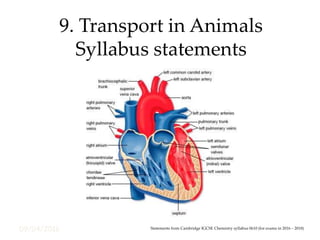
This document outlines the key concepts around transport in animals from the Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry syllabus. It discusses the circulatory system, describing single and double circulation. It also covers the structure and functioning of the heart, describing the layers of the heart wall and how it pumps blood through the body. Finally, it summarizes the components and functions of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma. It also briefly discusses the lymphatic system and blood clotting.