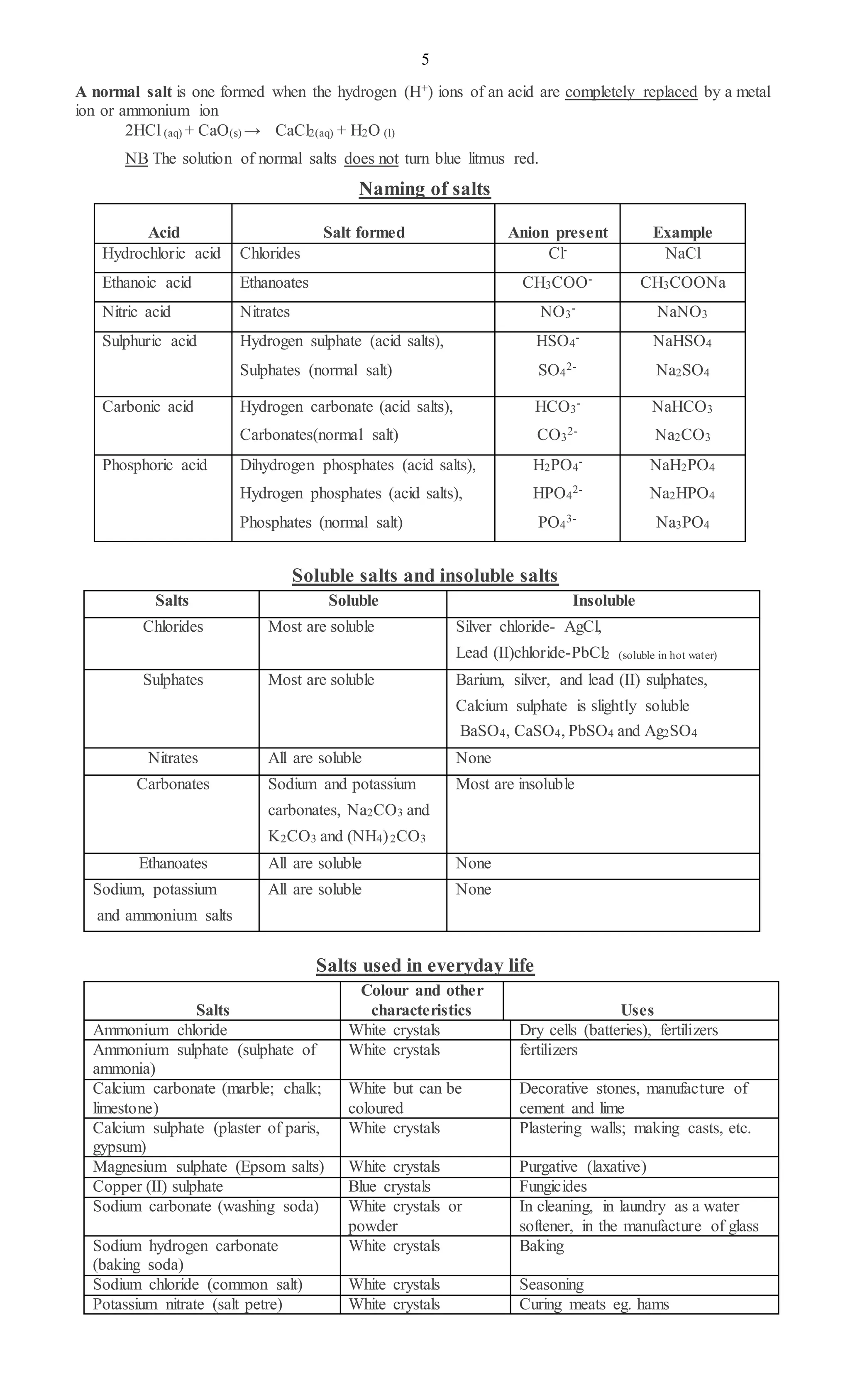
1. Oxides can be acidic, basic, neutral or amphoteric depending on whether they react with acids and bases to form salts and water. Acidic oxides form salts with bases while basic oxides form salts with acids.
2. Acids are compounds that form hydrogen ions in aqueous solution and have characteristic properties like turning litmus red. Strong acids fully ionize while weak acids partially ionize.
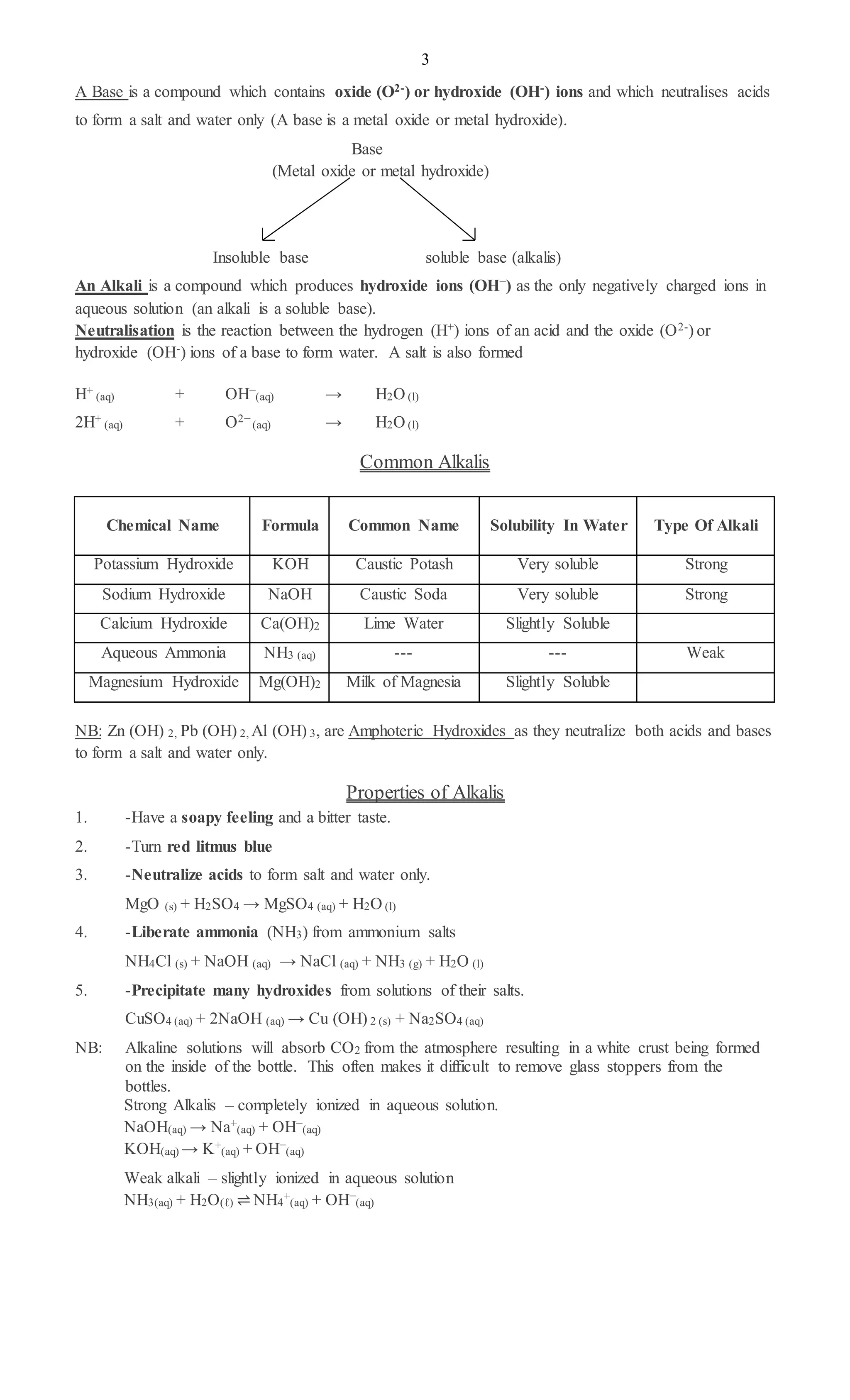
3. Bases are compounds that form hydroxide ions in aqueous solution and have properties like turning litmus blue. Alkalis are soluble bases that produce hydroxide ions in water.

![2
Properties of acids
1. -have a sharp, sour taste
2. -turn damp blue litmus red
3. -neutralise bases to form a salt and water only
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(ℓ)
Acid + base → salt + water
4. -liberate CO2 from carbonates (CO3
2-) and hydrogen carbonates (HCO3
-) with effervescence
[effervescence is the rapid bubbling of gas out of solution]
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
2NaHCO3 (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → Na2SO4 (aq) + 2CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
5. -The more reactive metals (Mg, Zn, and Fe) liberate hydrogen from dilute acids with
effervescence
Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
6. -liberate SO2 from sulphites (SO3
2-)
Na2SO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + SO2 (g) + H2O (l)
NB: The mineral acids (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3) are corrosive (burn) when concentrated
The basicity (proticity) of an acid is the number of moles of hydrogen (H+) ions produced from one
mole of the acid in aqueous solution.
(a) Examples of monobasic (monoprotic) acids
HCl (aq) → H+
(aq) + Cl−
(aq)
HNO3 (aq) → H+
(aq) + NO3
−
(aq)
CH3COOH (aq) (Ethanoic acid) ⇌ H+
(aq) + CH3COO-
(aq)
(b) Examples of dibasic (diprotic) acids
H2SO4 (aq) → 2H+
(aq) + SO4
2−
(aq)
H2CO3 (aq) ⇌ 2H+
(aq) + CO3
2−
(aq)
(c) Example of a tribasic (triprotic) acid
H3PO4 (aq) ⇌ 3H+
(aq) + PO4
3−
(aq)
Strong and weak acids
NB: The term `strength` relates to the degree of ionisation of the acid or alkali in aqueous solution.
The acidity of a solution is proportional to the number of H+ ions present.
The term `concentrated` relates to amount of solute (acid or alkali) used to make up a given
volume of solution.
.A Strong Acid is one which is completely ionised in aqueous solution
e.g. HCl (aq) → H+
(aq) + Cl−
(aq)
HNO3 (aq) → H+
(aq) + NO3
−
(aq)
H2SO4 (aq) → 2H+
(aq) + SO4
2−
(aq)
A Weak Acid is one which is partially ionised in aqueous solution. It consists mainly of acid
`molecules` and its ionisation is reversible.
e.g. H2CO3 (aq) 2H+
(aq) + CO3
2−
(aq)
CH3COOH (aq) H+
(aq) + CH3COO−
(aq)
Bases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cxcoxidesacidsbasesandsalts-211031035025/75/Cxc-oxides-acids-bases-and-salts-2-2048.jpg)