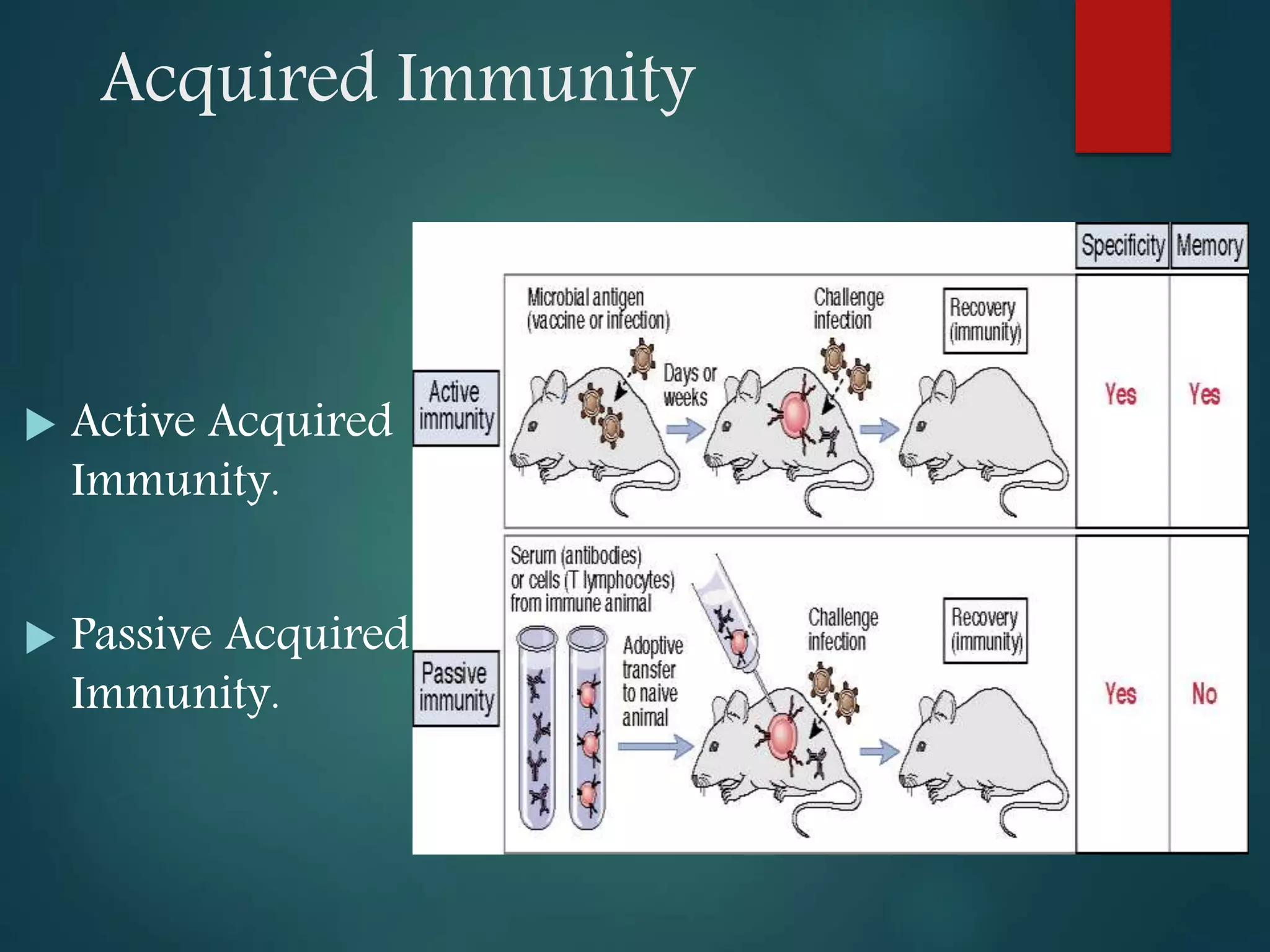
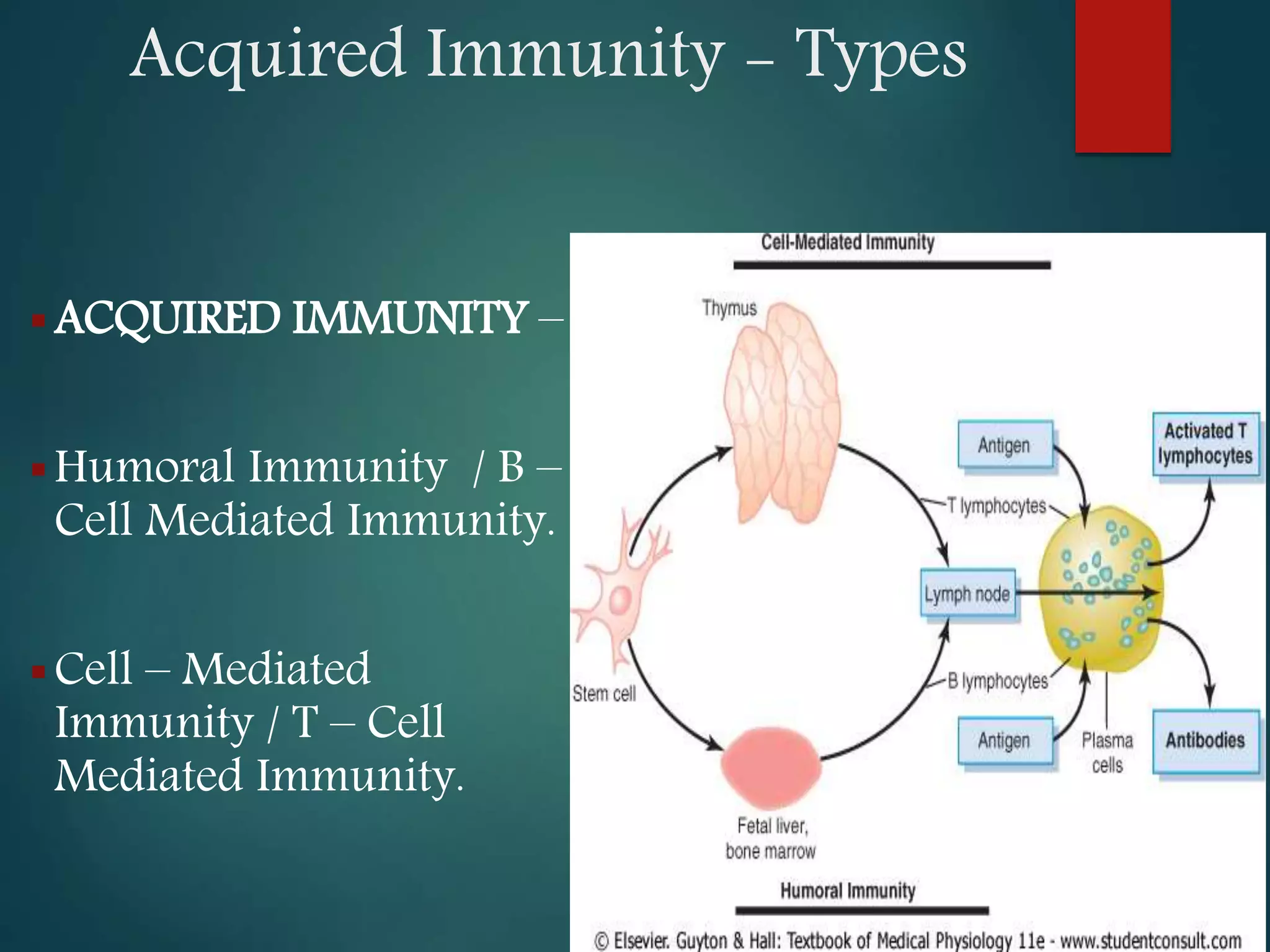
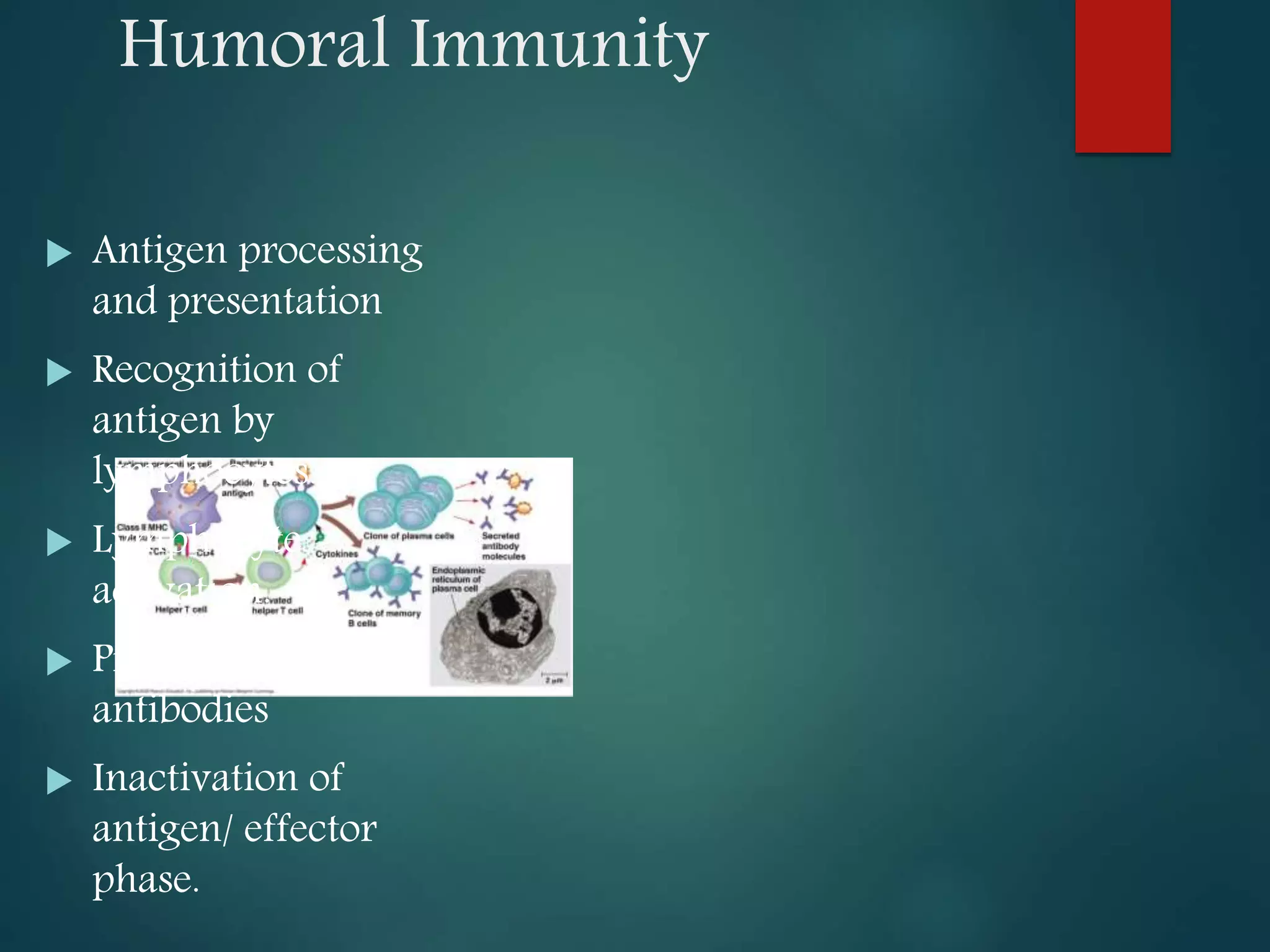
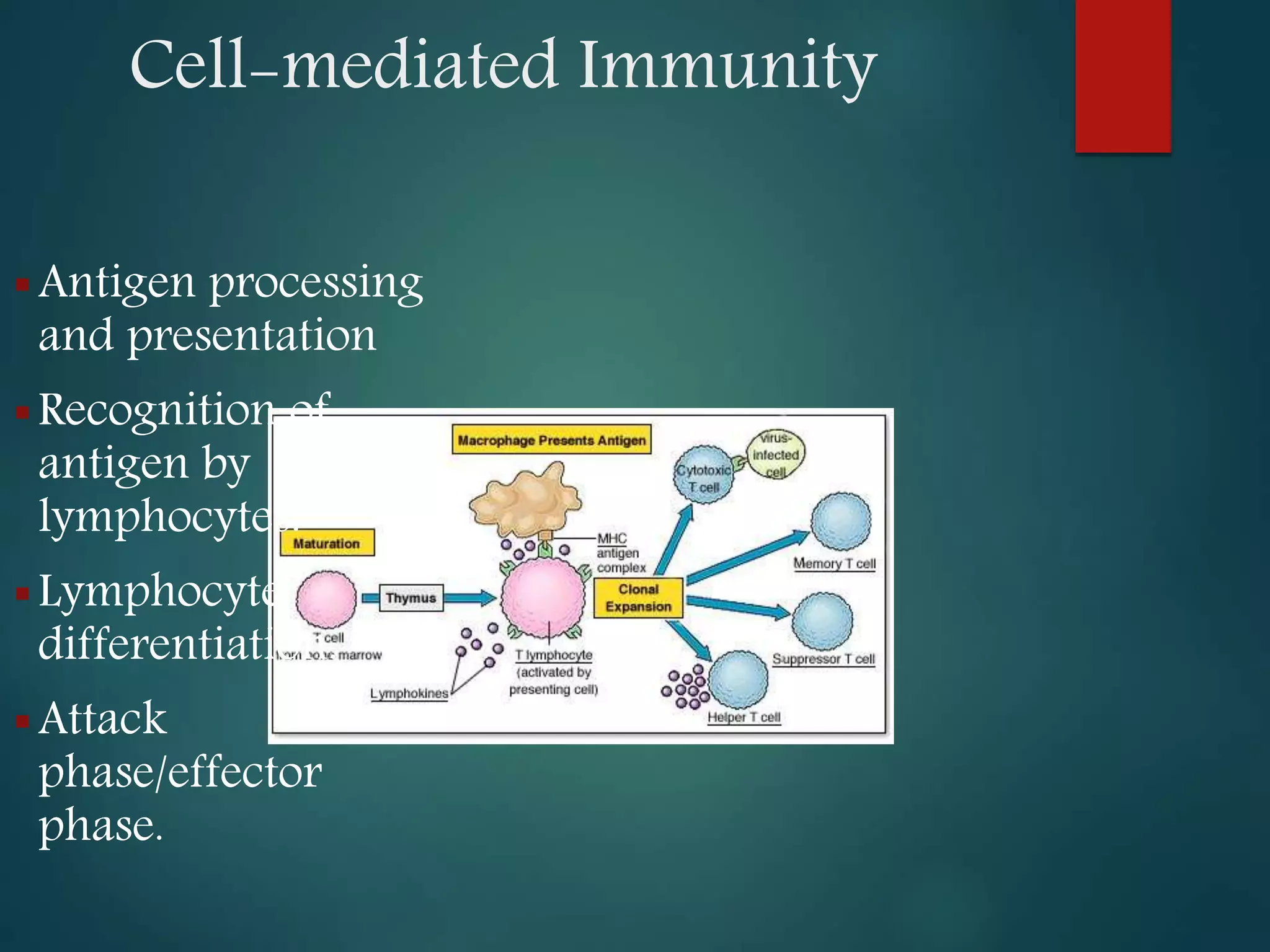
This document discusses acquired immunity and its types. It describes the roles of natural killer cells, T lymphocytes, and B lymphocytes in acquired immunity. There are two types of acquired immunity: active and passive. Acquired immunity can be humoral, mediated by antibodies and B cells, or cell-mediated, mediated by T cells. Humoral immunity defends against extracellular pathogens through antibody production and activation of the complement system. Cell-mediated immunity protects against intracellular pathogens and is carried out by T cell activation and attack. Cytokines regulate the immune response through various functions. Acquired immunity has applications in vaccination, transplantation, and treatment of immune disorders.