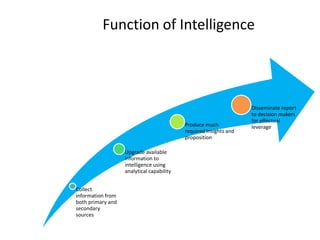
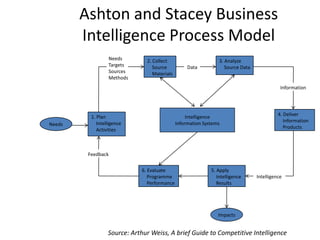
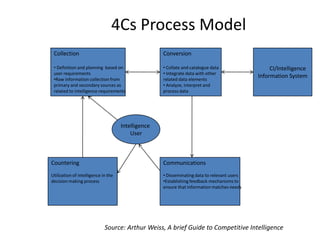
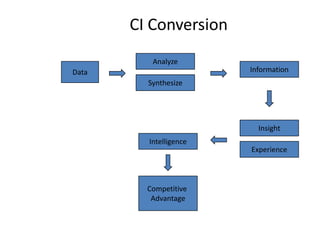
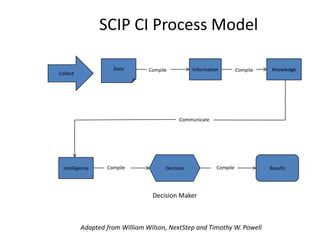
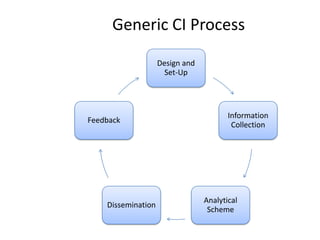
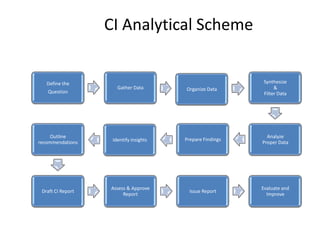
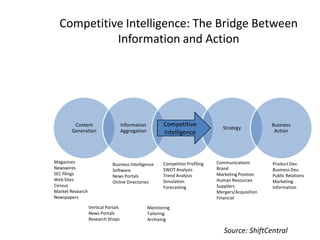
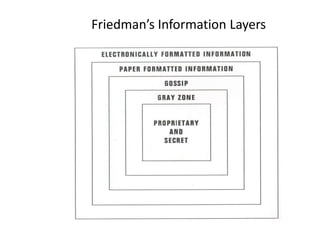
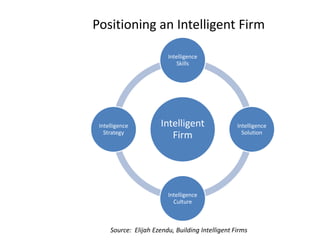
The document provides a comprehensive overview of competitive intelligence (CI), defining it as the ethical process of collecting and analyzing relevant information about the business environment, competitors, and the organization itself. It outlines various types of intelligence, methodologies, and applications in improving business performance and strategic decision-making. The document emphasizes the importance of CI as a tool for gaining competitive advantage and includes details on the roles and processes involved in effective CI implementation.