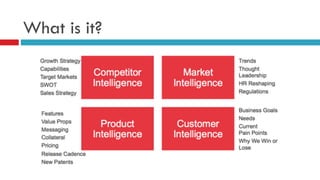
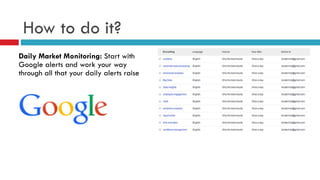
The document outlines the significance and methodology of competitive intelligence (CI), emphasizing the importance of gathering and analyzing competitor data to enhance a company's position in the market. It provides actionable strategies for effectively conducting CI through tools like Google Alerts, job data sites, and social media, while also addressing ethical considerations. Key aspects include understanding competitor strategies, daily market monitoring, and sharing findings within the organization to maximize the value of the intelligence gathered.