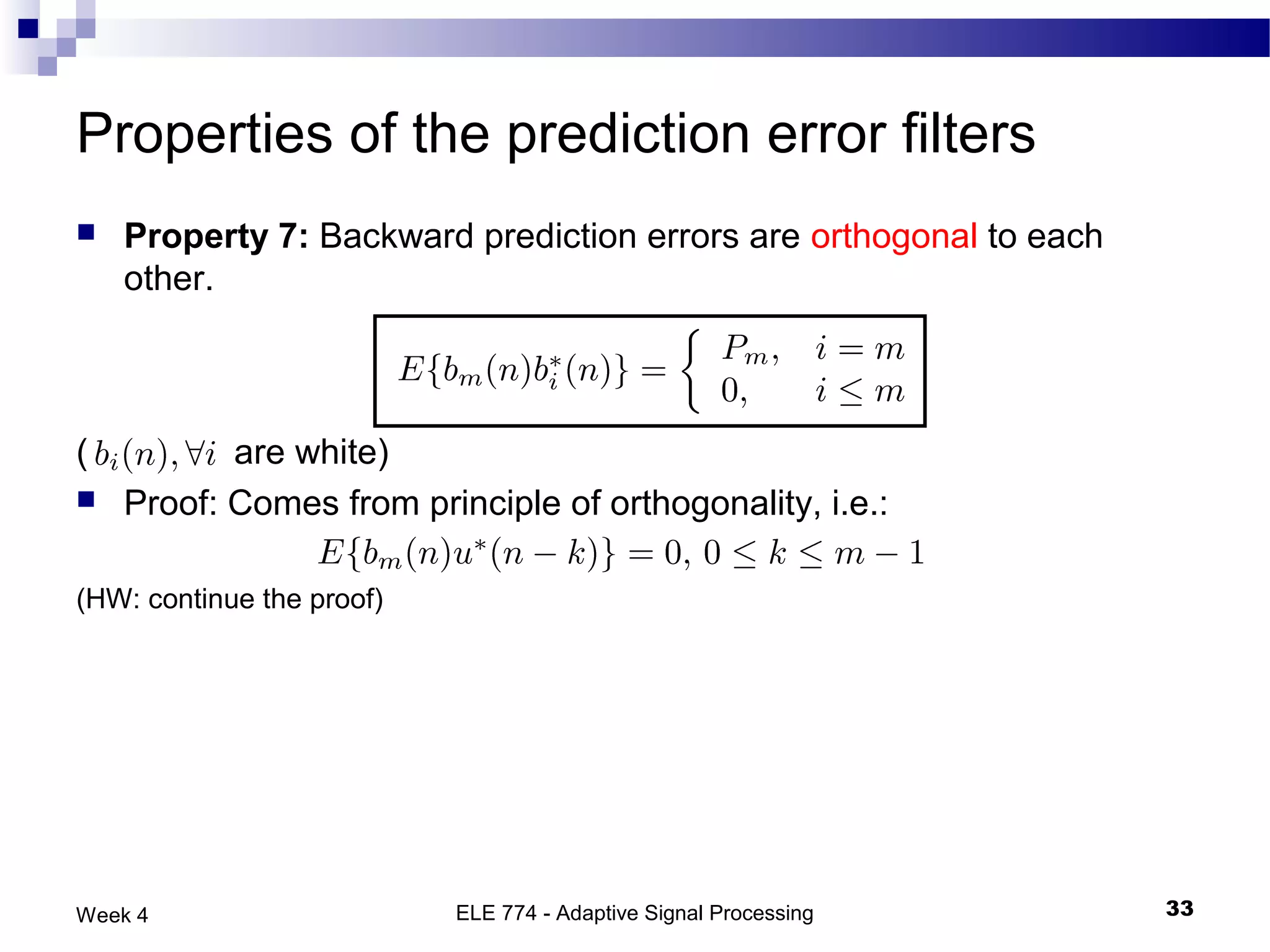
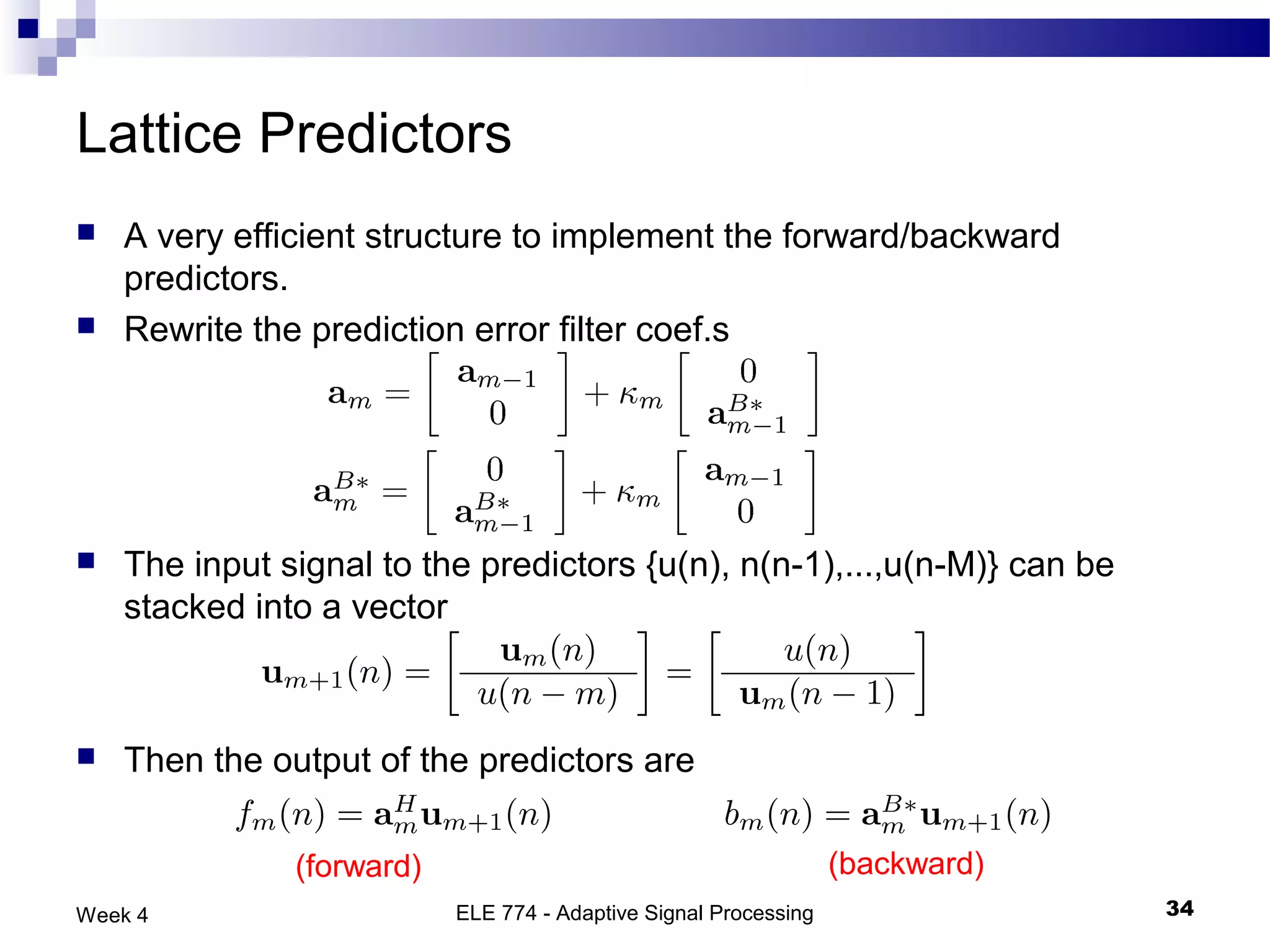
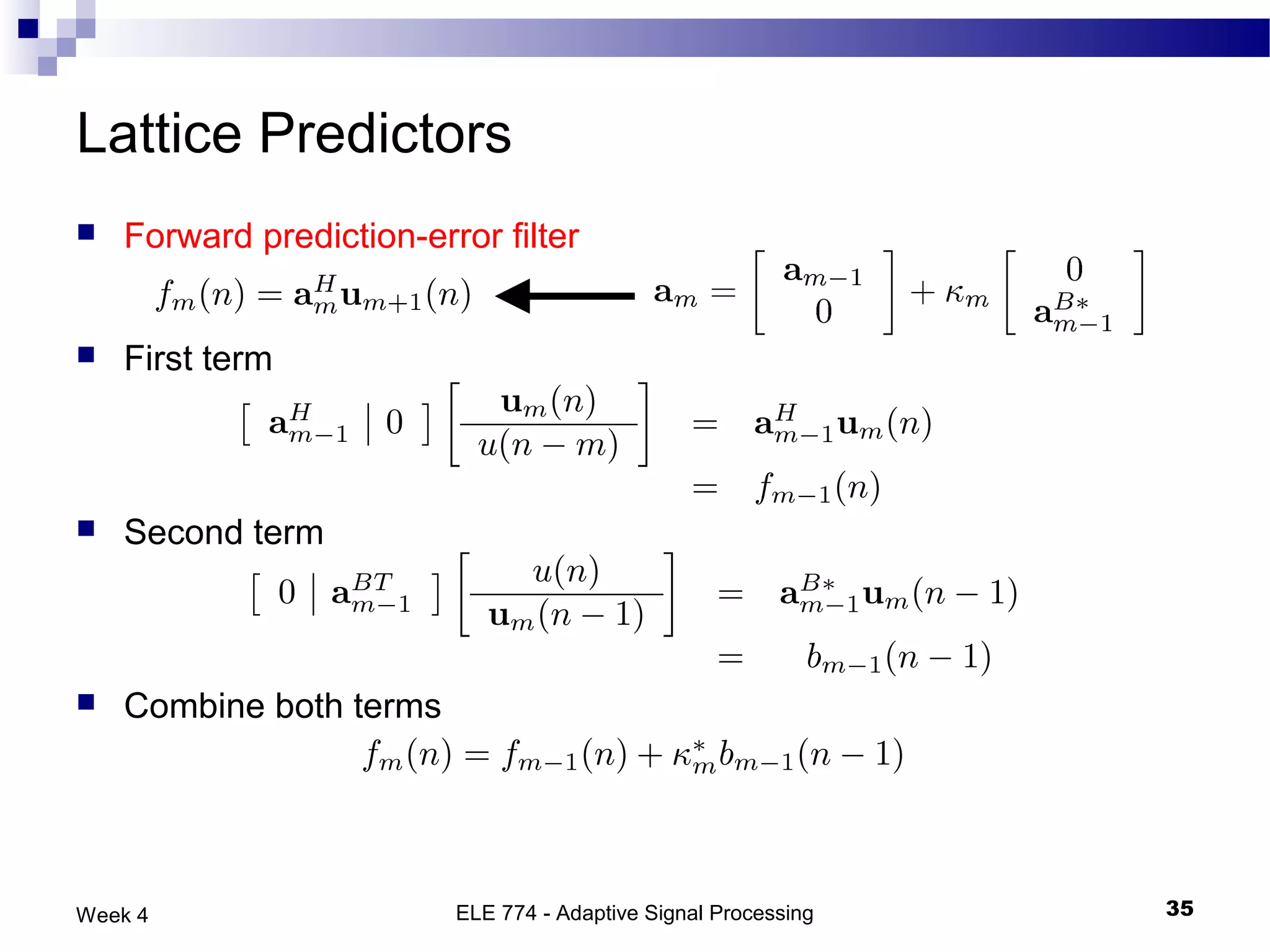
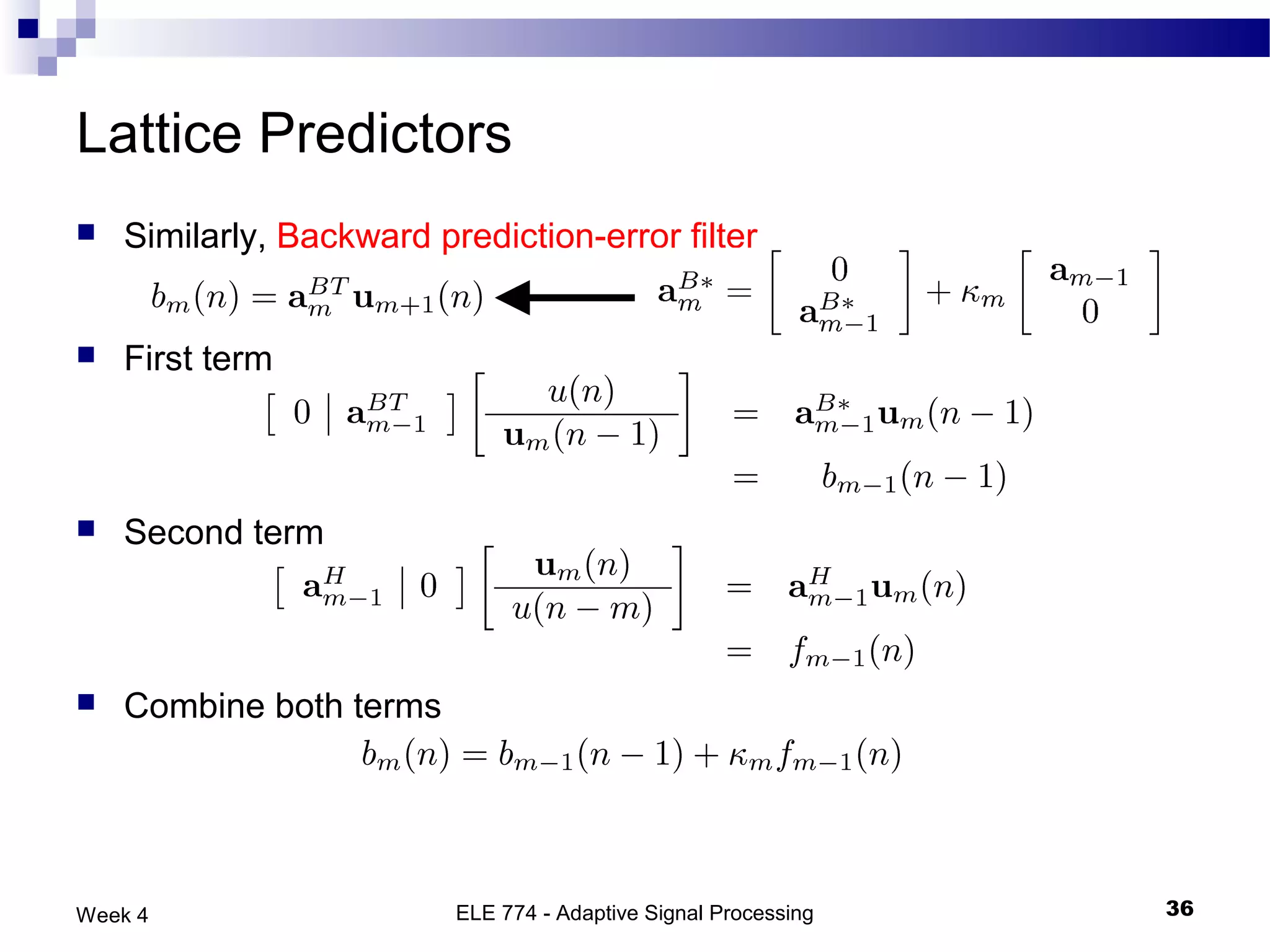
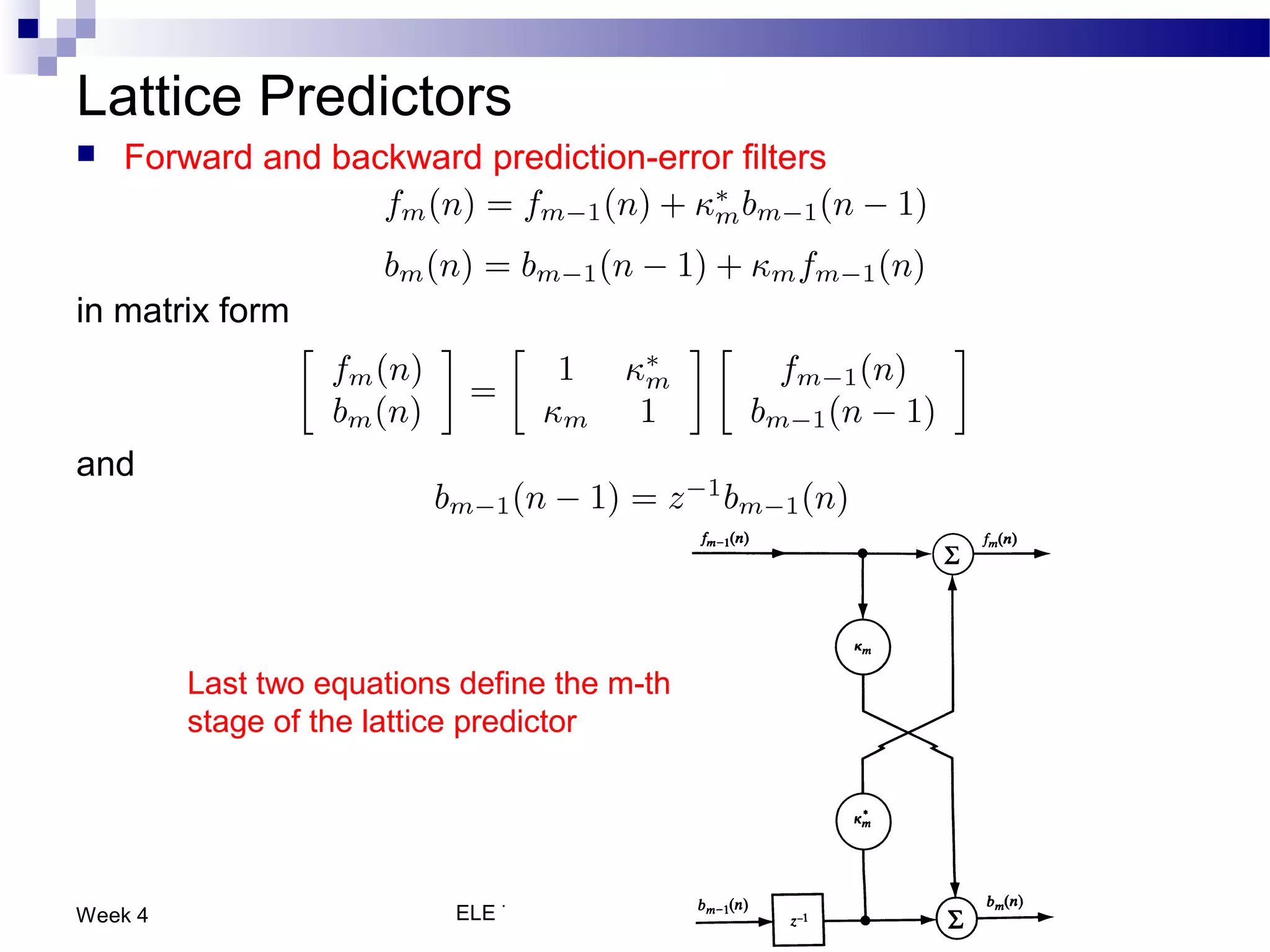
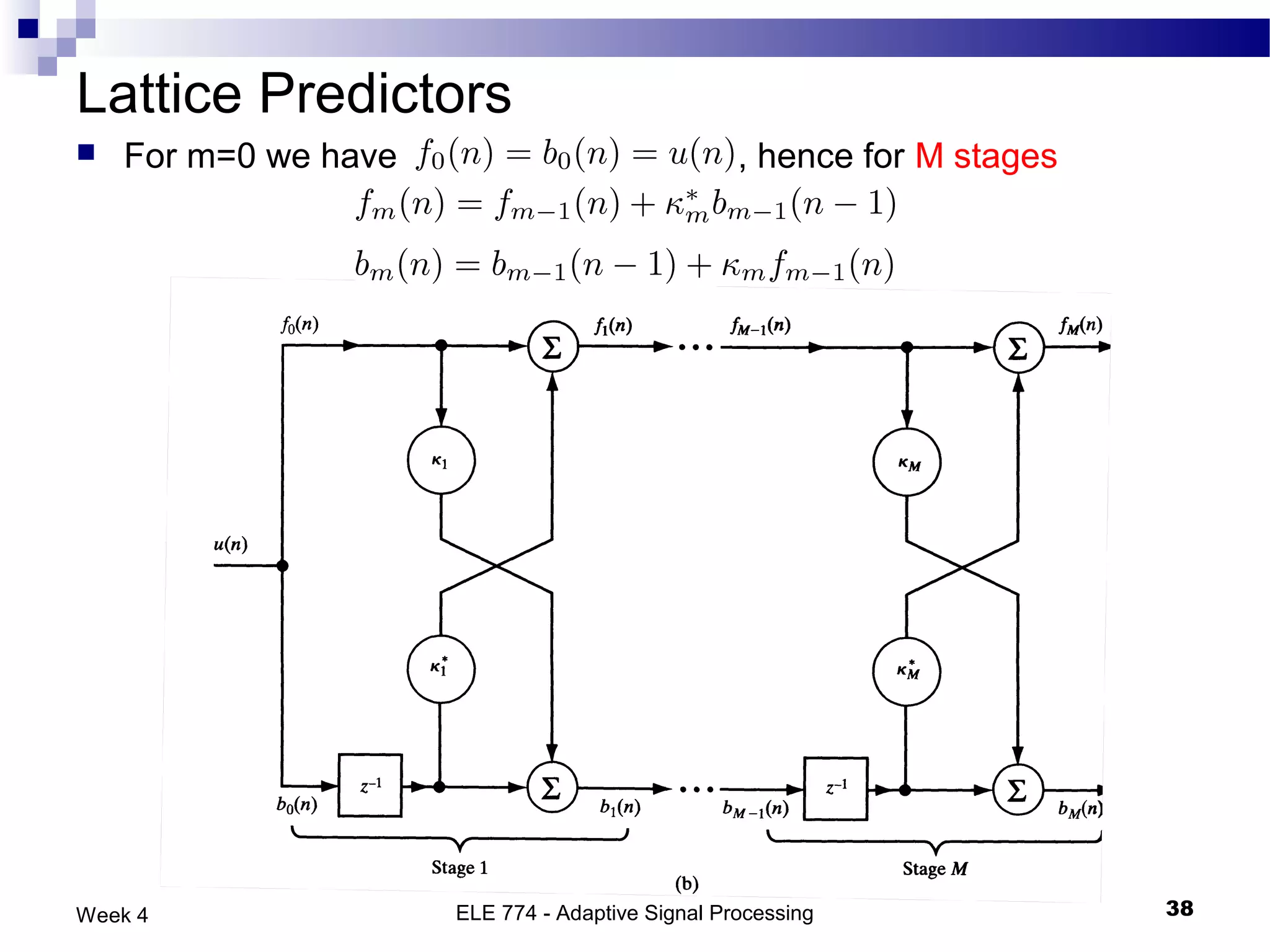
The document discusses linear prediction techniques including forward and backward prediction. Forward prediction involves observing past samples and predicting future samples, while backward prediction involves observing future samples and predicting past samples. Both techniques can be solved using Wiener filter theory and result in minimum mean-square prediction errors. The Levinson-Durbin algorithm provides an efficient recursive method for computing linear prediction filter coefficients. Lattice predictors provide an efficient implementation structure for forward and backward linear prediction filters.