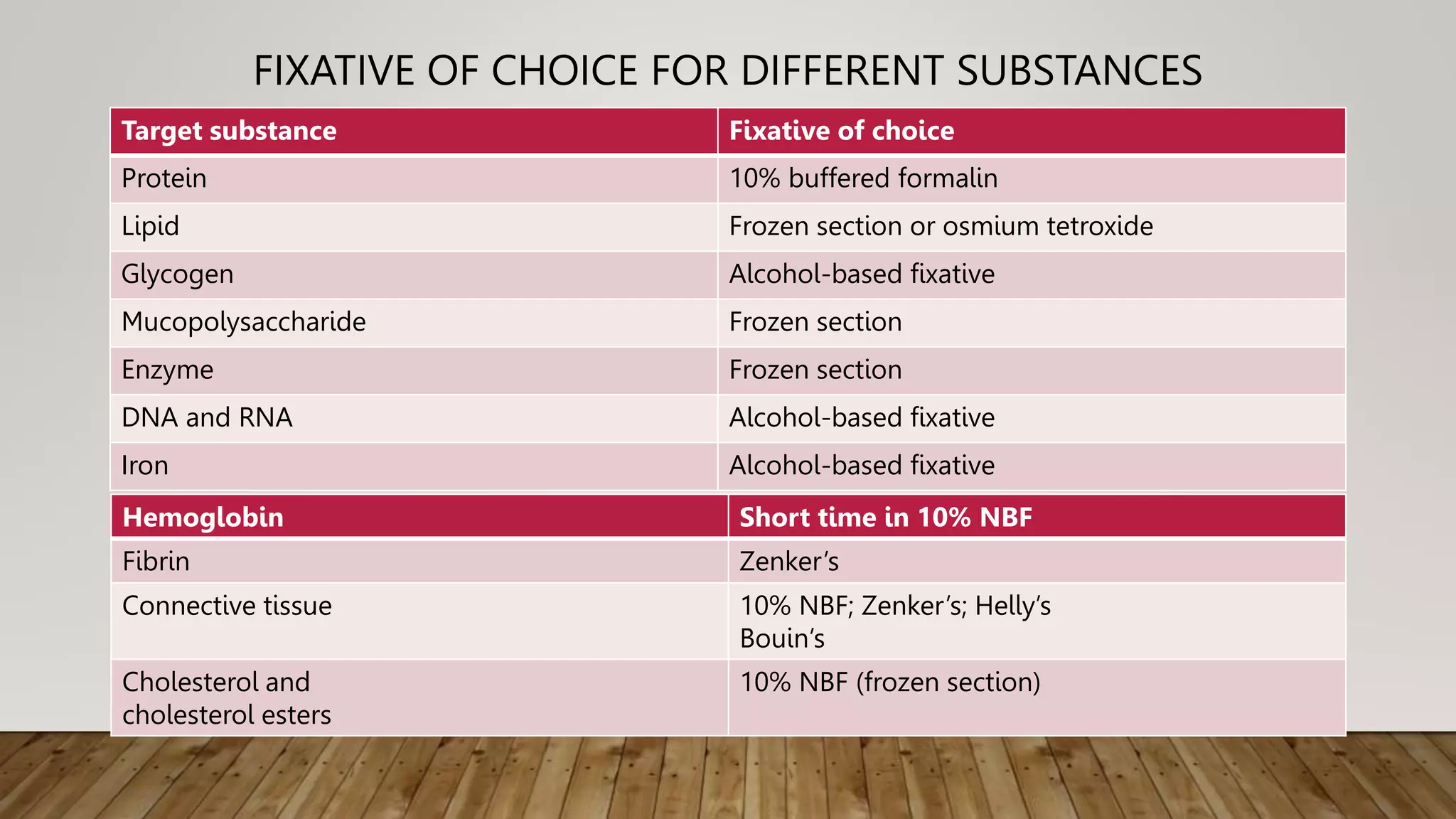
The document discusses fixation in histology and cytology. It describes the aims of fixation as preserving tissue structure and preventing autolysis and bacterial growth. Fixation causes some changes like tissue shrinkage and hardening. The types of fixation include immersion, coating, vapor and perfusion. Formalin and alcohol are common fixatives. Factors like pH, temperature, duration and osmolarity influence fixation quality. The choice of fixative depends on the tissue and technique used, for example glutaraldehyde for electron microscopy. Useful fixative formulas are also provided.