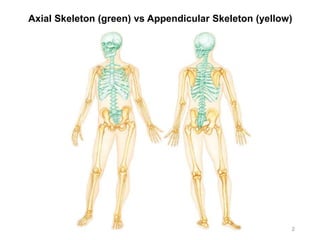
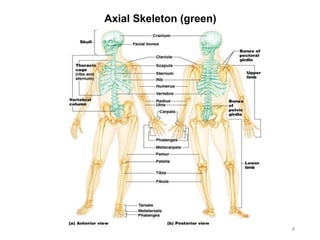
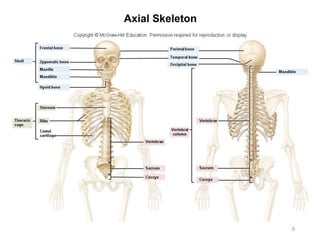
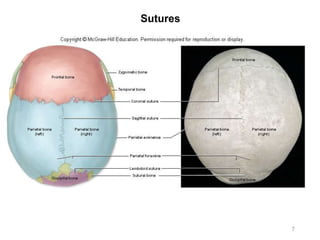
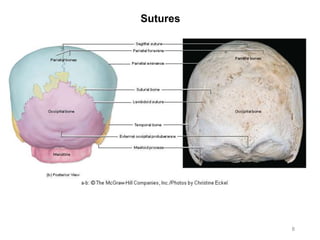
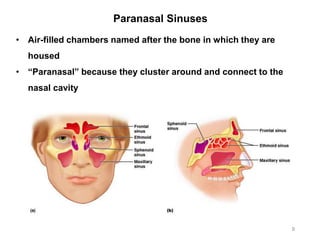
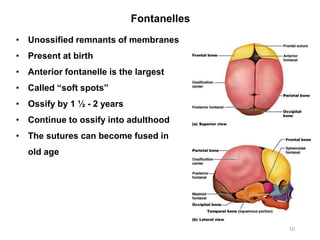
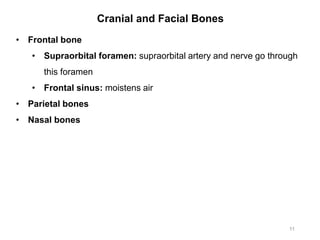
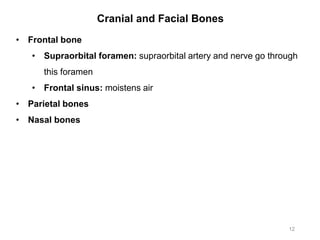
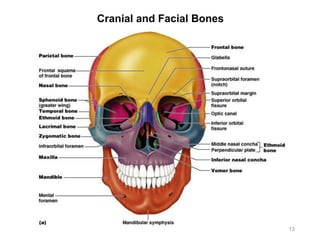
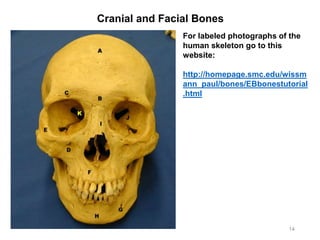
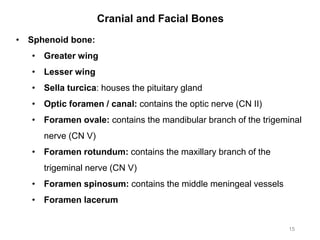
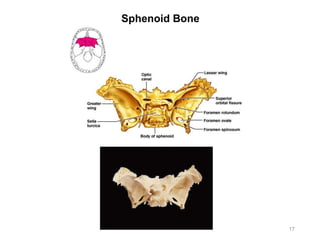
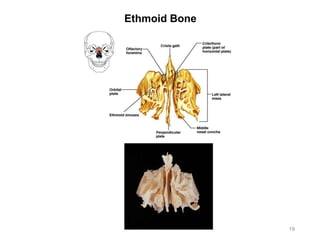
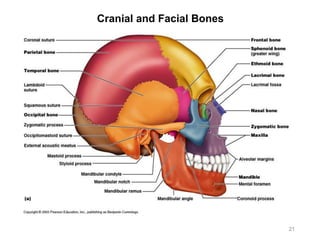
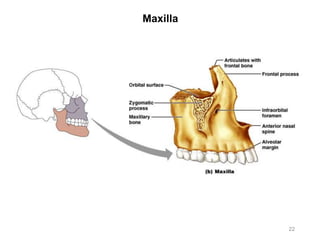
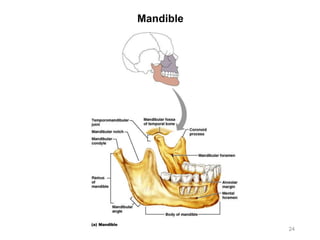
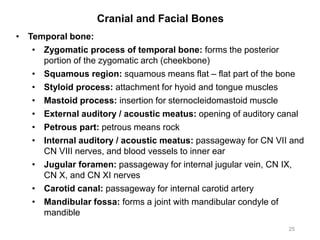
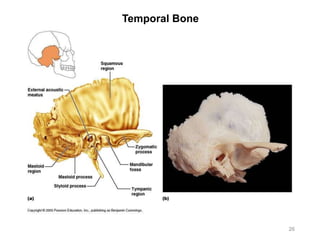
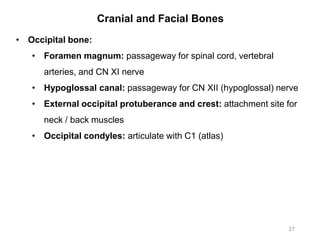
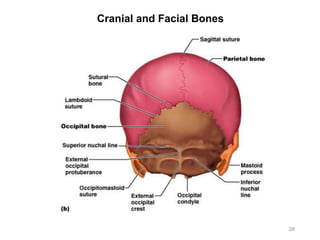
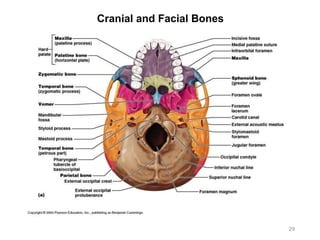
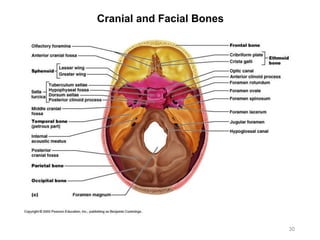
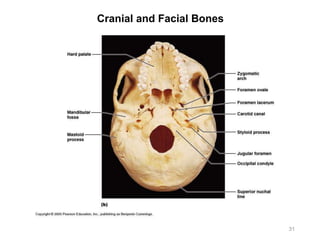
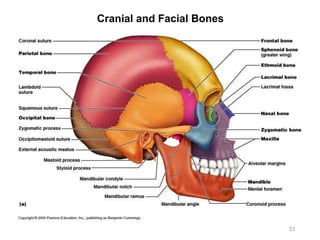
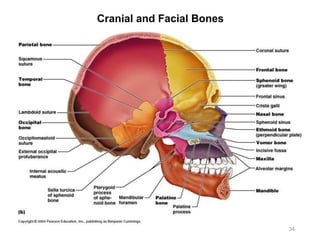
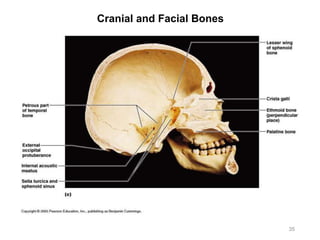
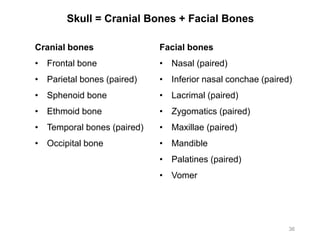
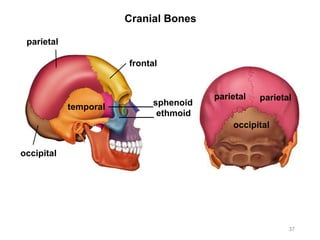
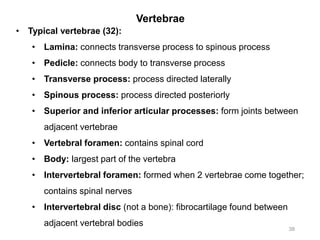
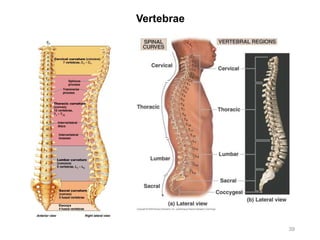
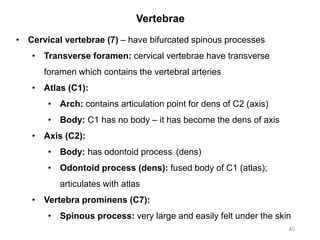
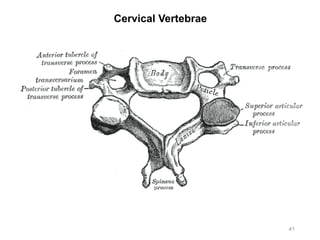
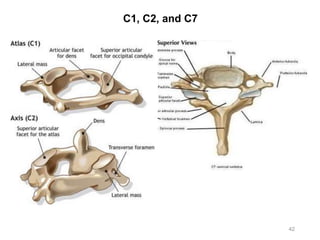
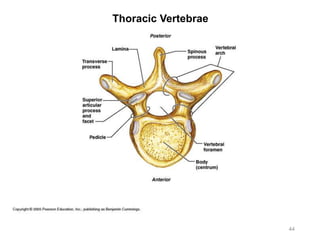
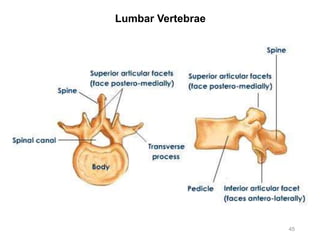
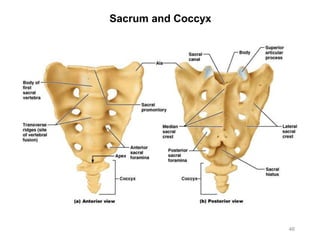
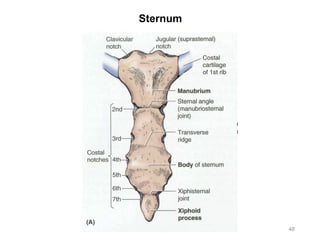
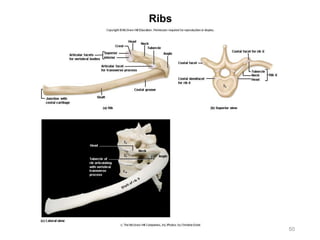
The document provides information about the axial skeleton, including the cranial and facial bones, vertebrae, sternum, and ribs. It lists the objectives of identifying these bones and their features. Descriptions are given for each bone, including locations of foramina, processes, plates, and other markings. Diagrams are included to illustrate bone positions and features.