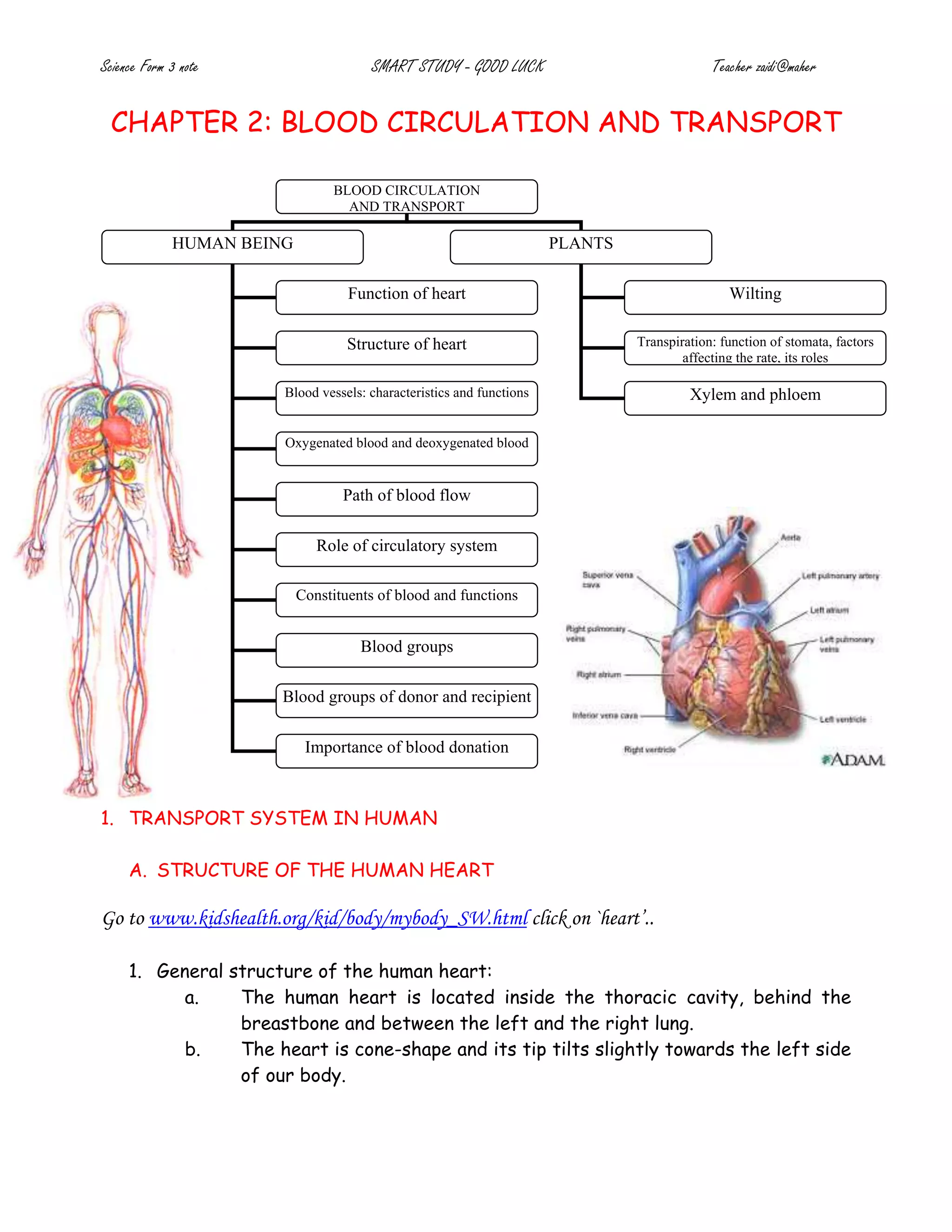
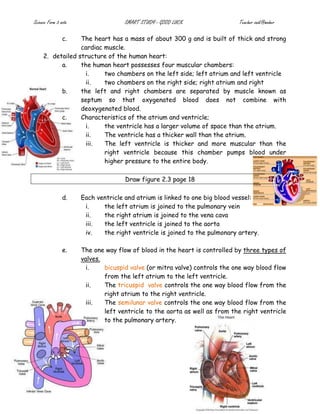
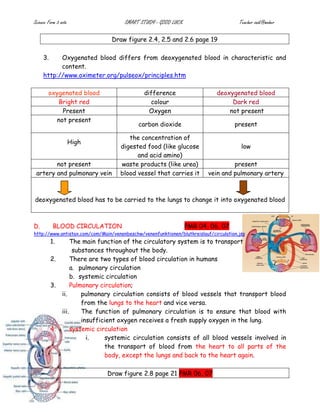
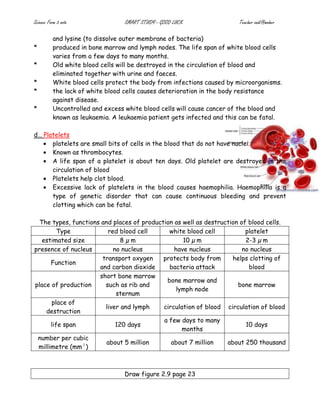
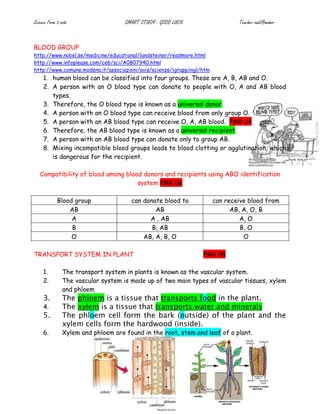
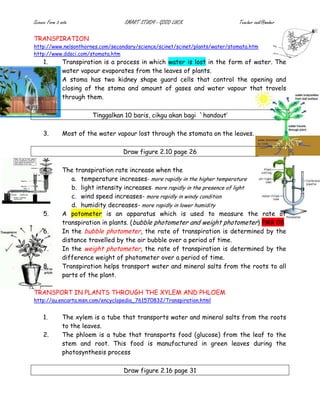
The document provides details on the structure and function of the human circulatory system. It describes the structure of the heart including the four chambers and major blood vessels. It explains that the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood around the body. It also discusses the composition of blood including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma. The document outlines the pathways of pulmonary and systemic circulation and defines the roles of arteries, veins and capillaries. It provides information on blood groups and compatibility for transfusions. The transport systems in plants including xylem and phloem are also summarized.