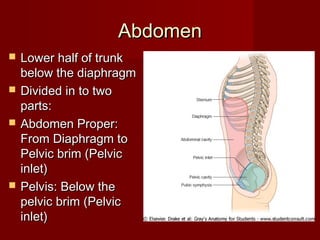
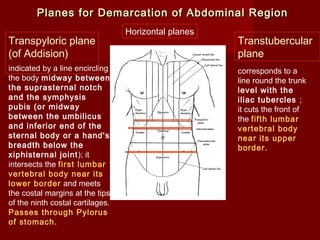
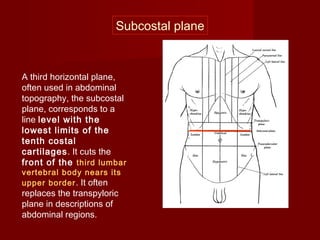
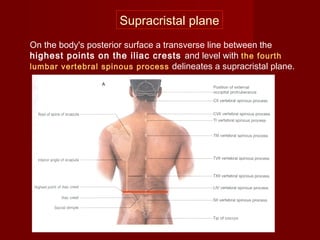
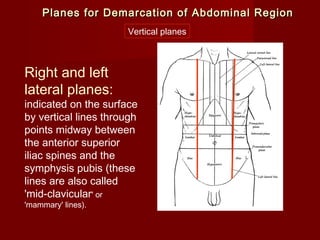
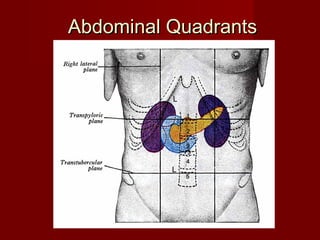
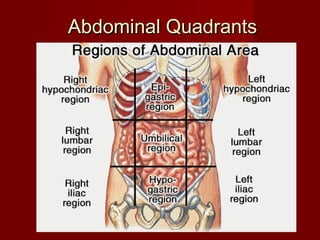
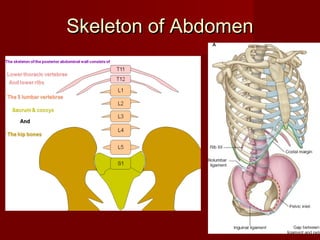
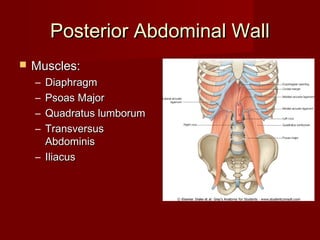
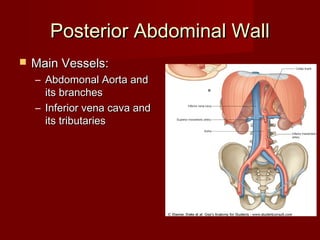
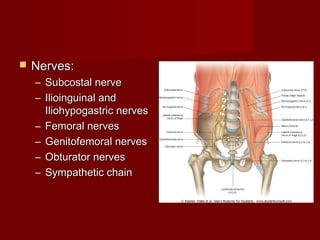
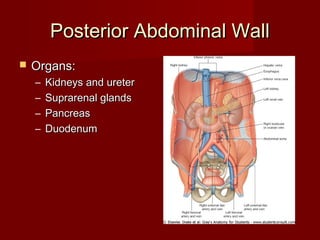
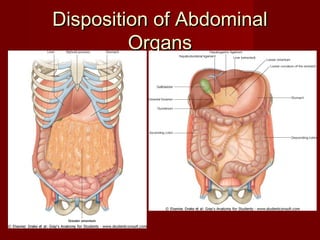
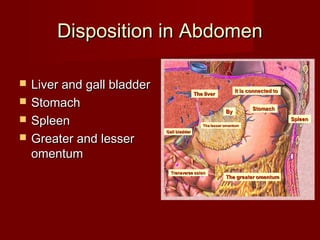
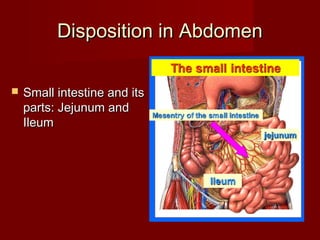
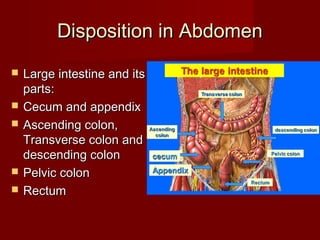
The document discusses the planes, divisions, and structures of the abdomen. It describes how the abdomen is divided into nine quadrants by two horizontal planes (transpyloric and transtubercular) and two vertical planes. Each quadrant contains specific organs and structures. The key structures arranged in the abdomen include the skeleton, muscles of the posterior abdominal wall, blood vessels such as the aorta and IVC, nerves like the femoral nerve, and organs like the liver, stomach, intestines, kidneys and pancreas.