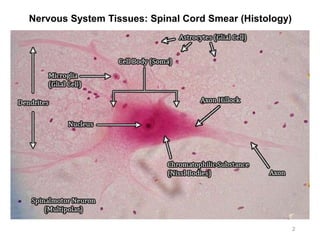
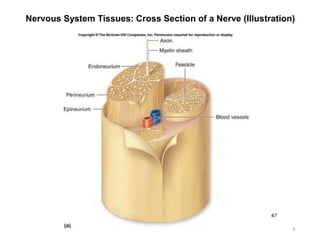
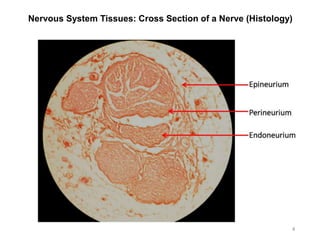
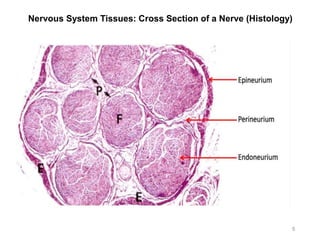
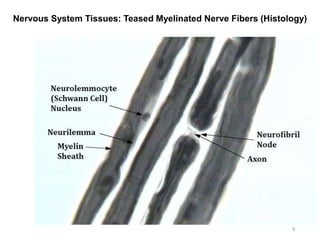
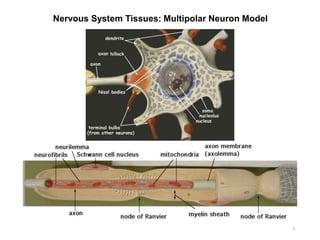
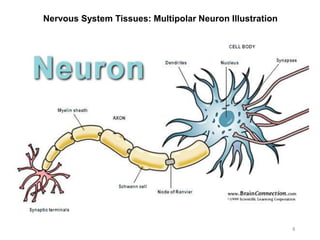
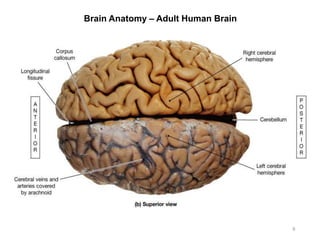
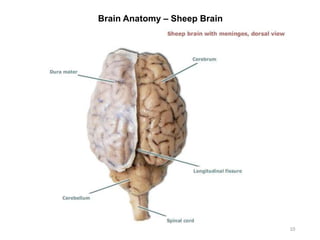
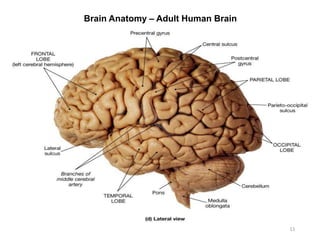
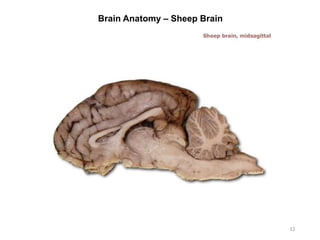
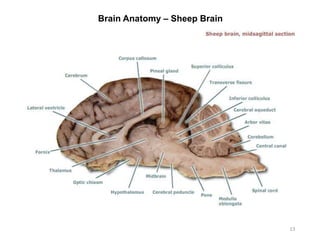
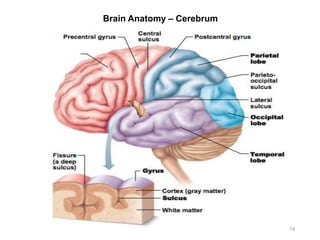
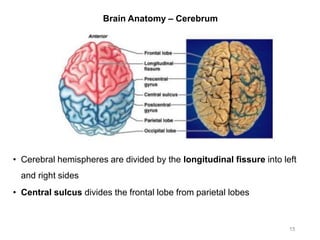
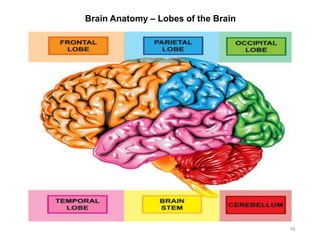
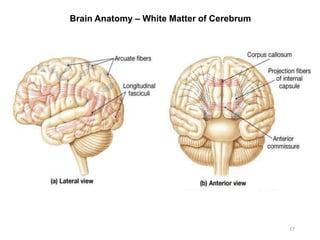
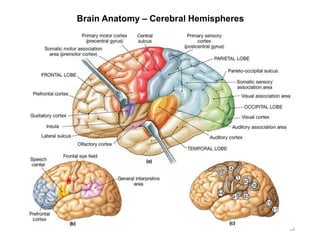
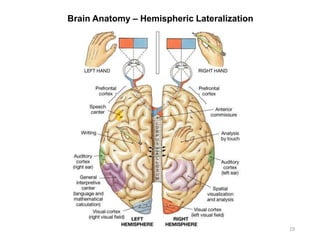
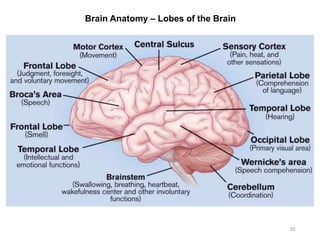
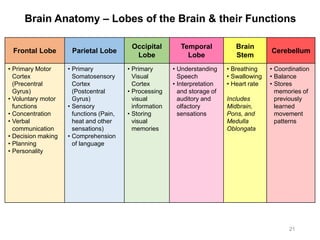
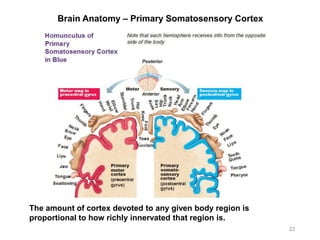
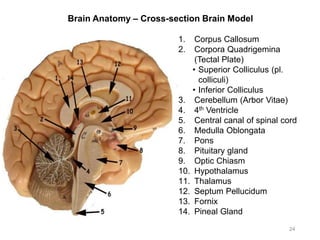
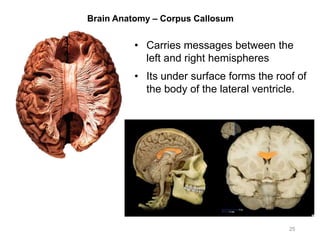
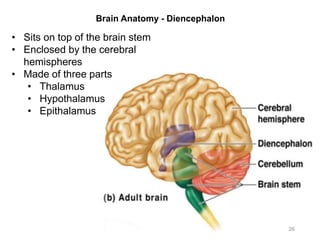
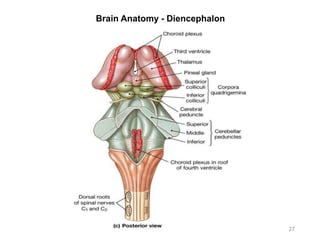
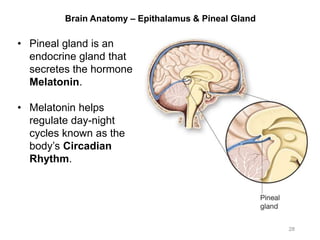
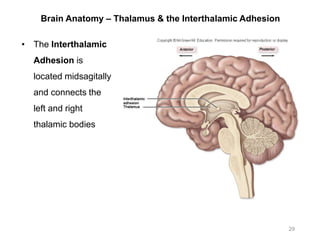
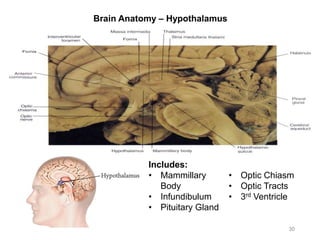
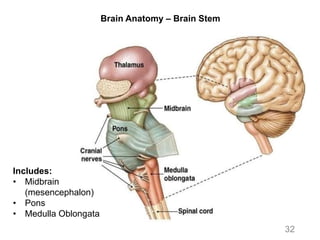
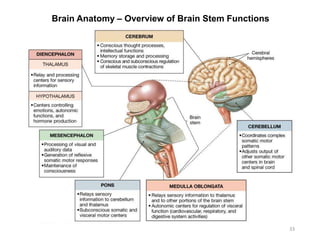
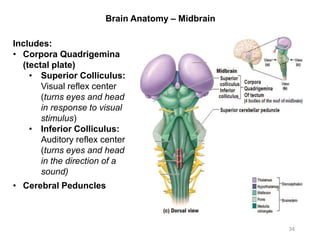
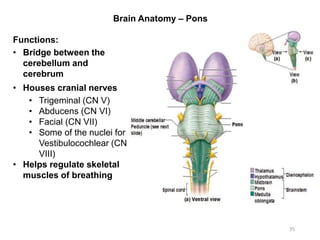
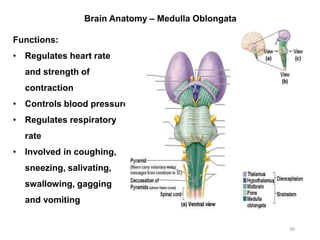
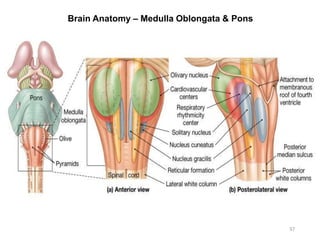
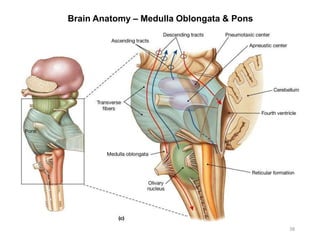
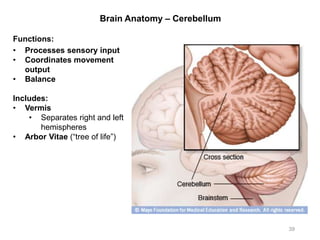
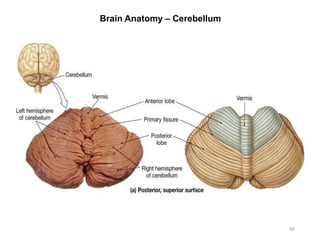
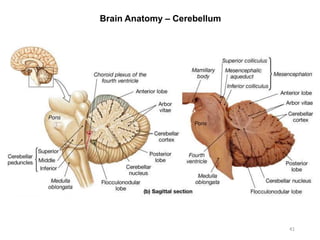
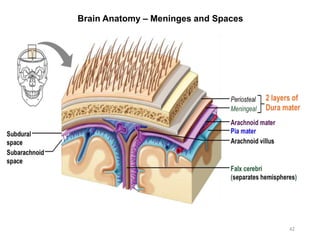
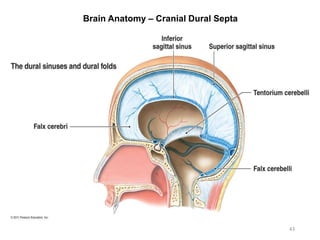
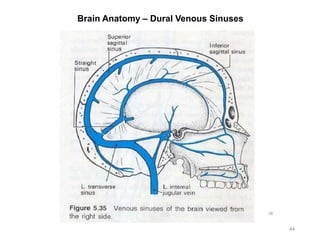
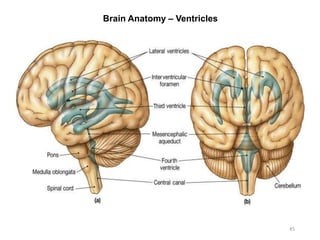
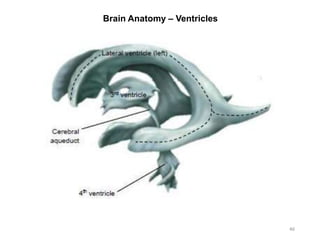
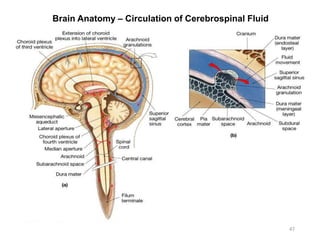
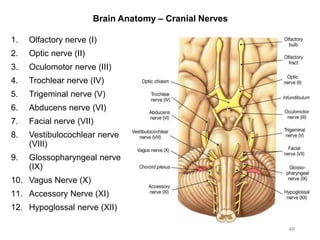
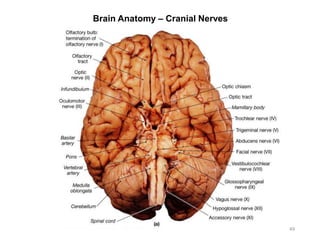
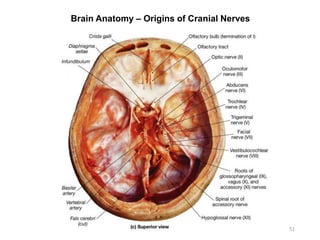
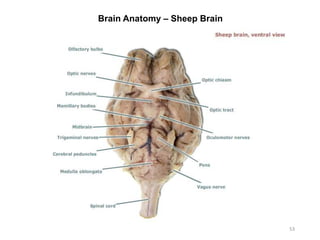
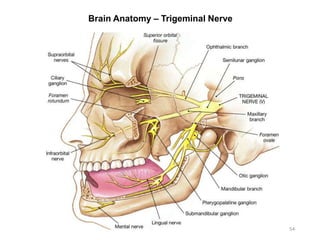
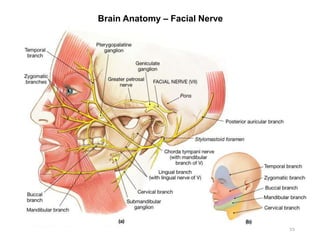
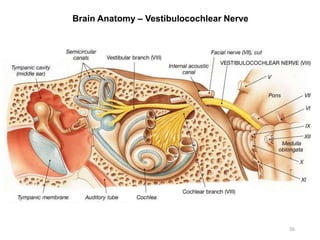
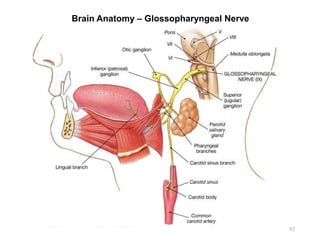
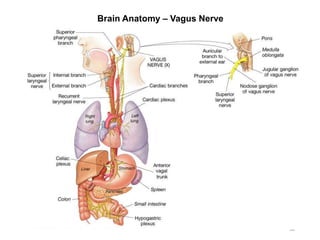
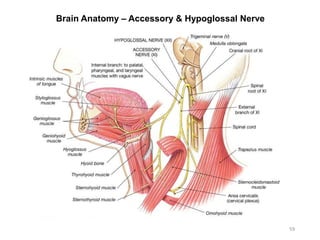
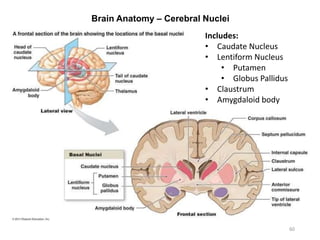
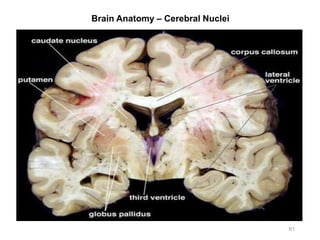
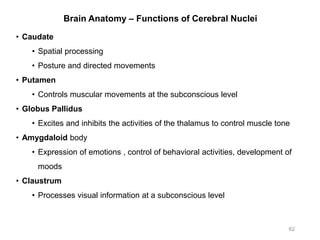
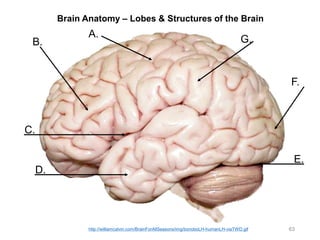
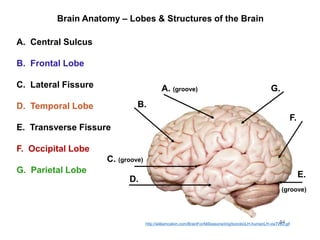
This document provides objectives and materials for an activity on the nervous system histology, brain, and cranial nerves. The activity involves identifying structures from slides and illustrations of nervous system tissue, as well as identifying brain structures and cranial nerves from models of human and sheep brains. The document includes numerous slides and illustrations of nervous system tissues, brain structures such as lobes, ventricles, and nuclei, as well as images of cranial nerves. It also provides information on the functions of various brain structures.