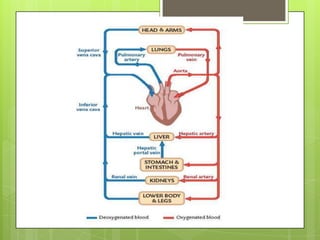
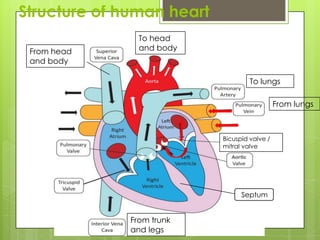
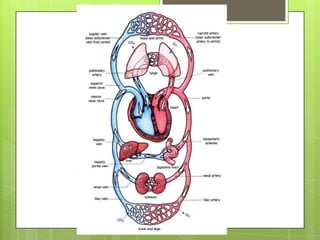
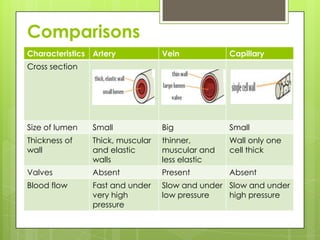
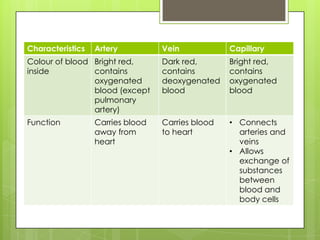
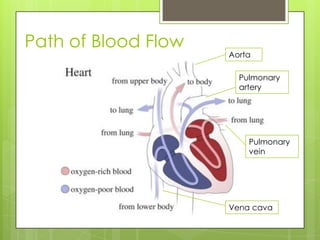
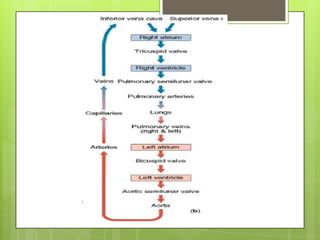
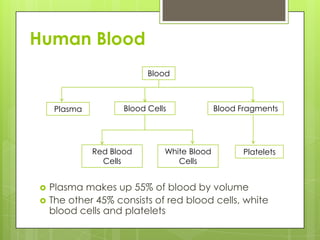
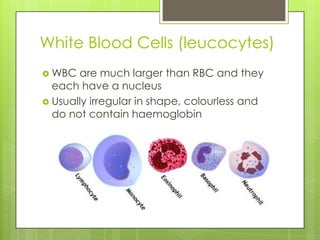
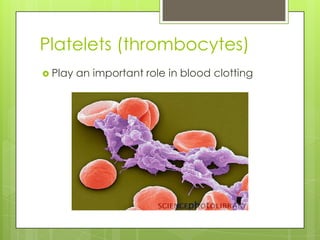
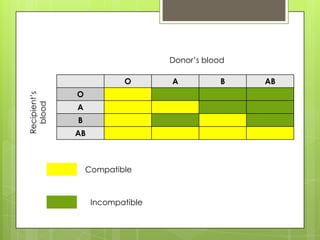
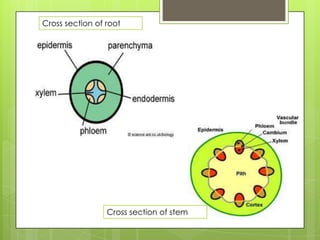
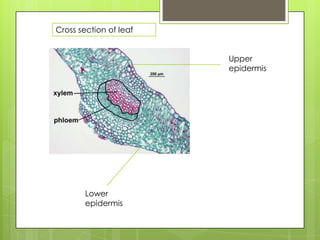
The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body using the heart as a pump through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. It is a double circulatory system, with pulmonary and systematic circulation. Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products. The three main blood vessel types are arteries, which carry blood away from the heart; veins, which carry blood toward the heart; and capillaries, which connect arteries and veins and allow for the exchange of substances between blood and body cells.