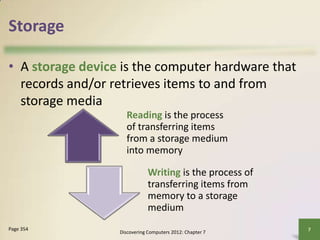
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various storage devices and media, including internal hard disks, solid state drives, and cloud storage, describing their characteristics and functionalities. It details the differences between storage types such as optical discs and magnetic tape, alongside explanations of access times, capacities, and storage methods. Additionally, it covers the importance of backing up data and the specific uses of each storage medium in various user scenarios.