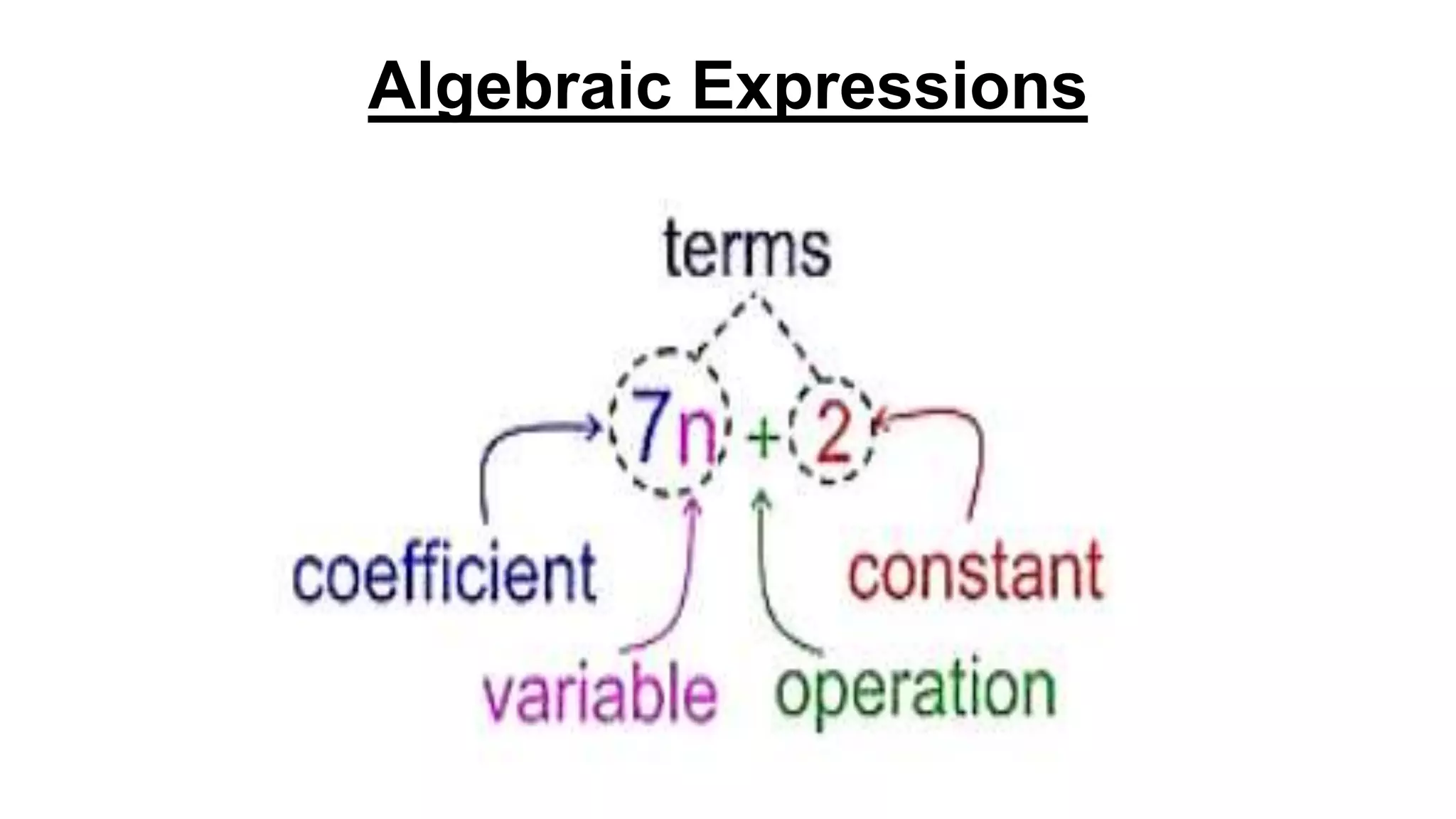
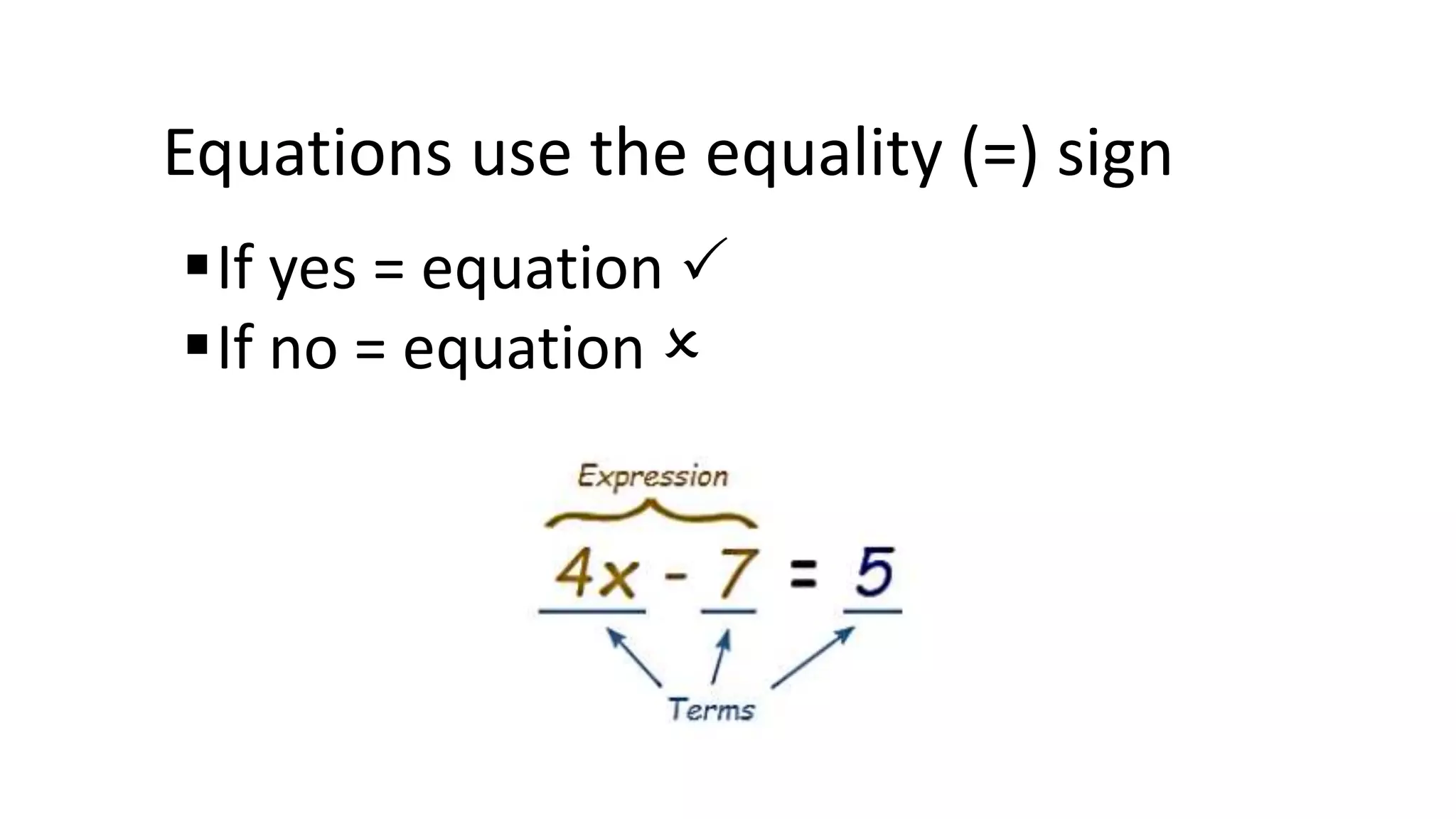
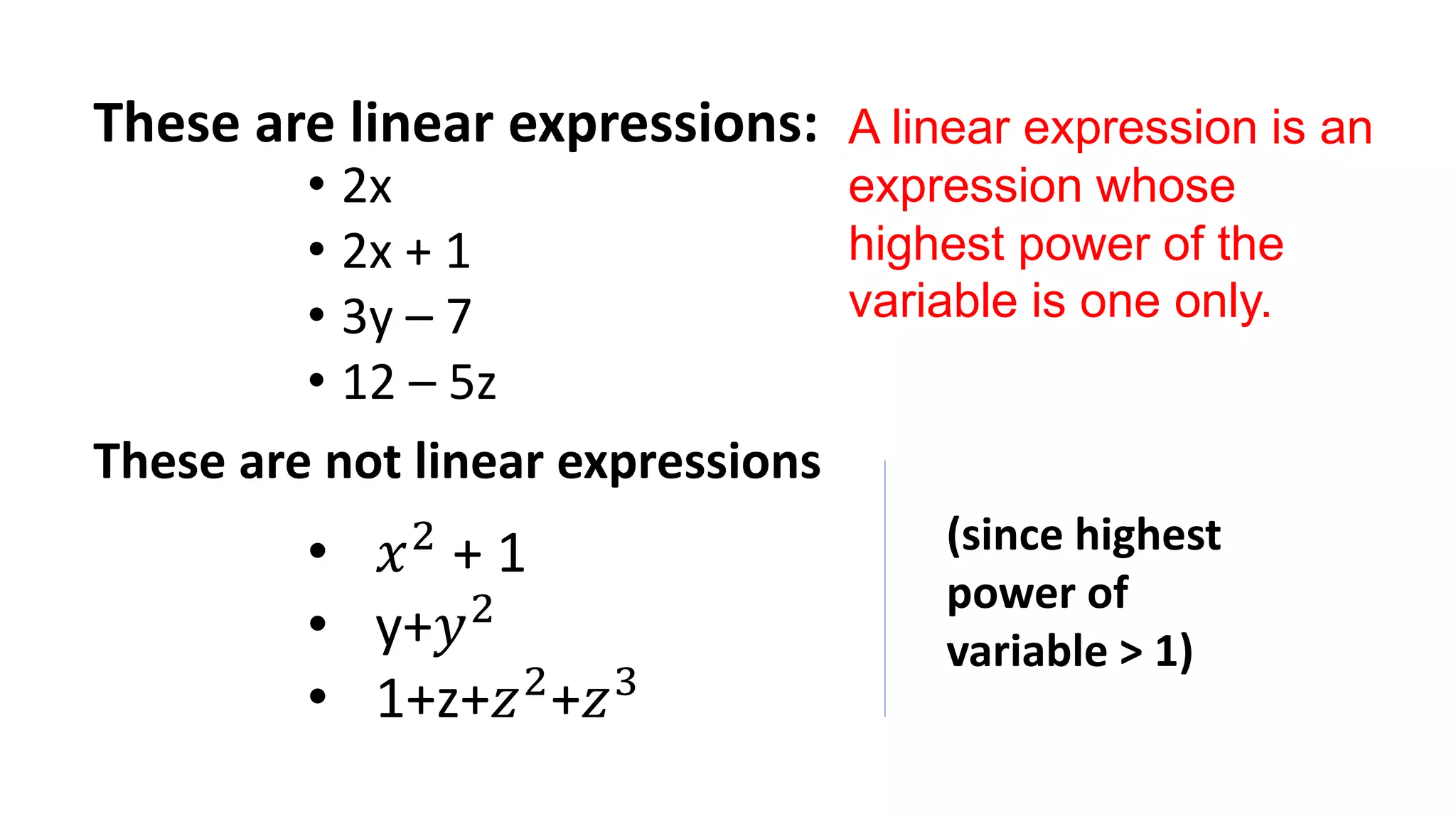
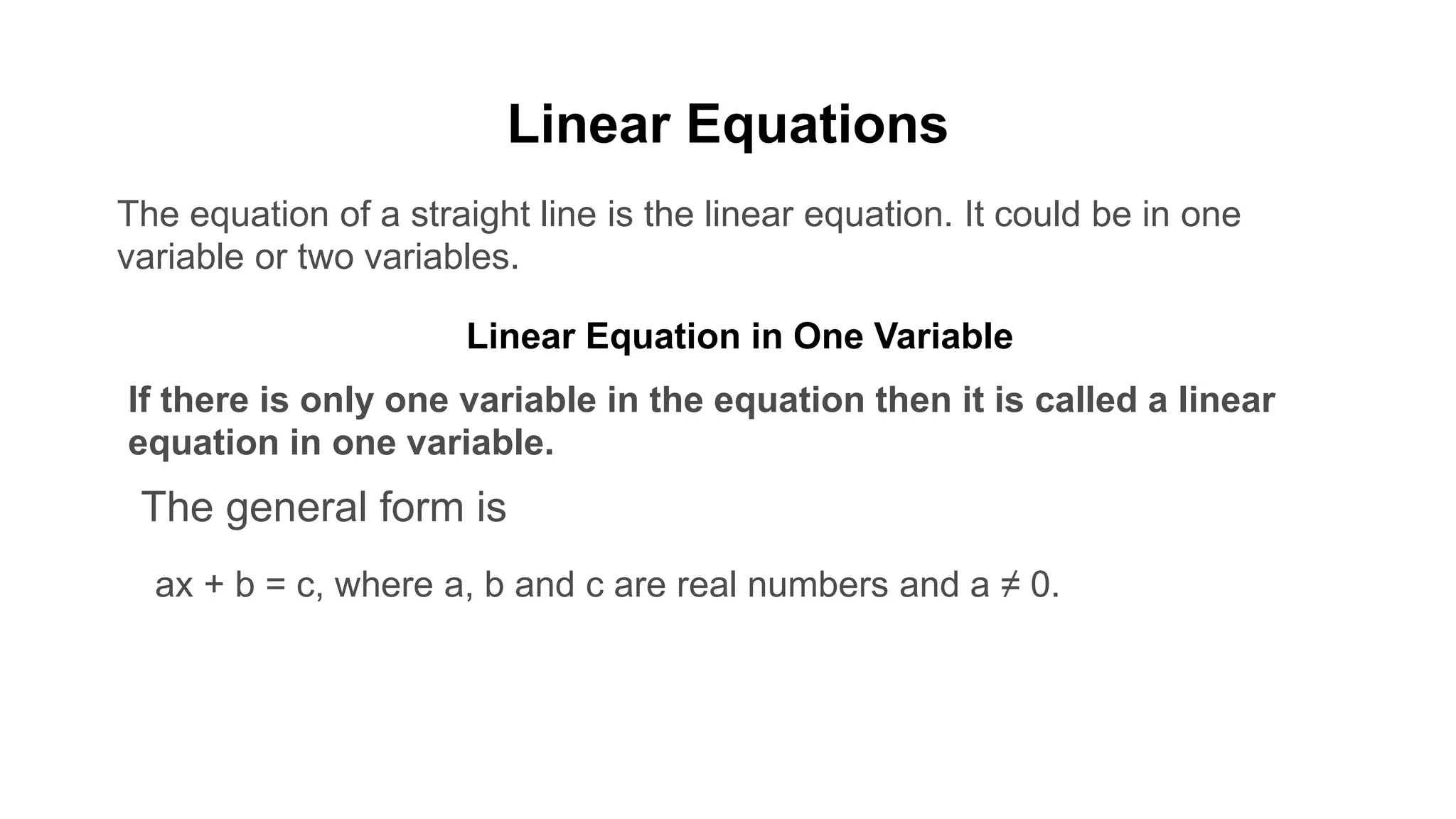
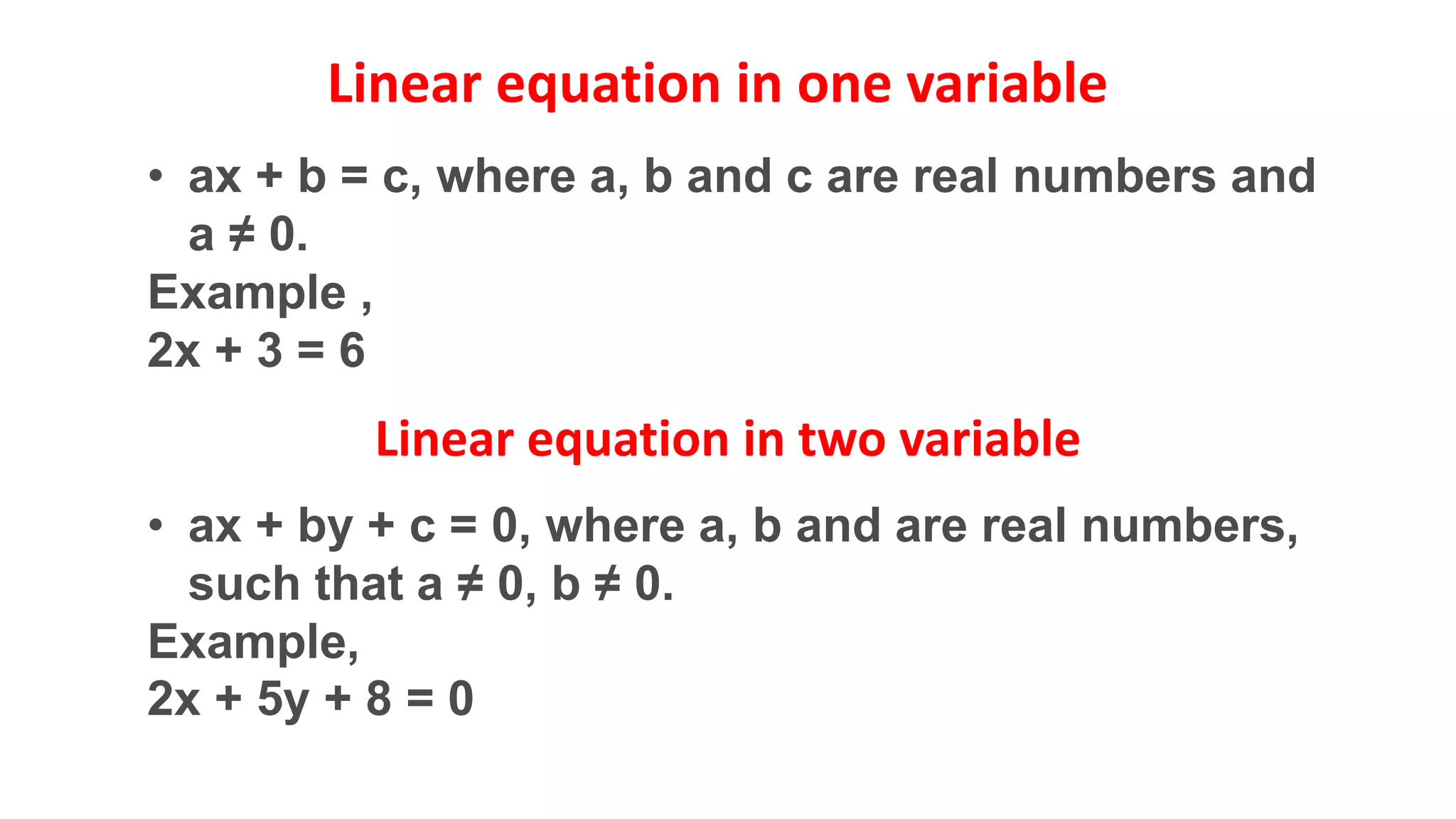
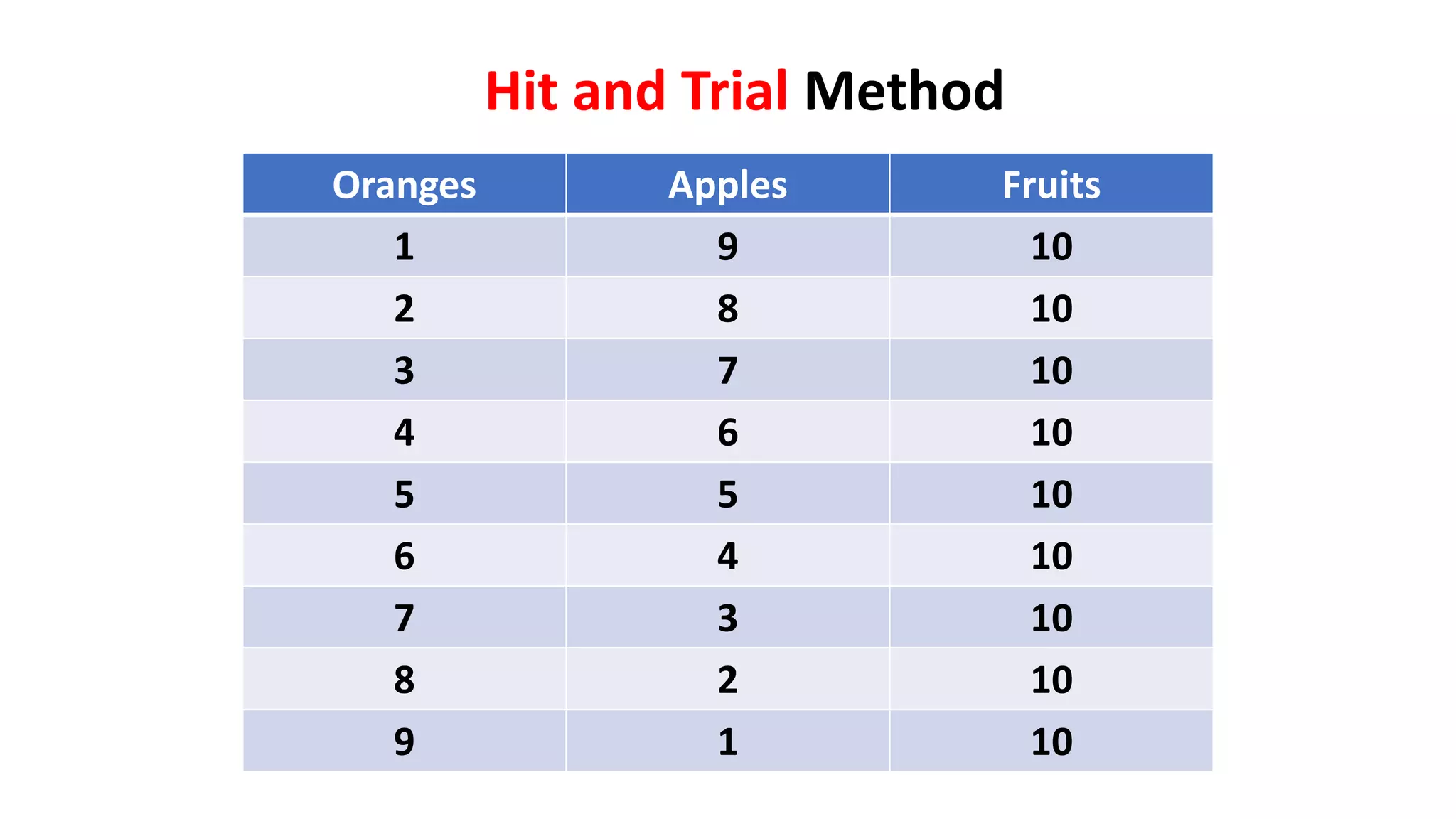
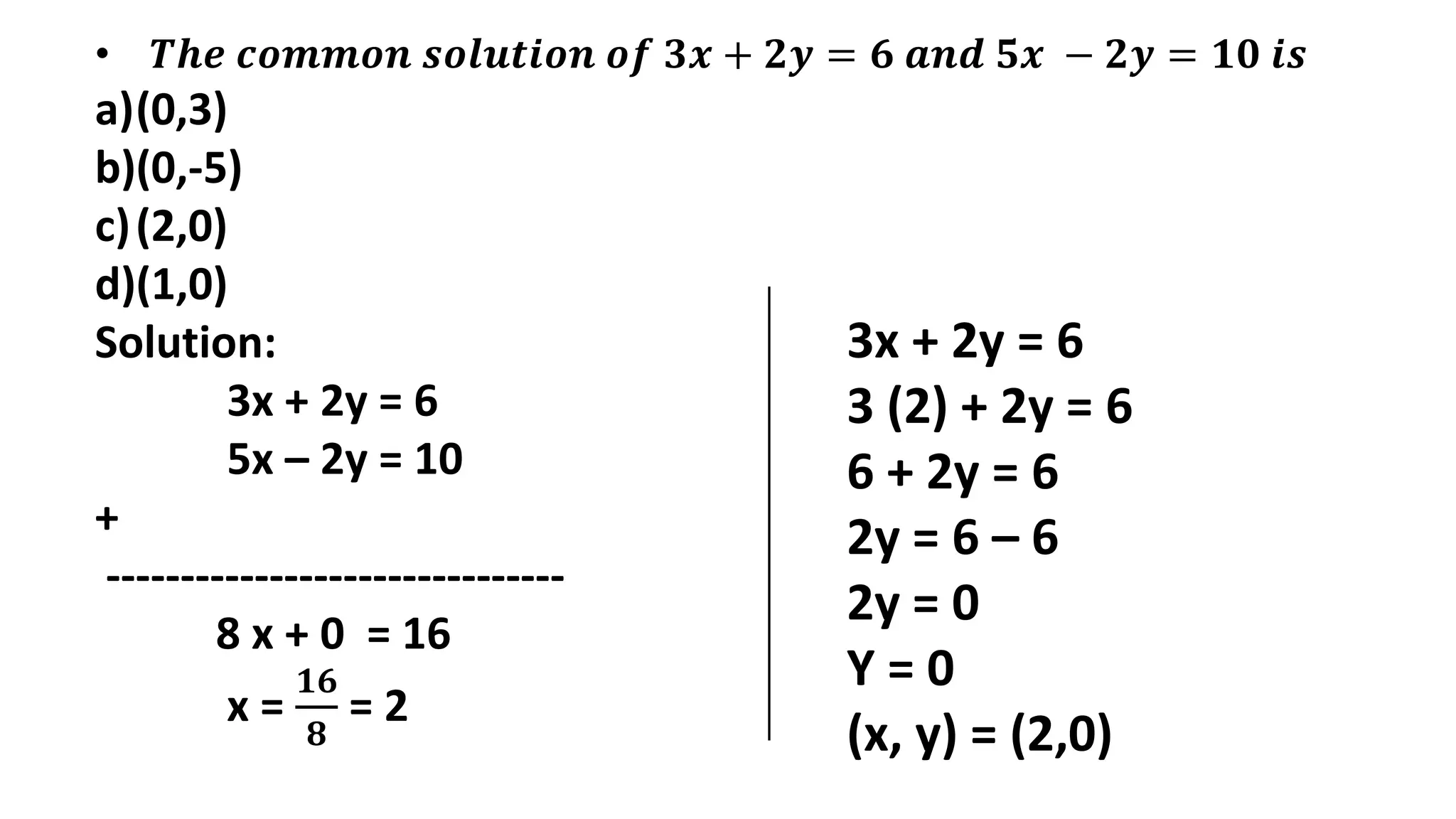
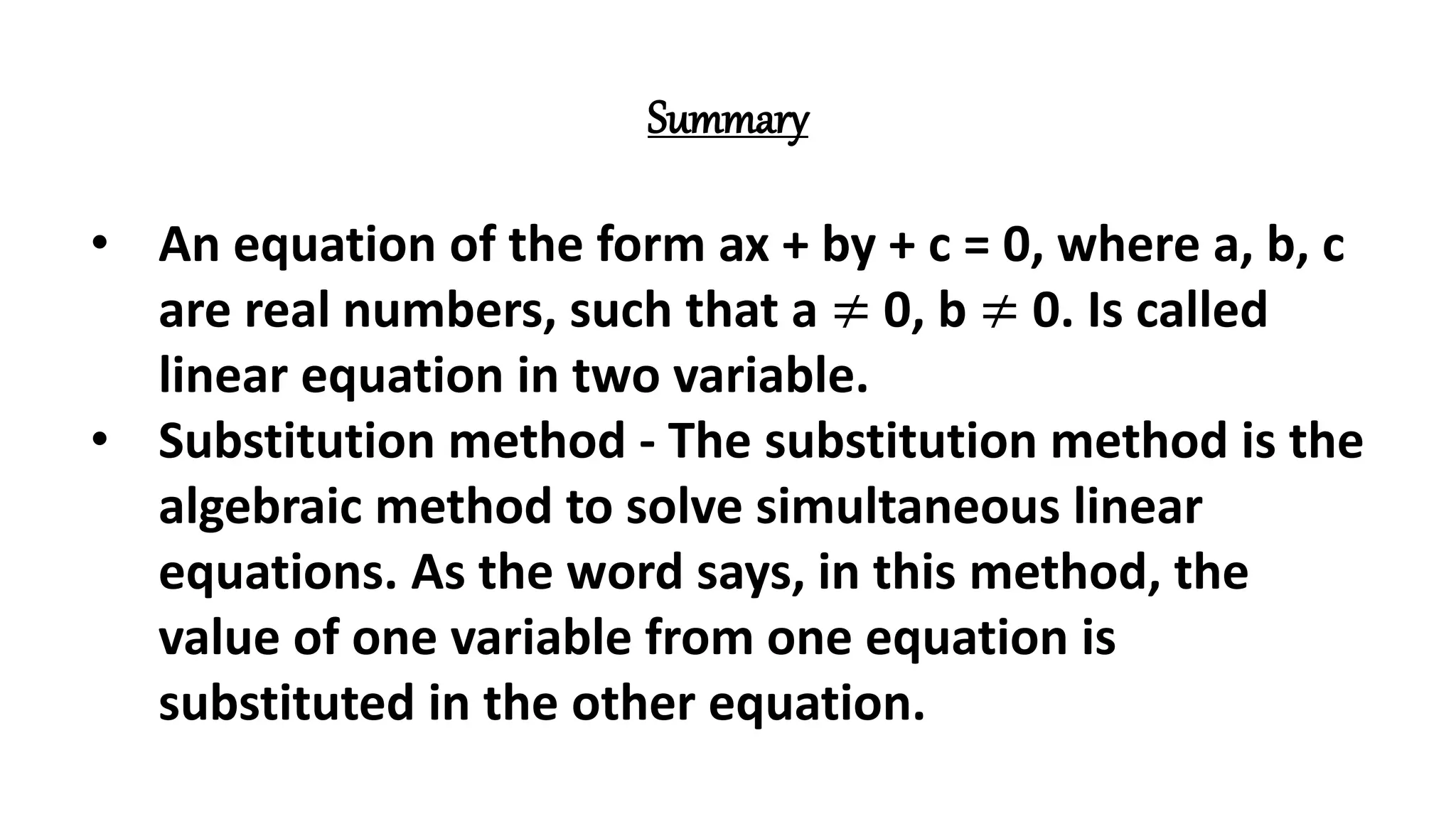
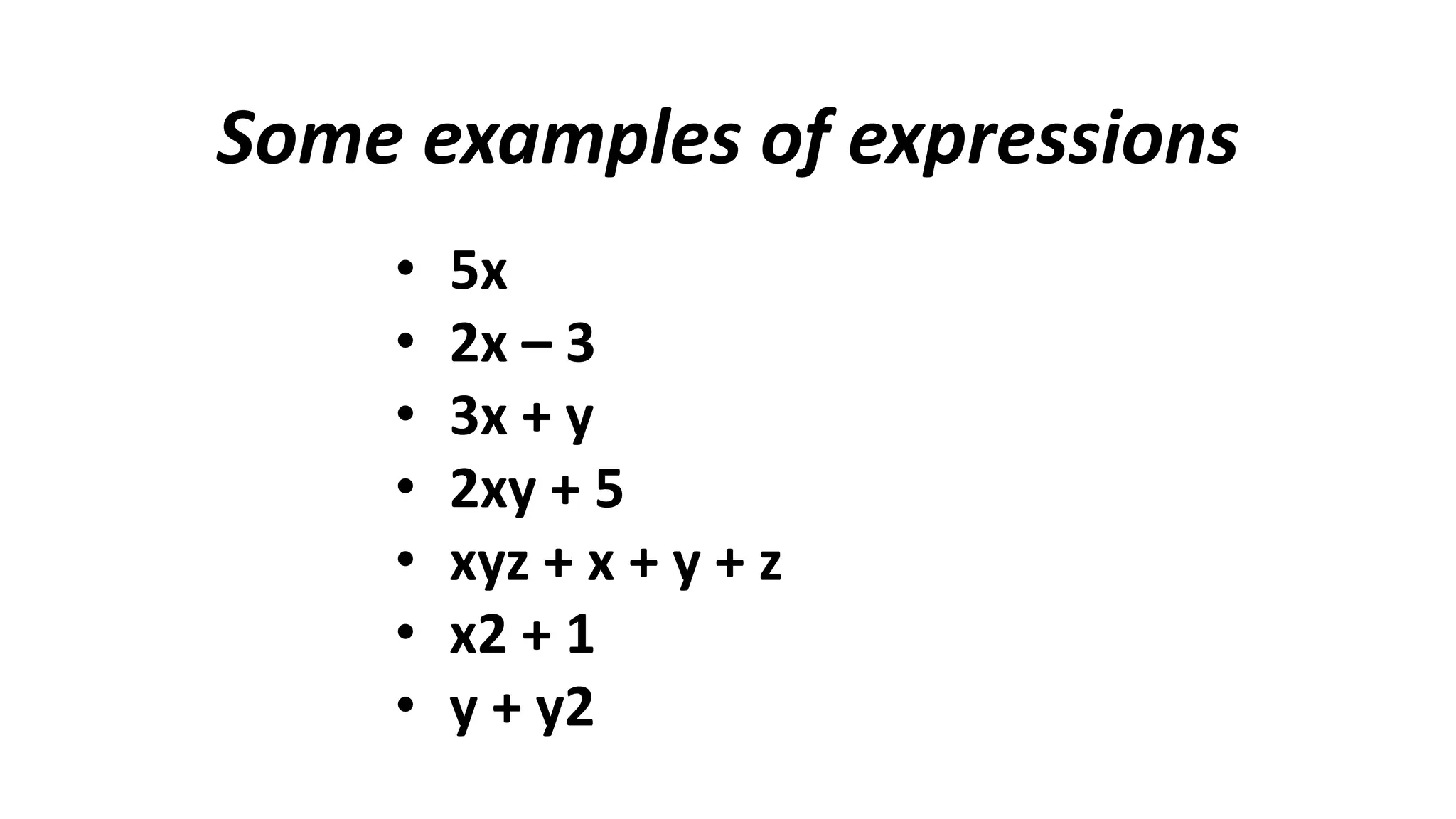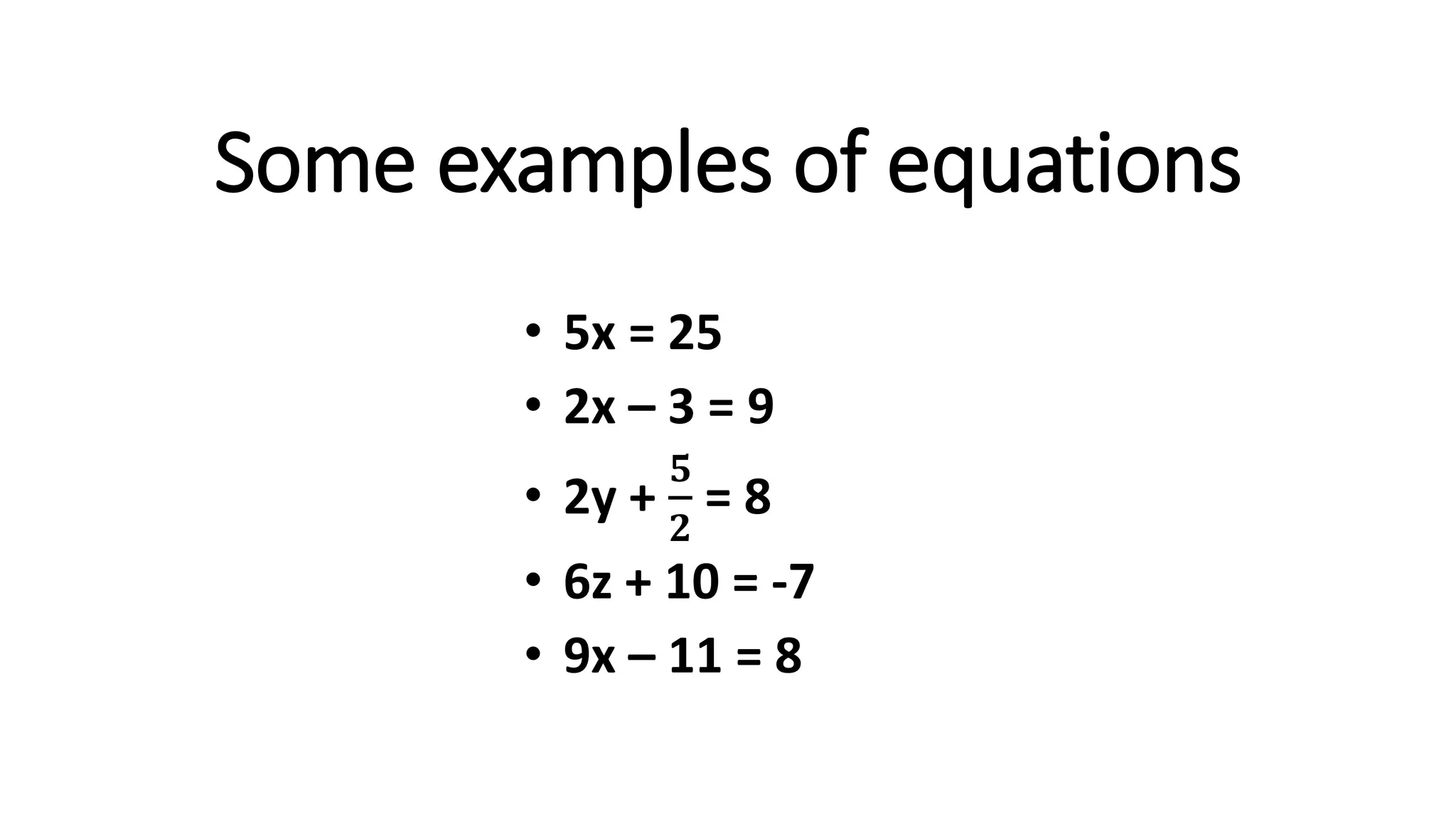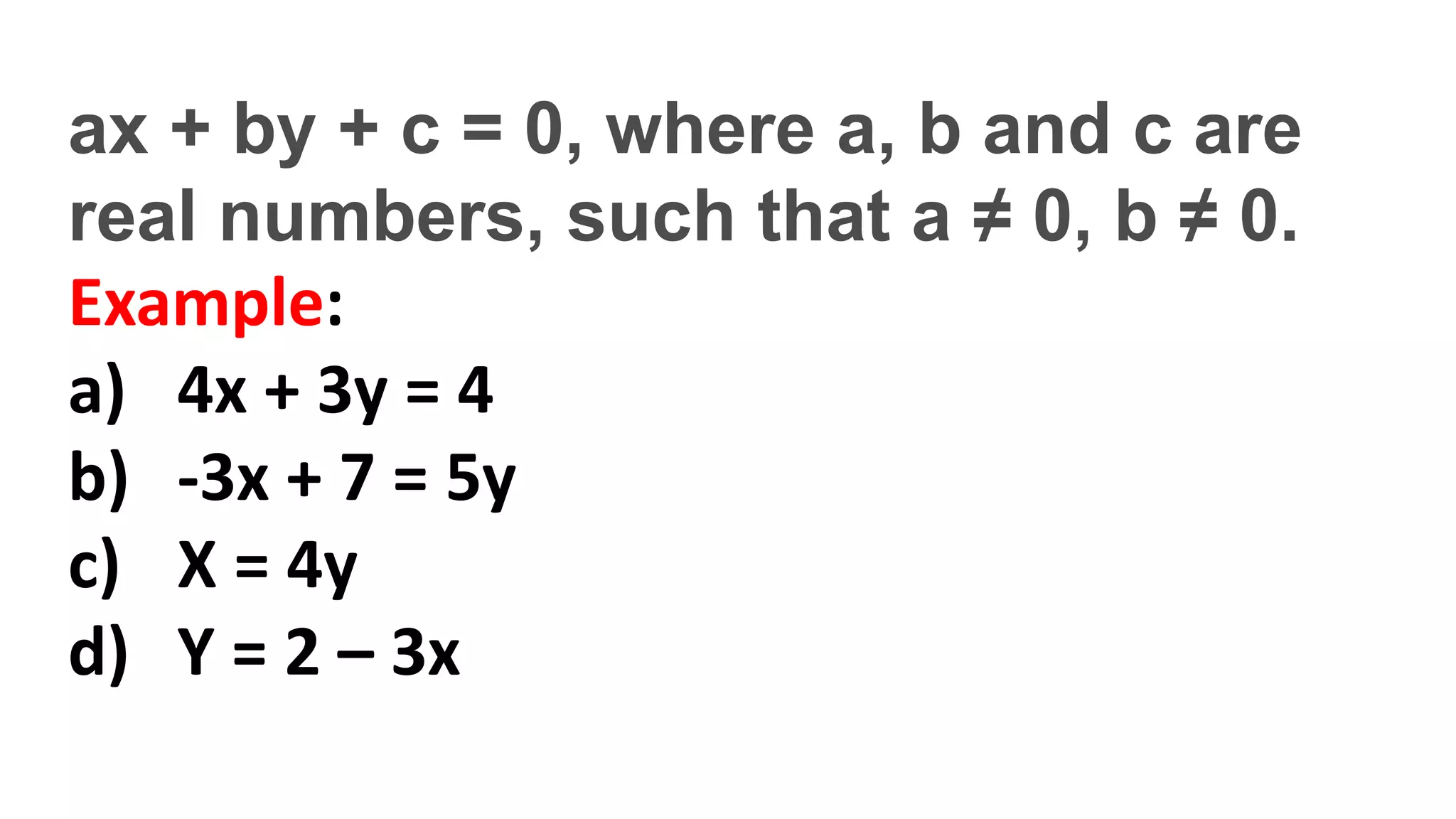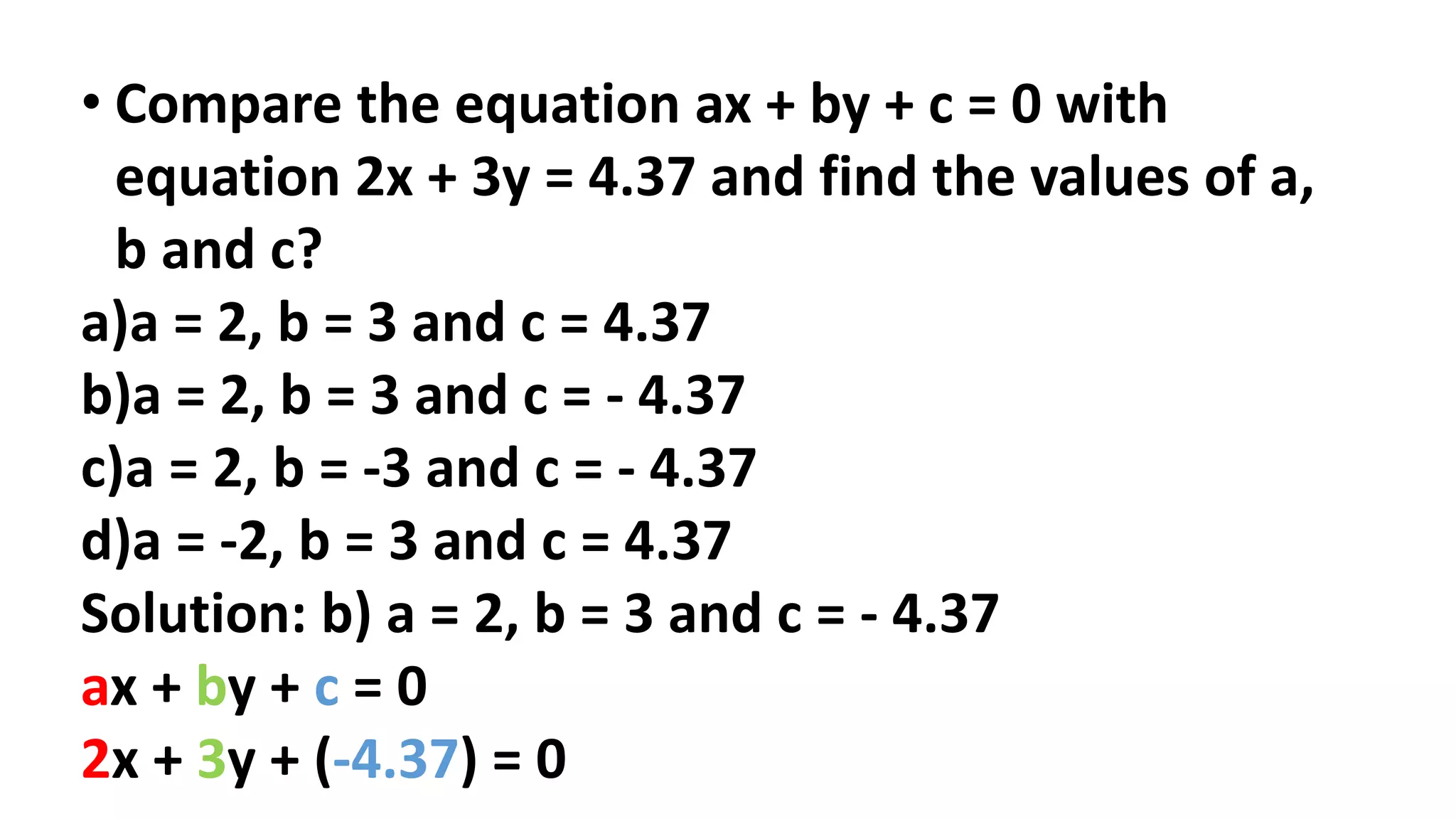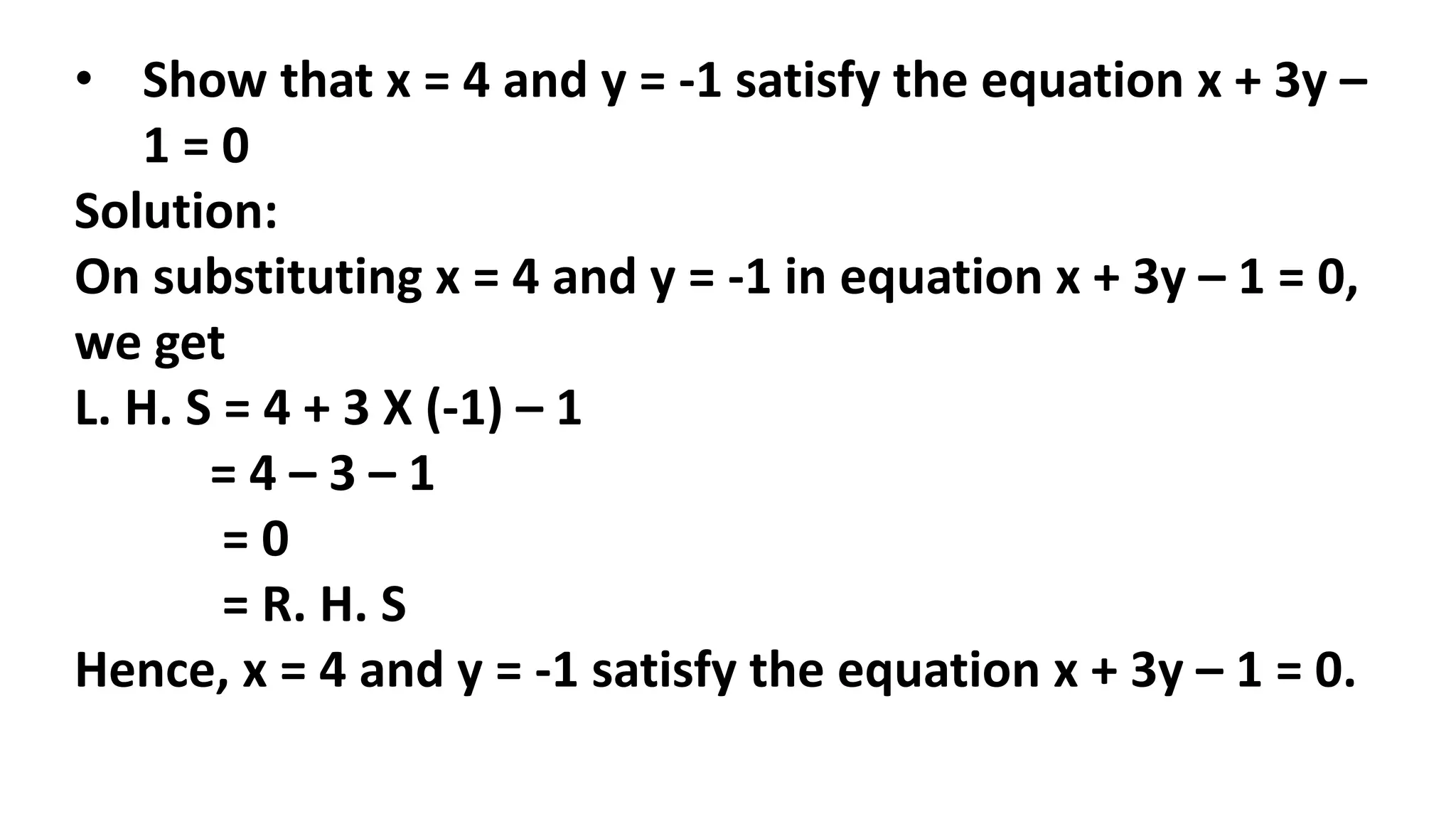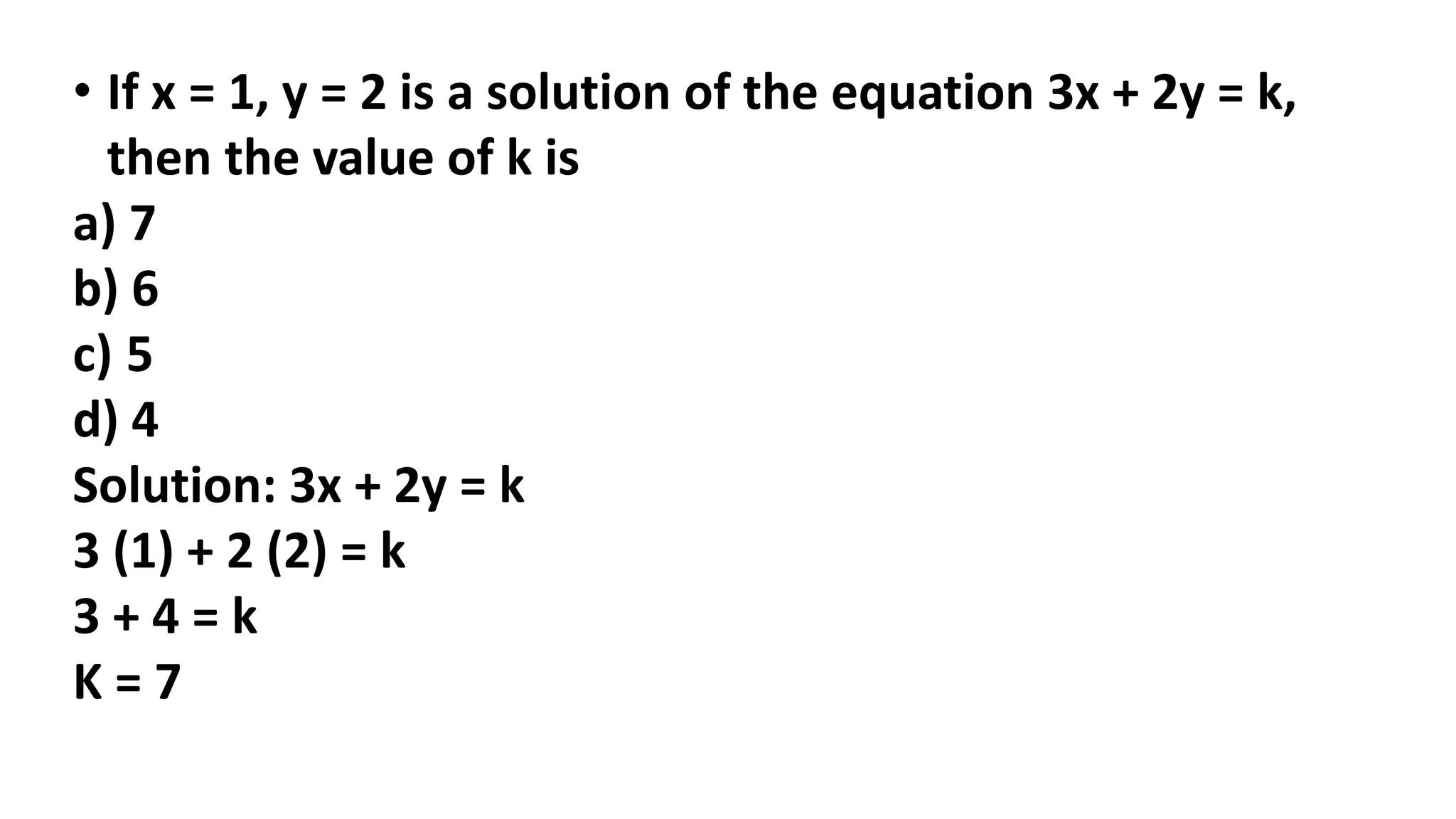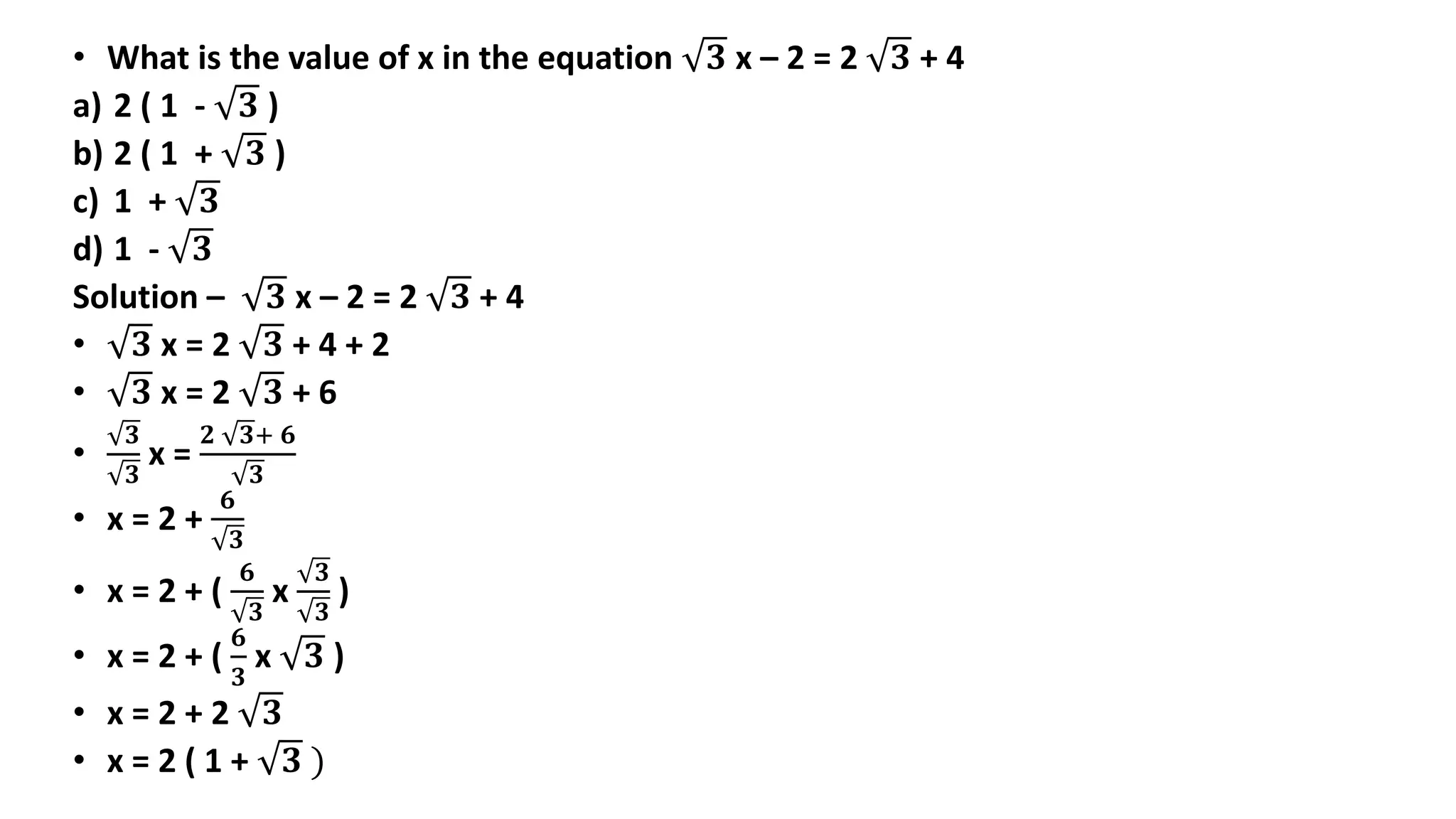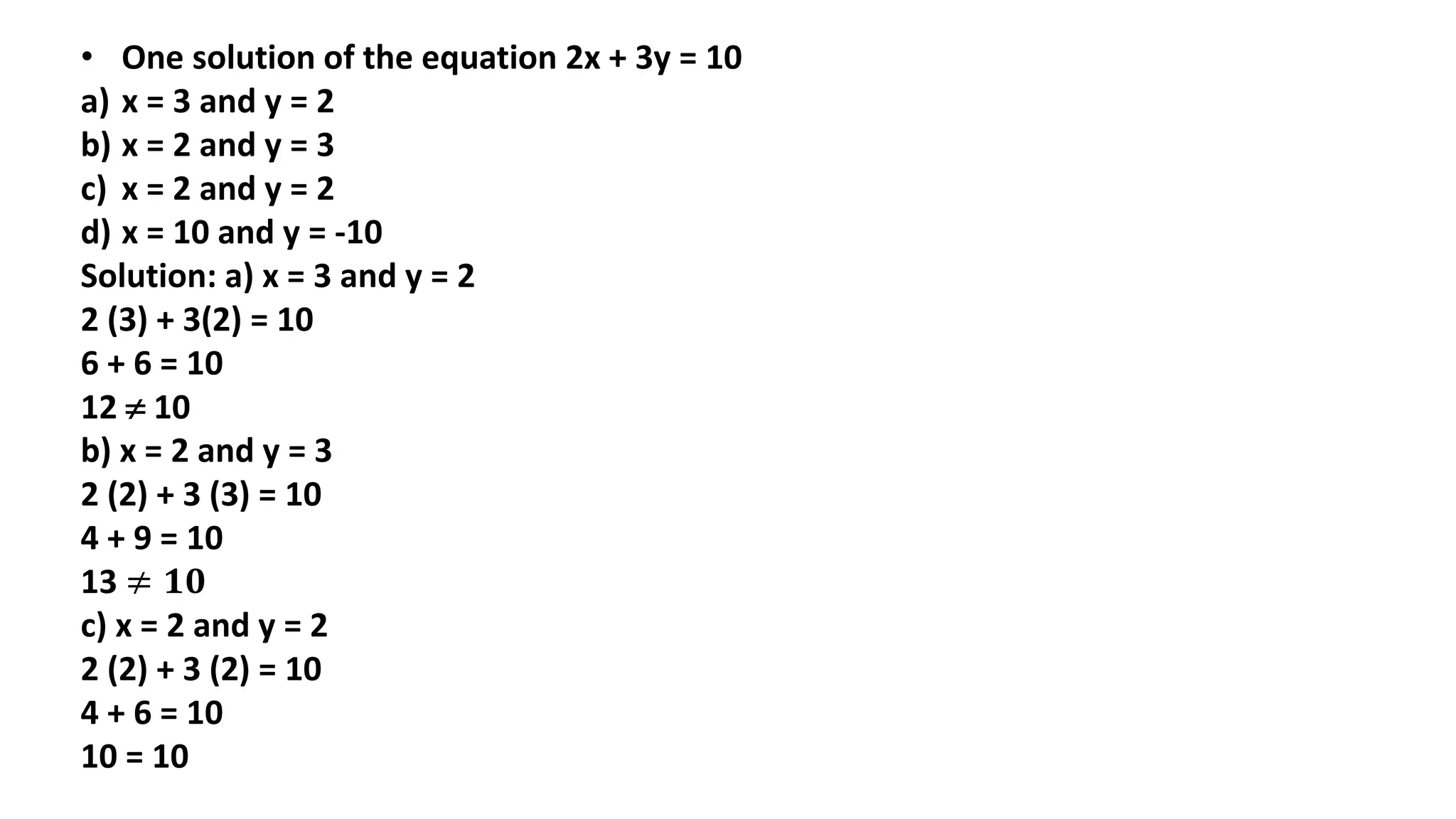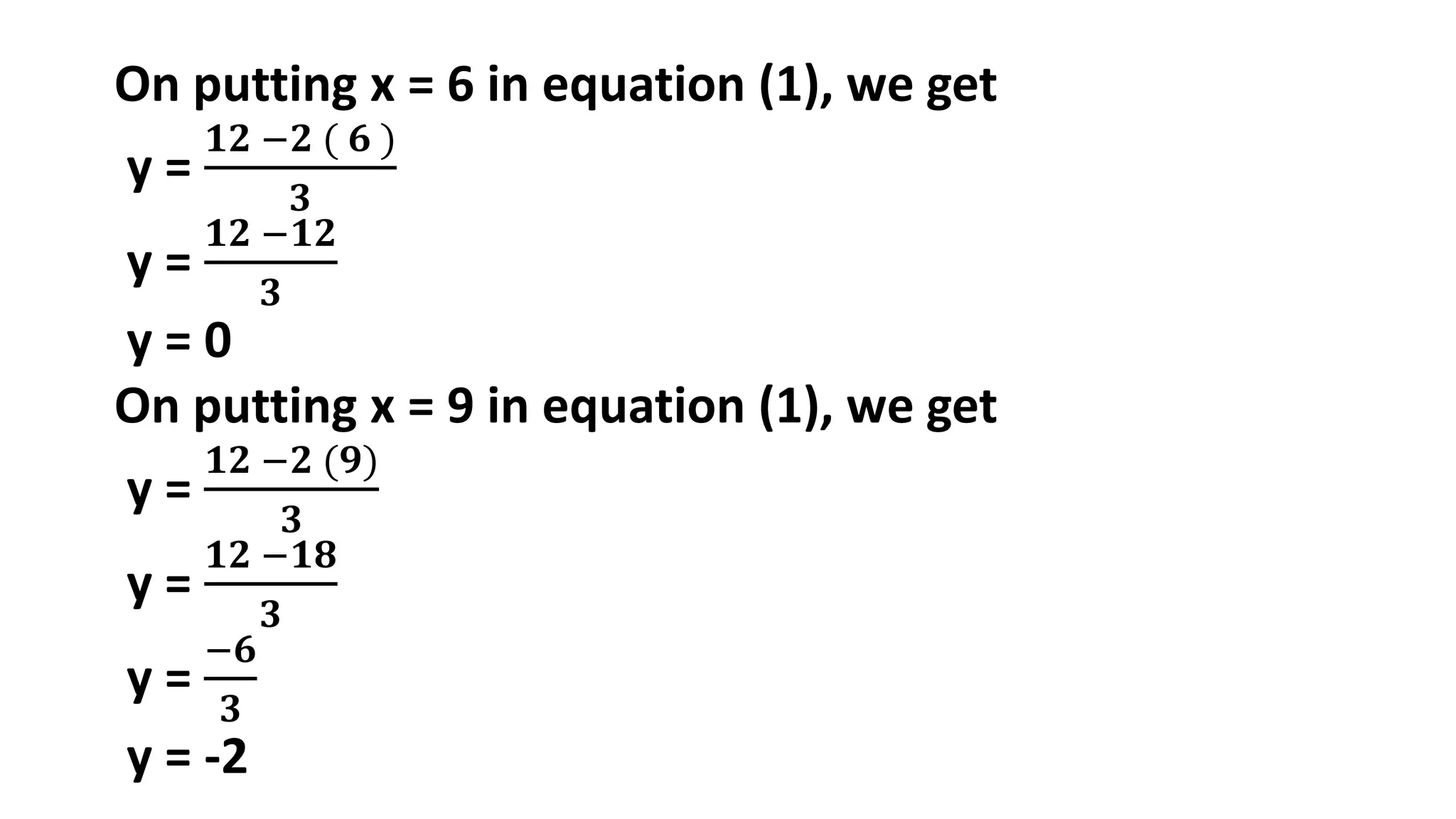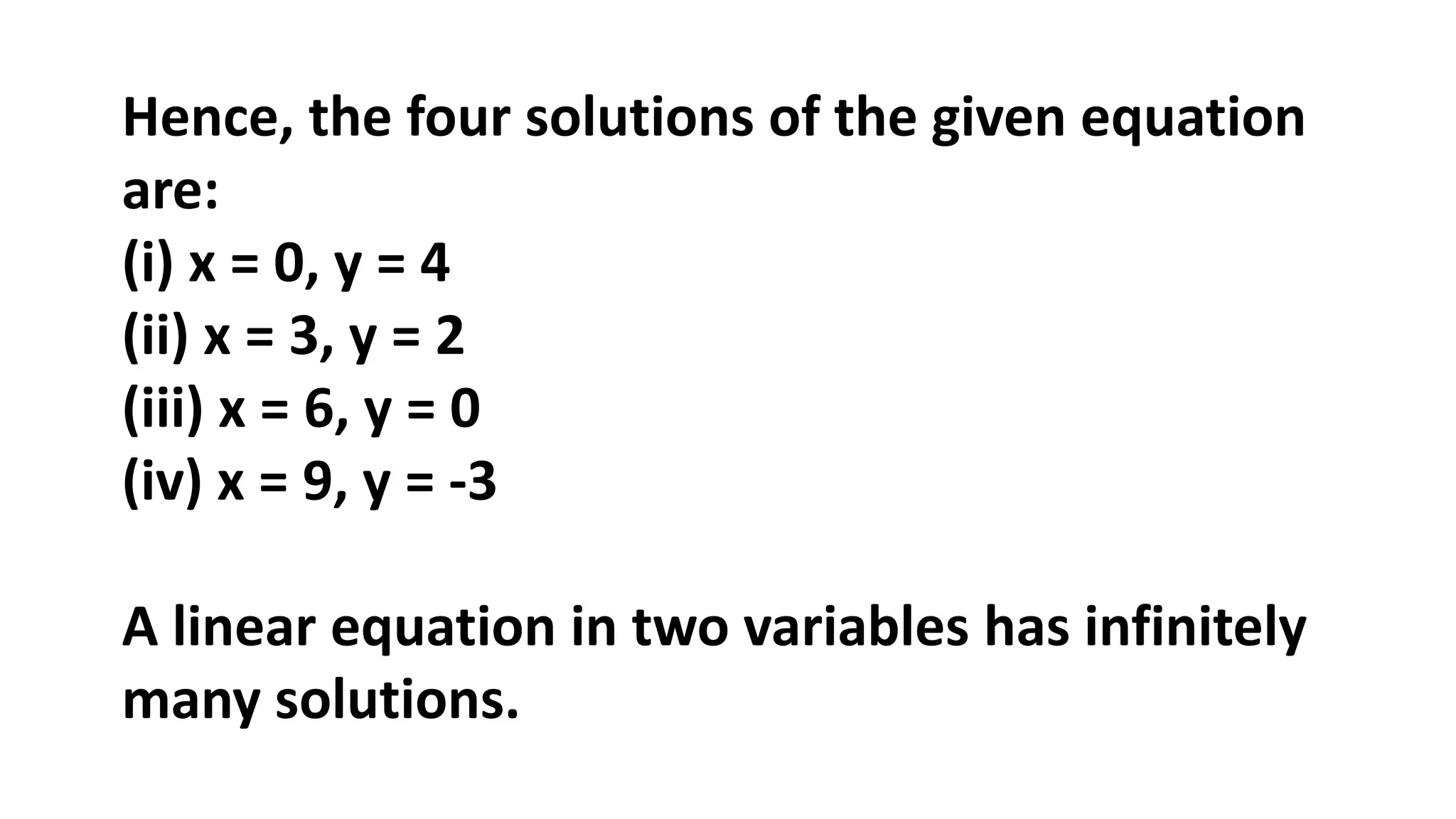The document discusses algebraic expressions, linear equations in one and two variables, providing definitions, examples, and methods to solve them. It explains how to find solutions to equations and illustrates with various examples, including the substitution method for simultaneous equations. Additionally, it highlights the graphical representation of equations and concludes with a quiz to reinforce knowledge.