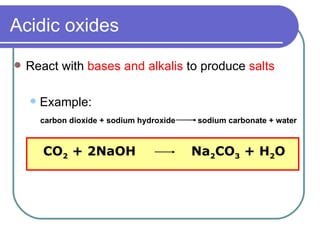
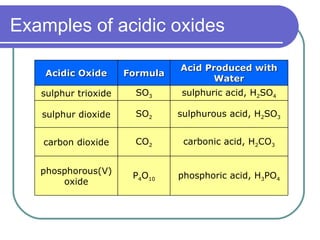
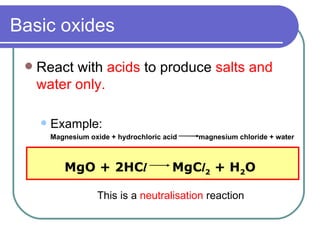
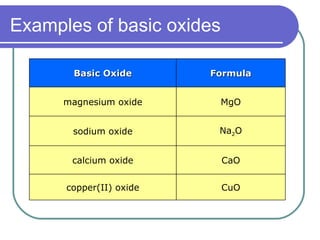
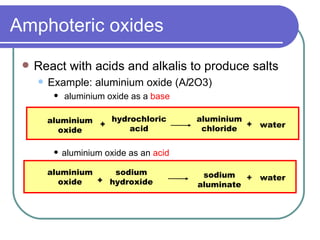
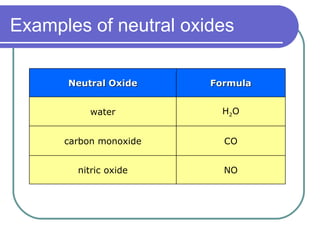
This document discusses different types of oxides based on their reactions with water and acids or bases. It defines acidic, basic, amphoteric, and neutral oxides. Acidic oxides react with water to form acids, while basic oxides react with acids to form salts and water. Amphoteric oxides can behave as either acidic or basic oxides depending on the reaction. Neutral oxides show no acidic or basic properties and are insoluble in water. The document provides examples of common oxides that fall into each category and an decision tree for classifying an unknown oxide based on its solubility properties.