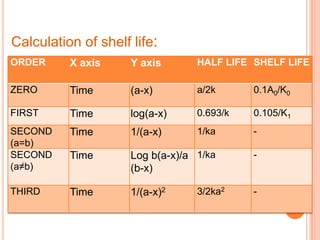
The document discusses accelerated stability testing which uses exaggerated storage conditions to rapidly assess a drug product's stability over time. It describes the Arrhenius equation which relates reaction rate to temperature and activation energy. Common accelerated tests involve storing samples at elevated temperatures, humidity, oxygen, or light levels. While useful, accelerated testing has limitations when degradation depends on other factors like microbes or diffusion. ICH guidelines provide standard methods for stability testing and data analysis.