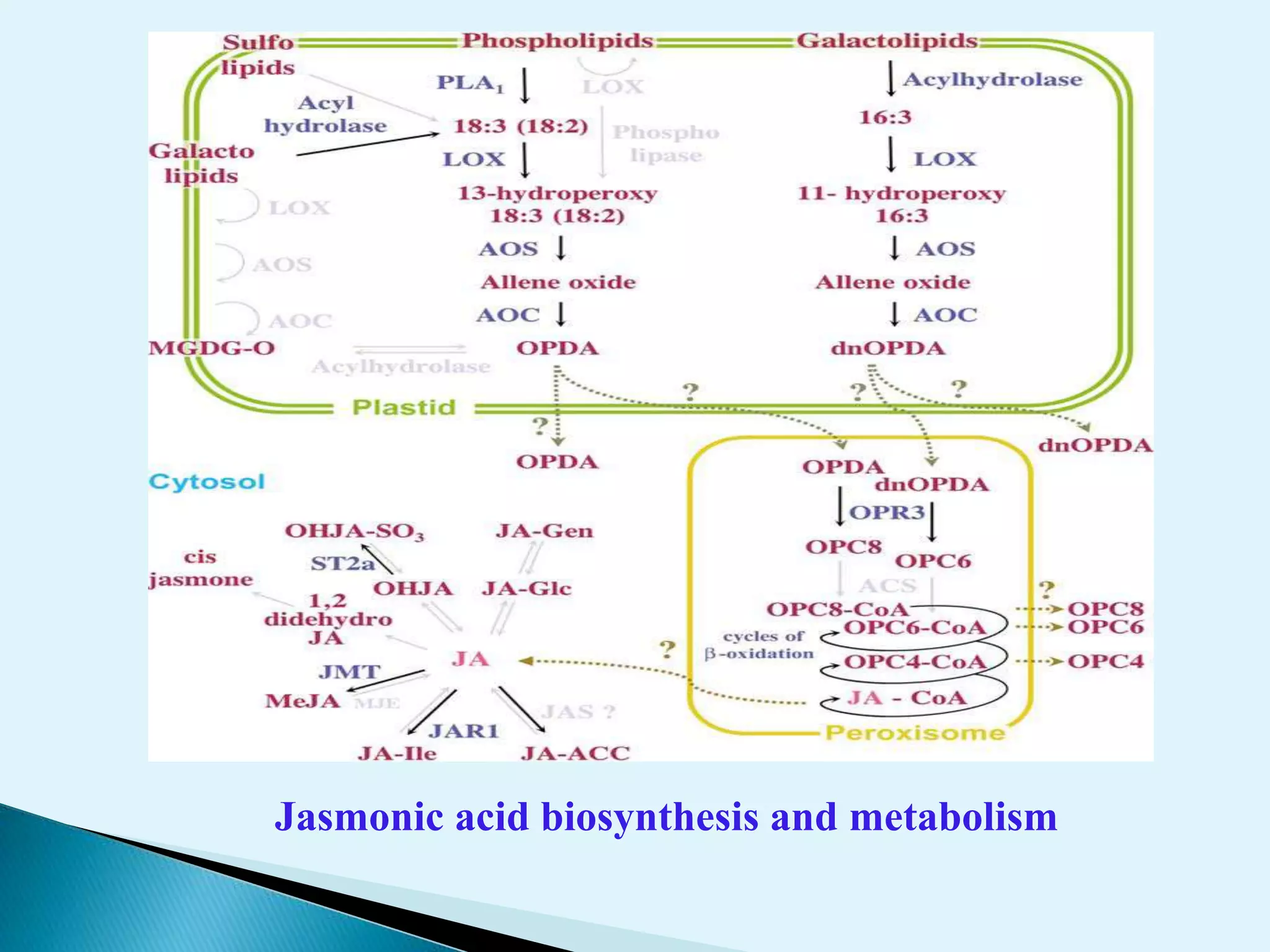
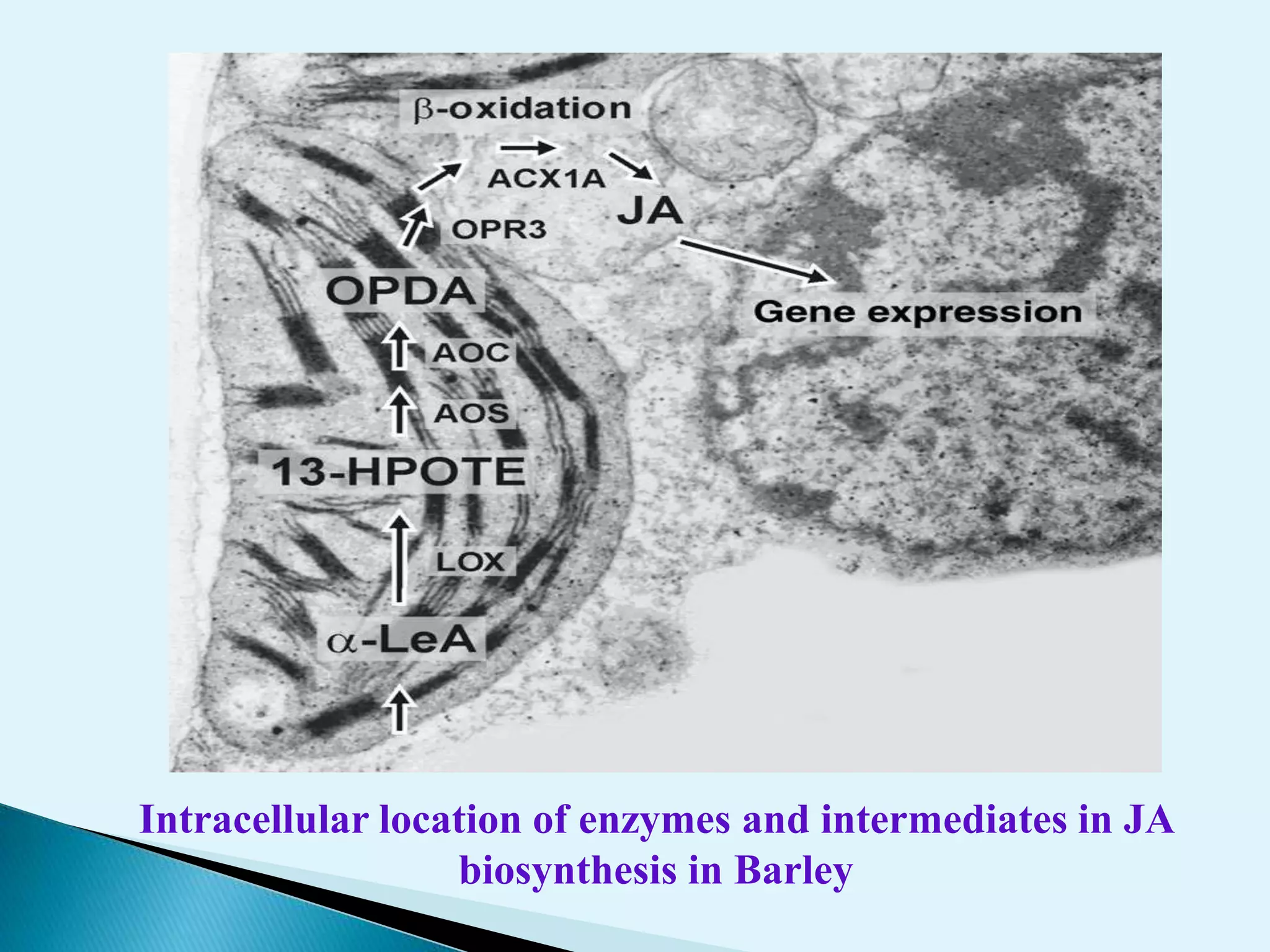
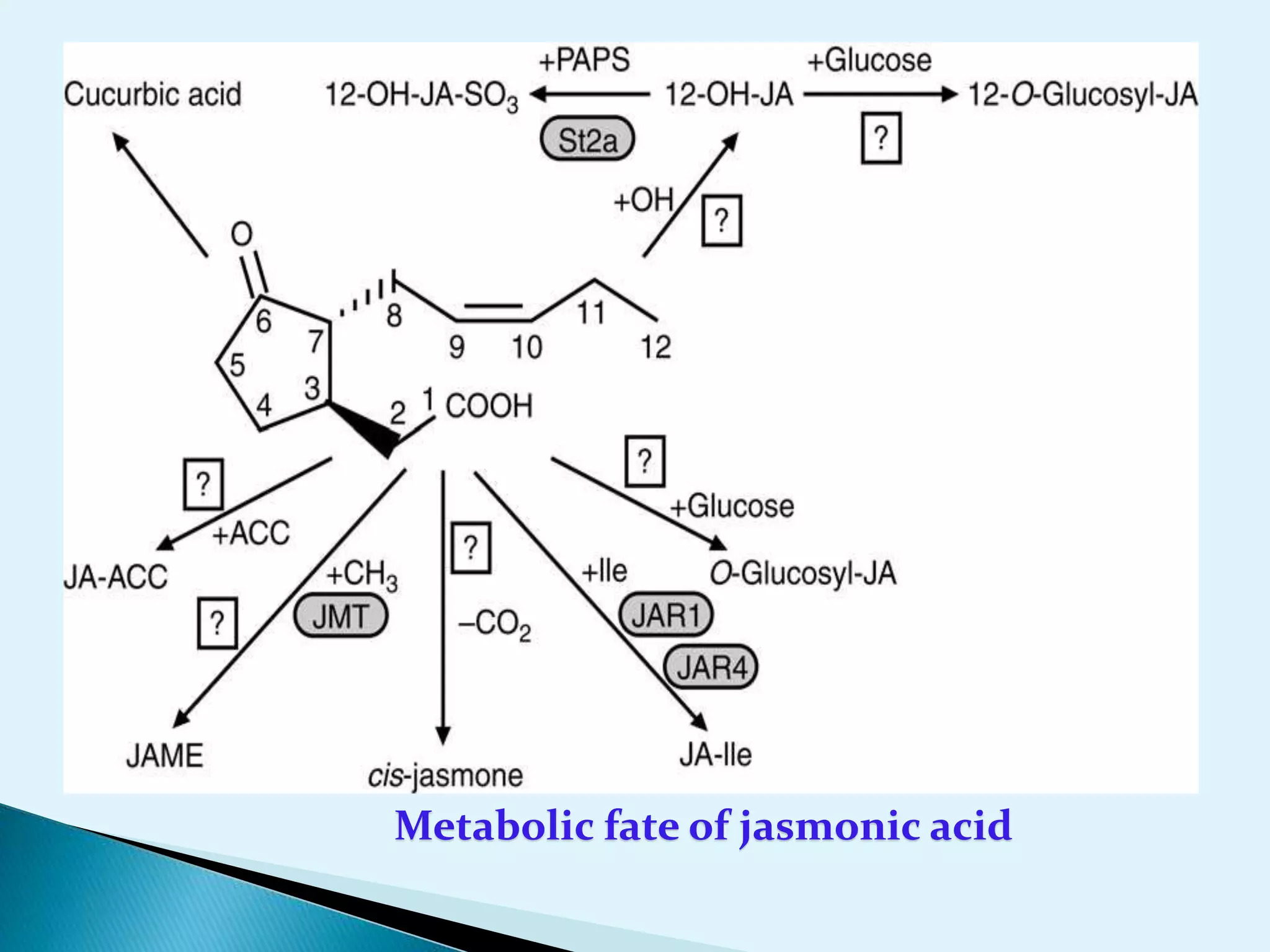
Plants utilize chemical defense strategies against wounding, primarily through the action of jasmonic acid (JA) and its derivatives, which play crucial roles in signaling and the synthesis of defense proteins. JA is synthesized through a specific biosynthesis pathway from linolenic acid and regulates various physiological processes, including responses to herbivory and environmental stress. The application of JA can enhance plant defenses and improve pest management strategies in agriculture.