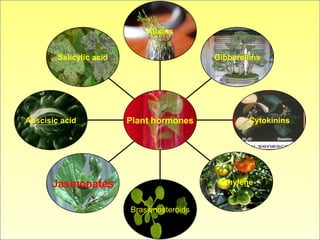
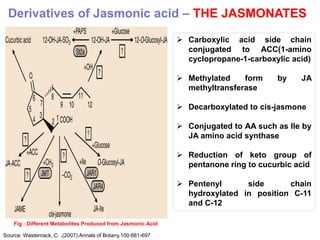
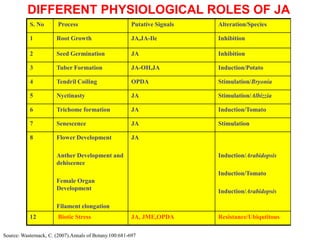
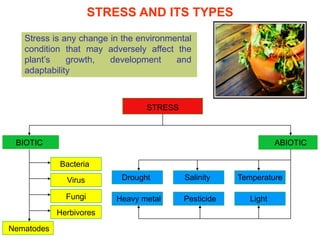
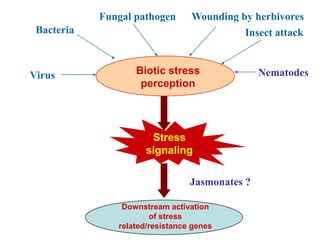
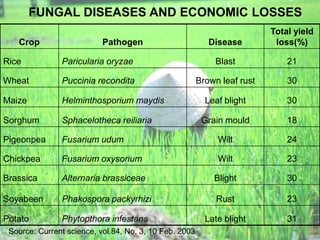
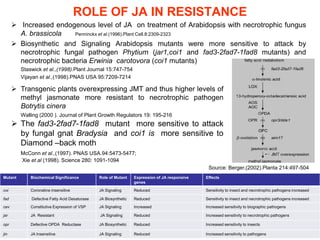
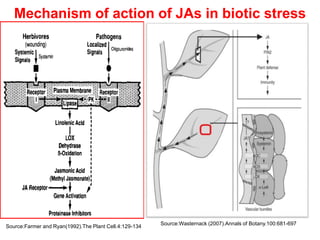
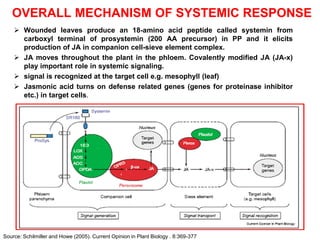
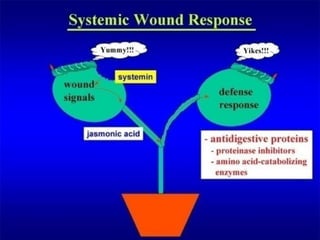
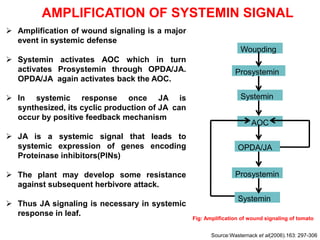
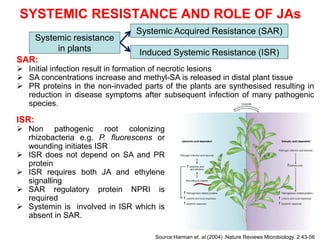
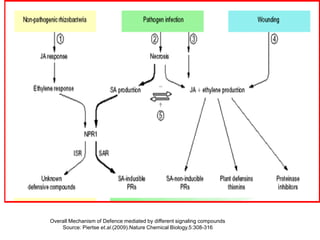
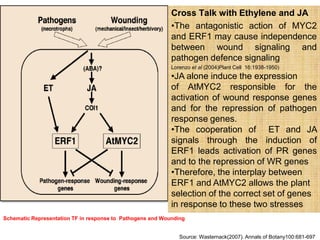
The document discusses jasmonates, a group of plant hormones involved in stress responses, including their biosynthesis, physiological roles, and mechanisms of action against biotic stressors. It highlights the importance of jasmonates in plant defense, detailing how they interact with various signaling pathways and can enhance resistance to pathogens and pests. The significance of jasmonate research for improving crop yield and stress resistance is emphasized, particularly in the context of addressing global food security challenges.