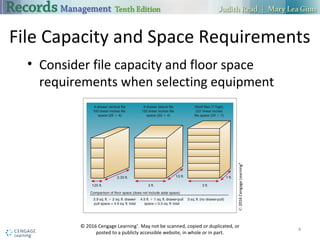
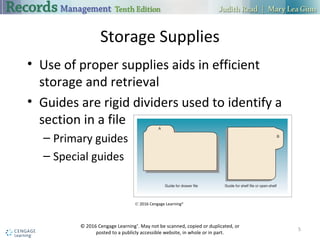
The document discusses alphabetic records management and storage. It describes various equipment, supplies, and procedures used to store physical records alphabetically, including file cabinets, guides, folders, labels, and sorters. The advantages of alphabetic storage include its ease of use and ability to group related records, while disadvantages include potential for misfiling and inability to group records for different names together. Selection of a storage system depends on volume of records and expected activity.