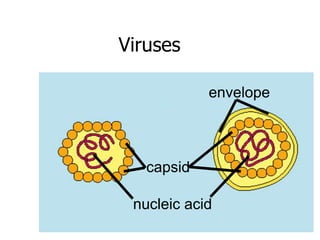
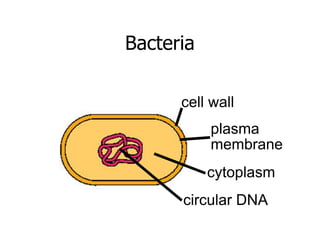
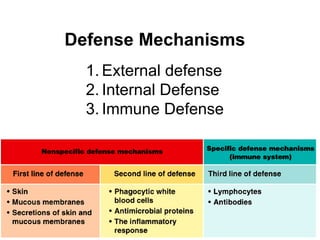
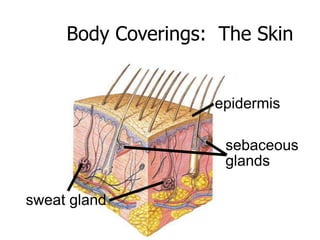
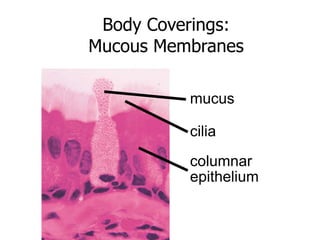
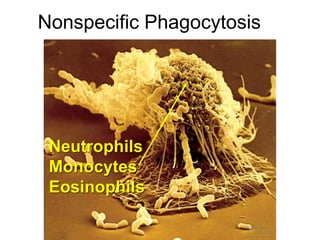
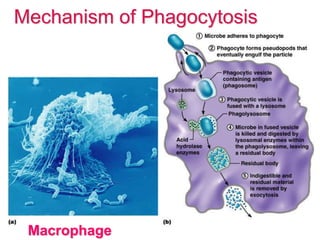
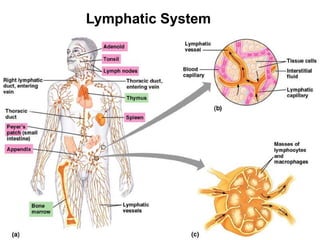
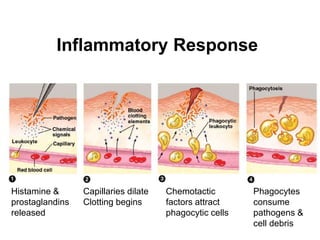
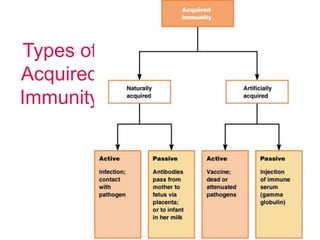
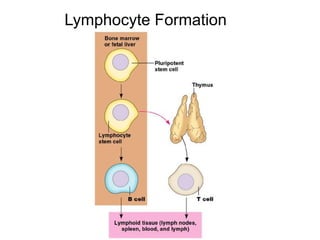
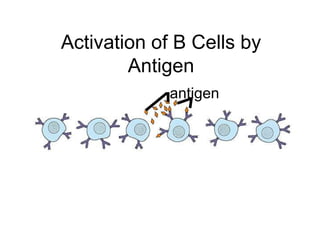
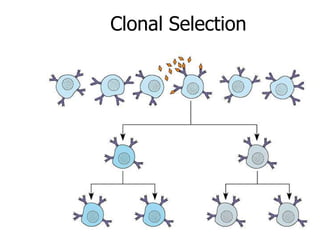
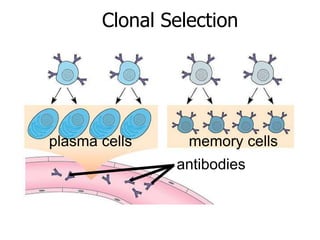
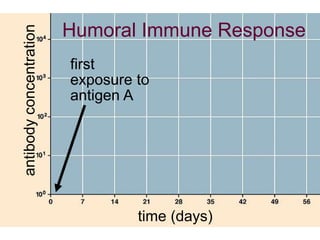
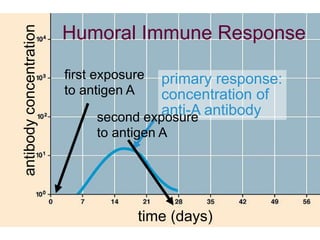
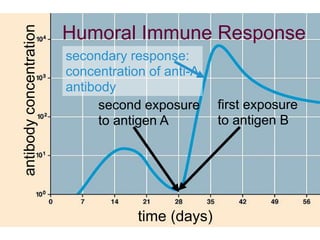
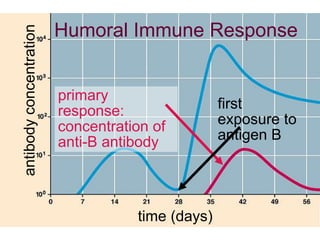
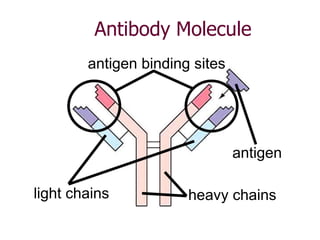
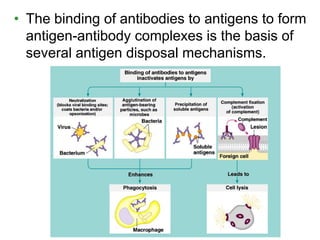
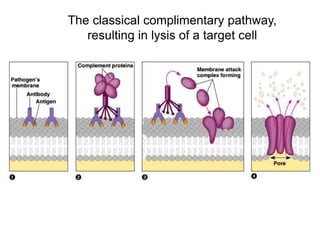
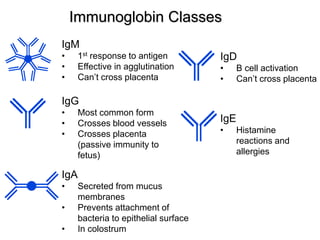
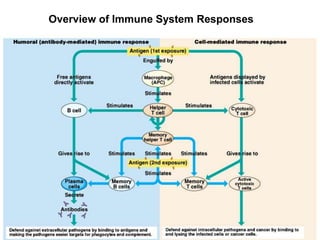
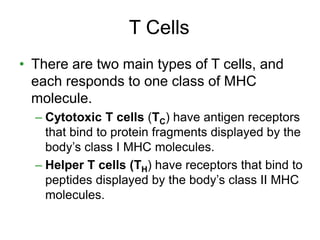
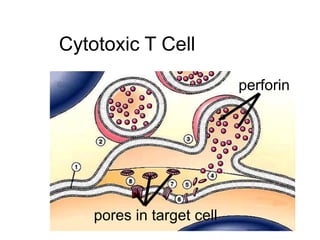
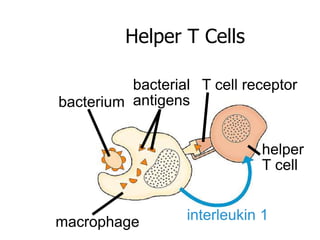
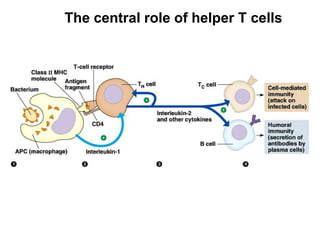
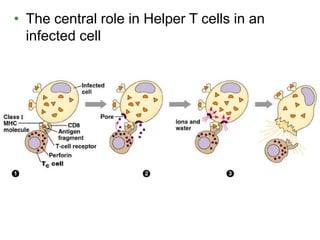
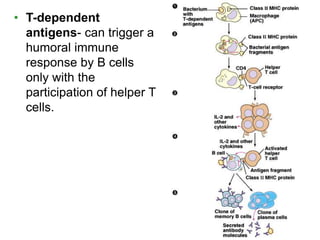
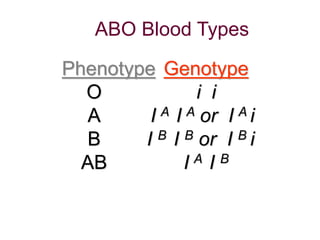
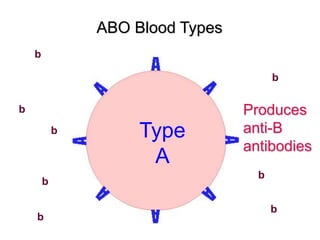
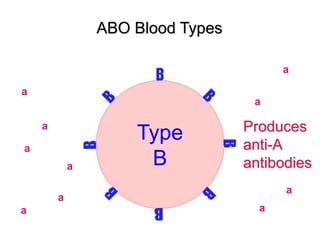
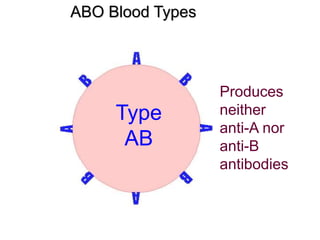
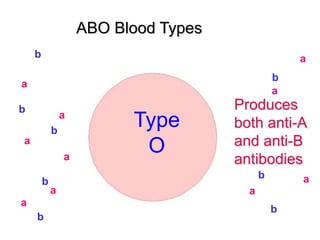
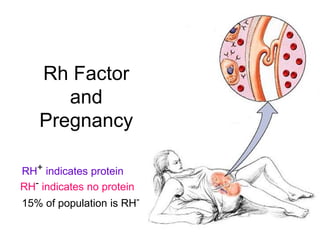
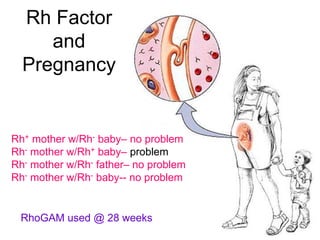
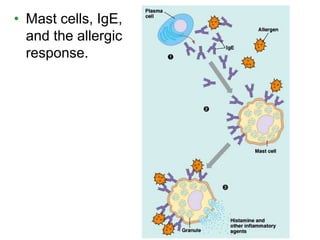
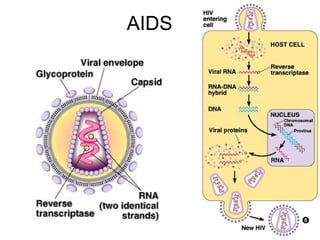
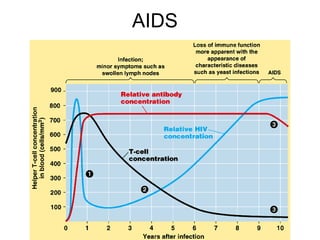
This document provides an overview of the human immune system and its defenses against disease. It discusses the external barriers of skin and mucus, internal responses like phagocytosis and inflammation, and the adaptive immune system involving B and T cells and antibody production. It covers active and passive immunity, immune responses, antigen recognition, and immune system disorders like autoimmunity, allergy, and AIDS. The immune system provides multilayered defenses that have largely evolved to protect the body from infectious diseases, toxins, and other foreign invaders.