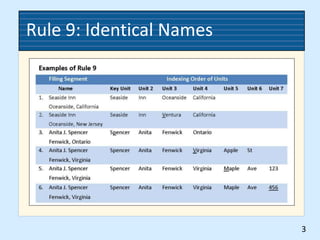
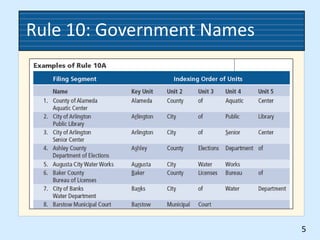
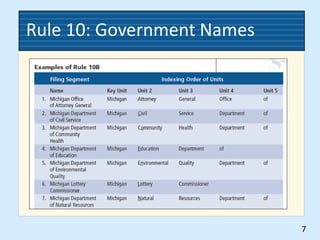
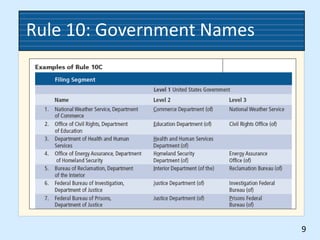
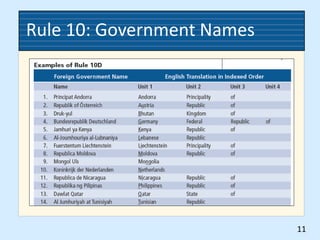
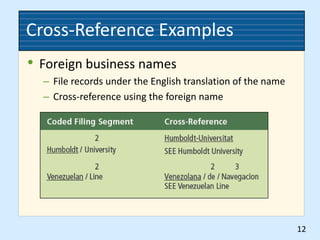
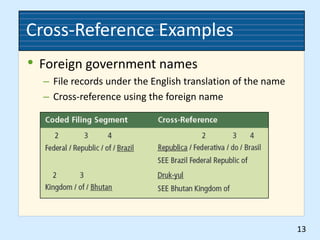
This document provides rules for alphabetic indexing of records. Rule 9 discusses sorting identical names by city, state/province, street, and house number. Rule 10 covers indexing government names, with the level of government (local, state, federal, foreign) determining the order of units in the name. Cross-references are suggested for foreign names. Subject titles may also be used as key indexing units, with subdivisions and correspondent names following.