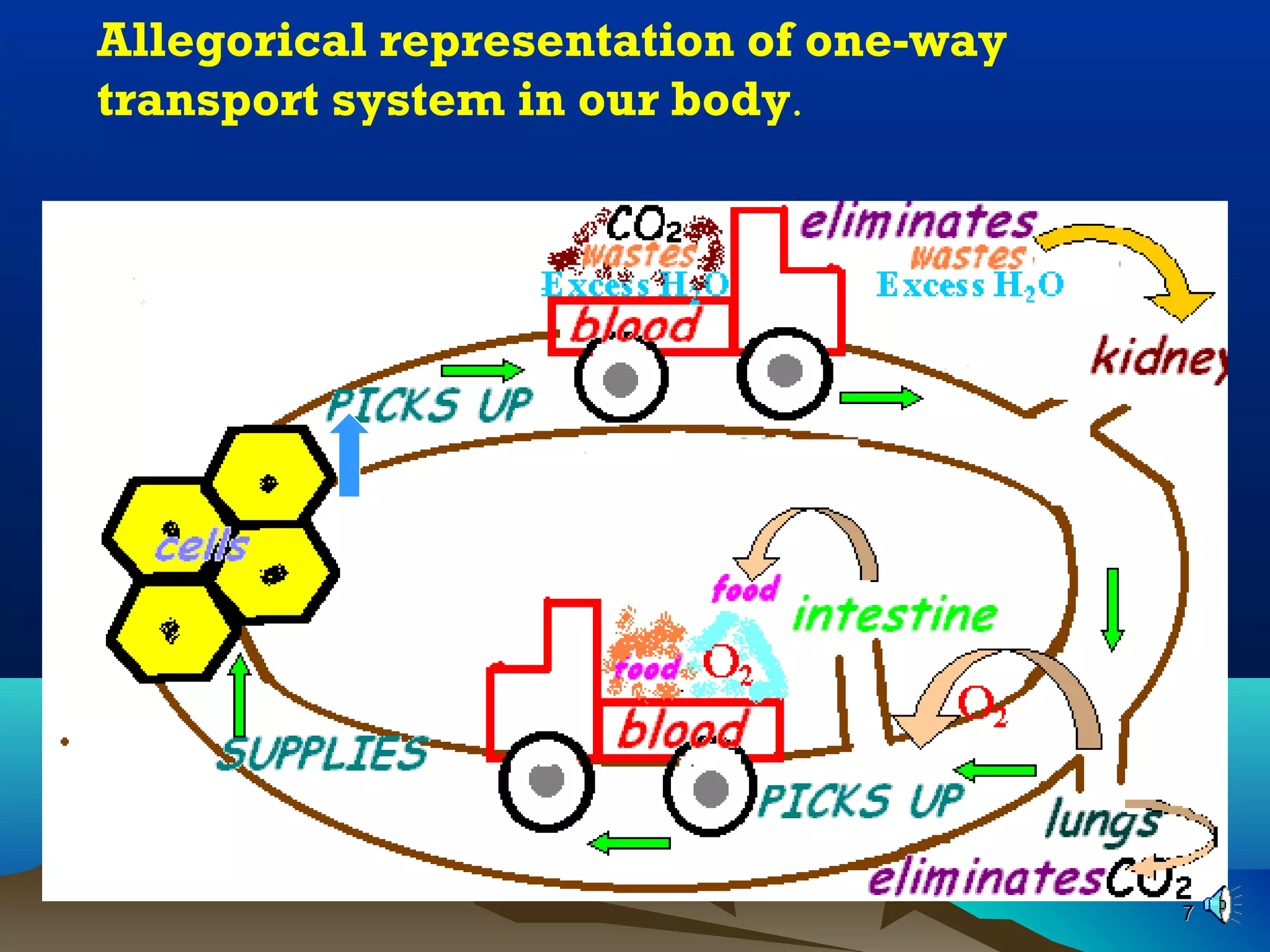
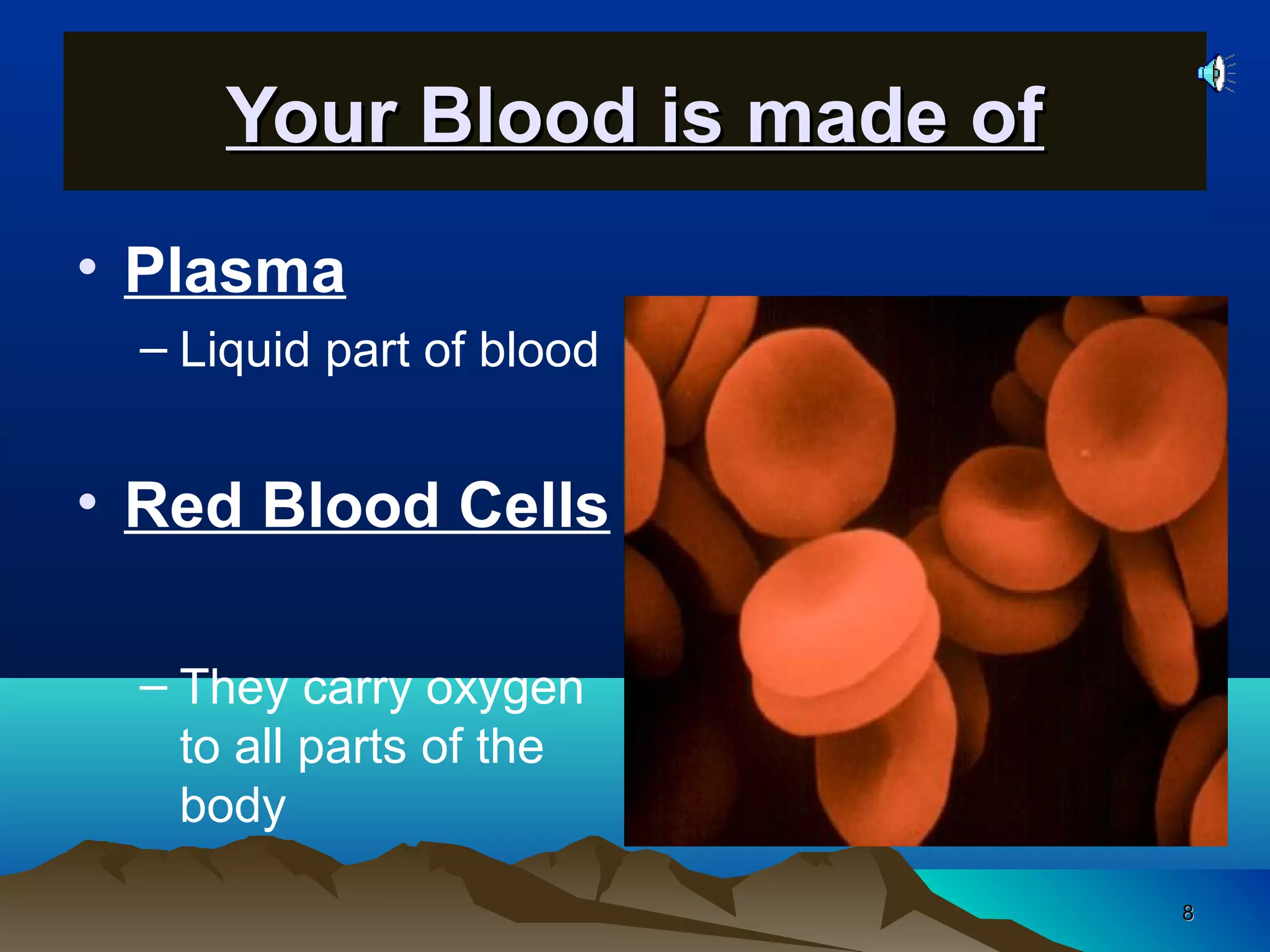
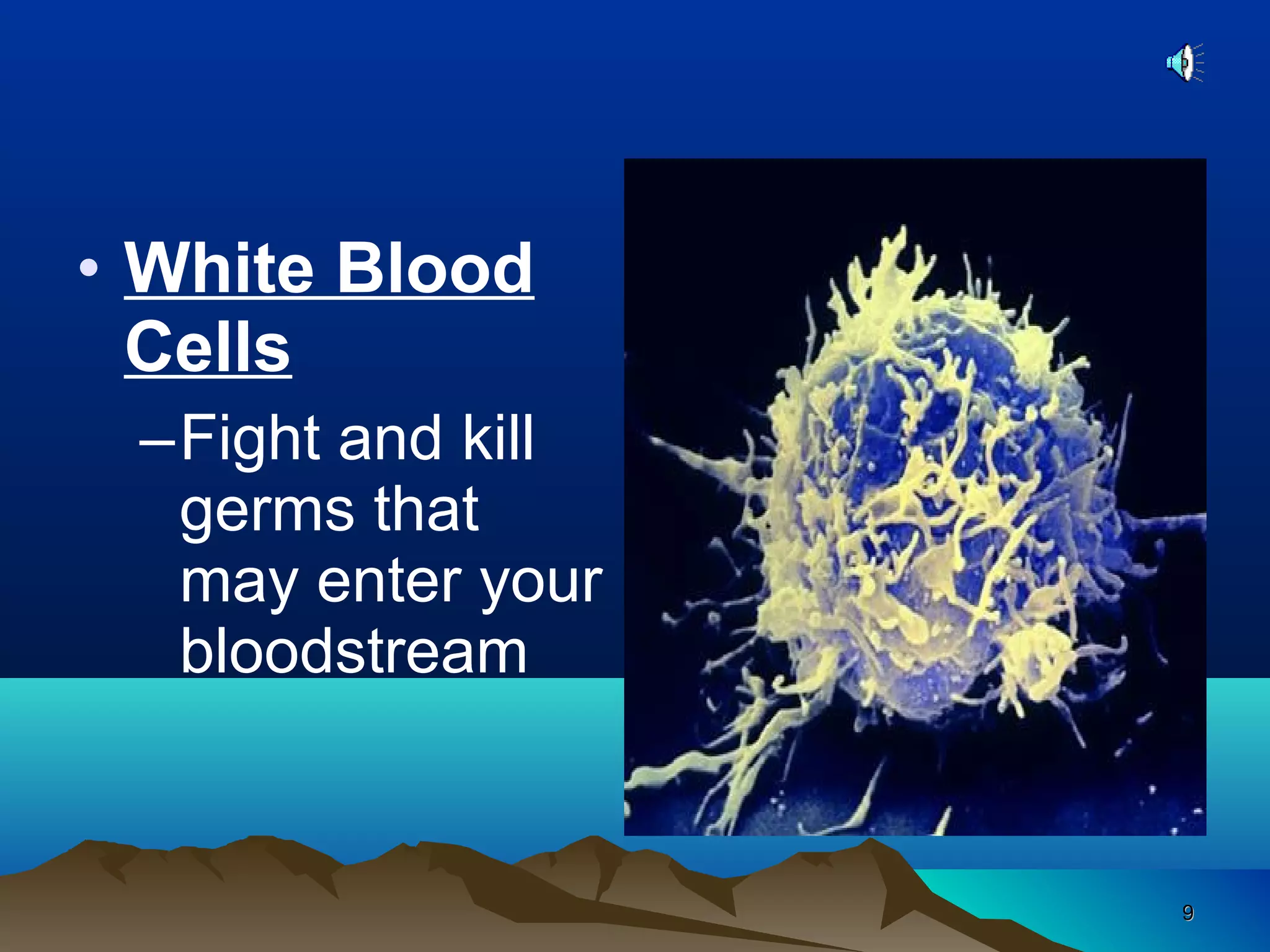
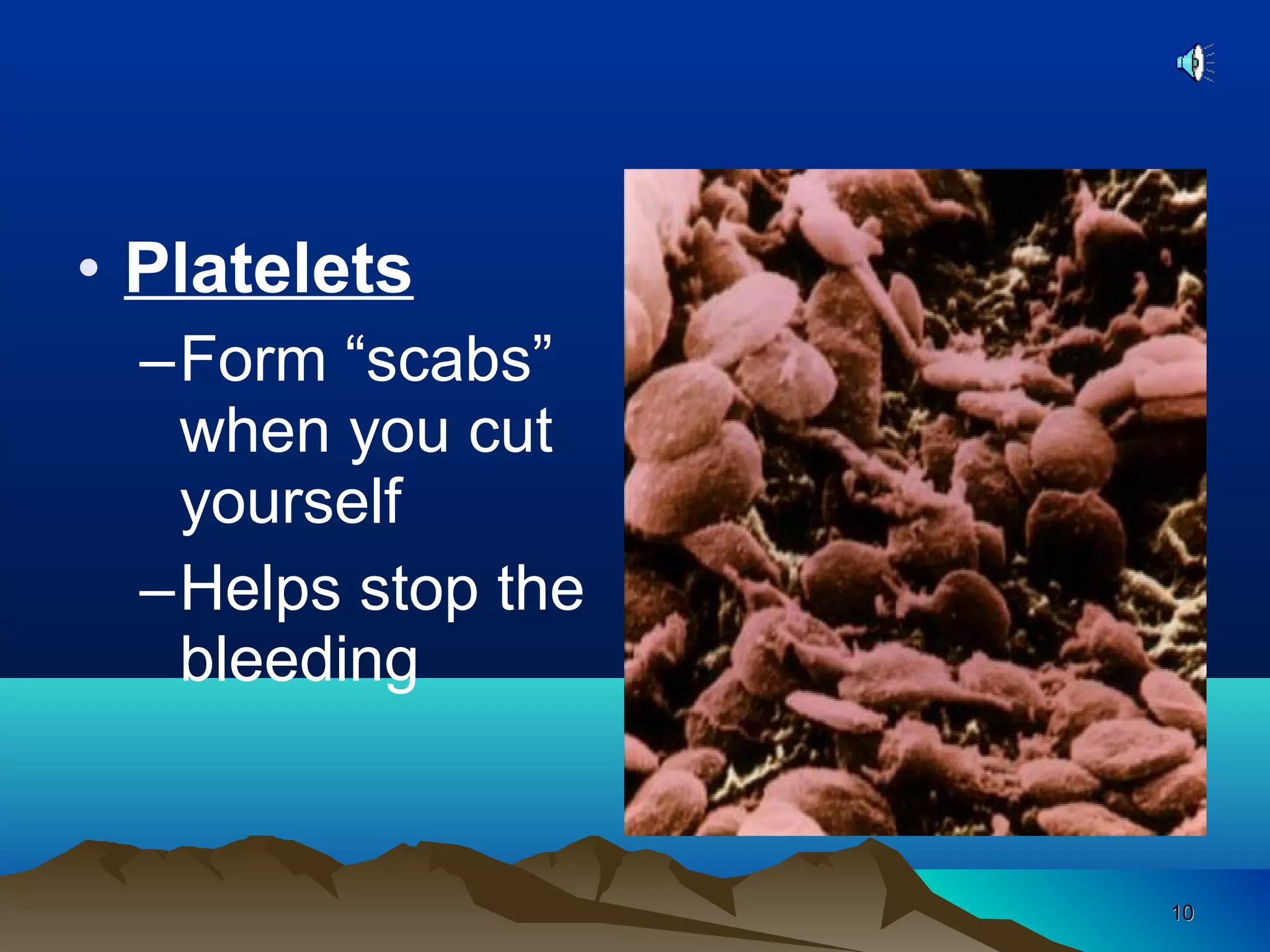
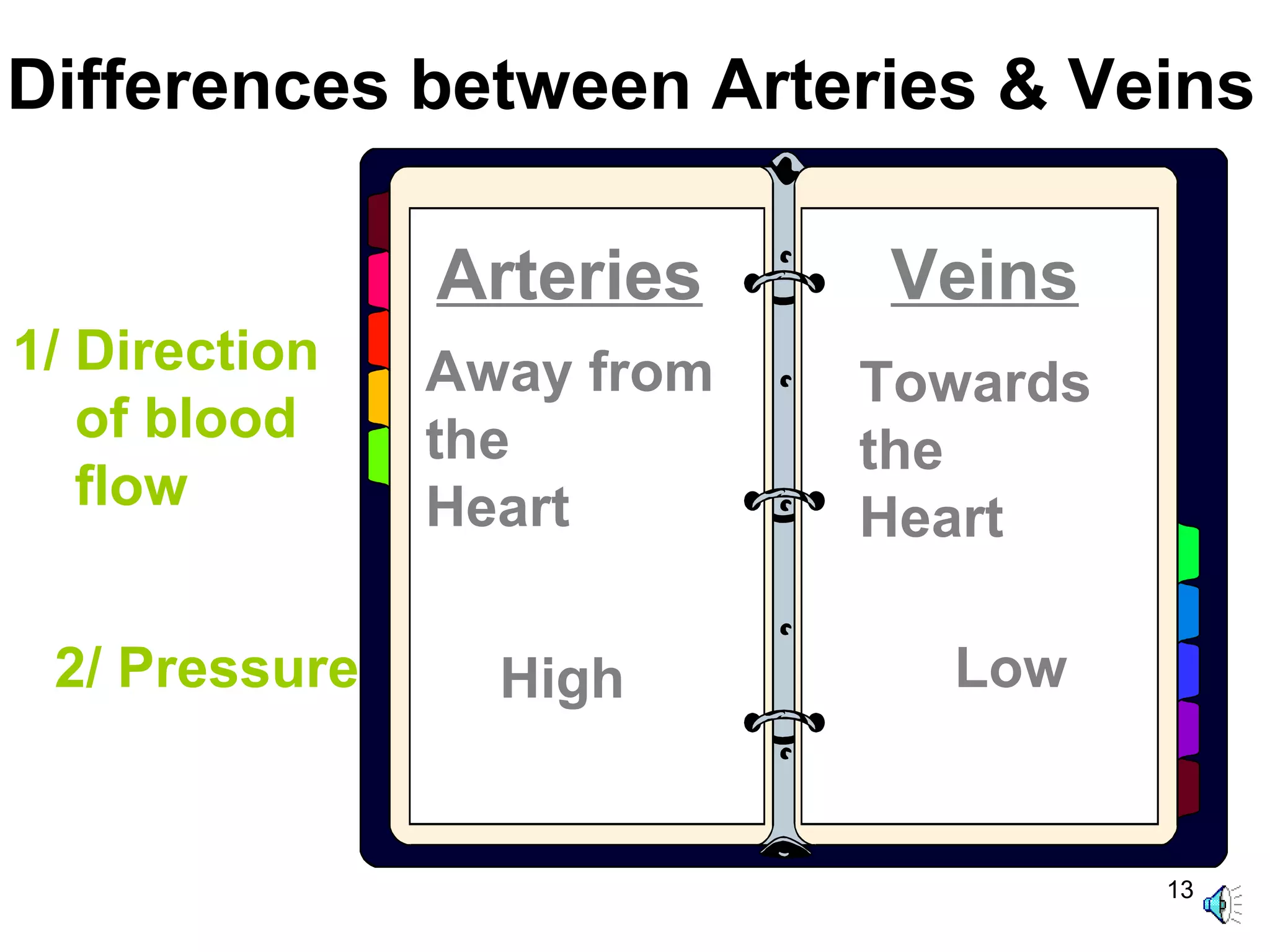
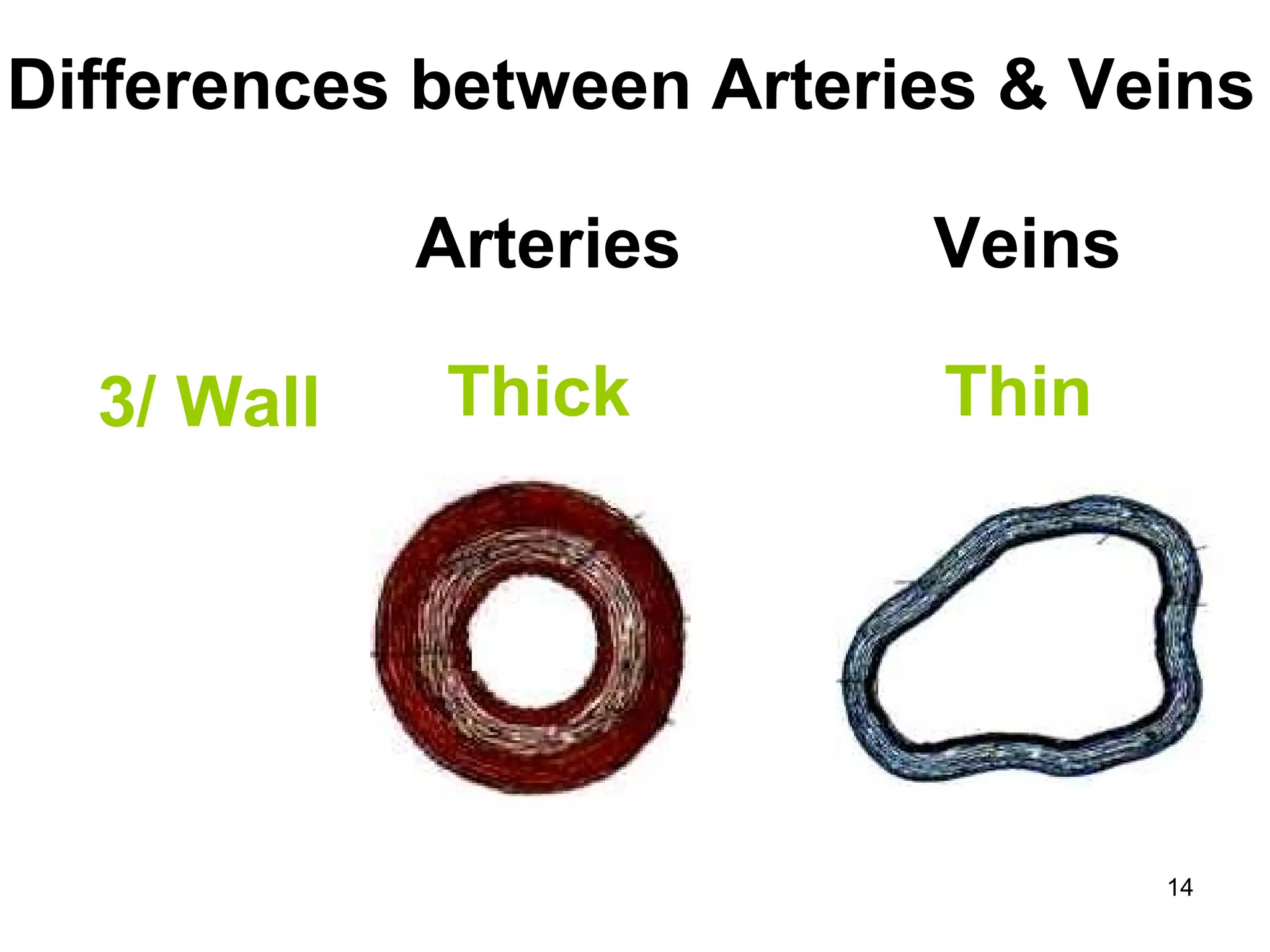
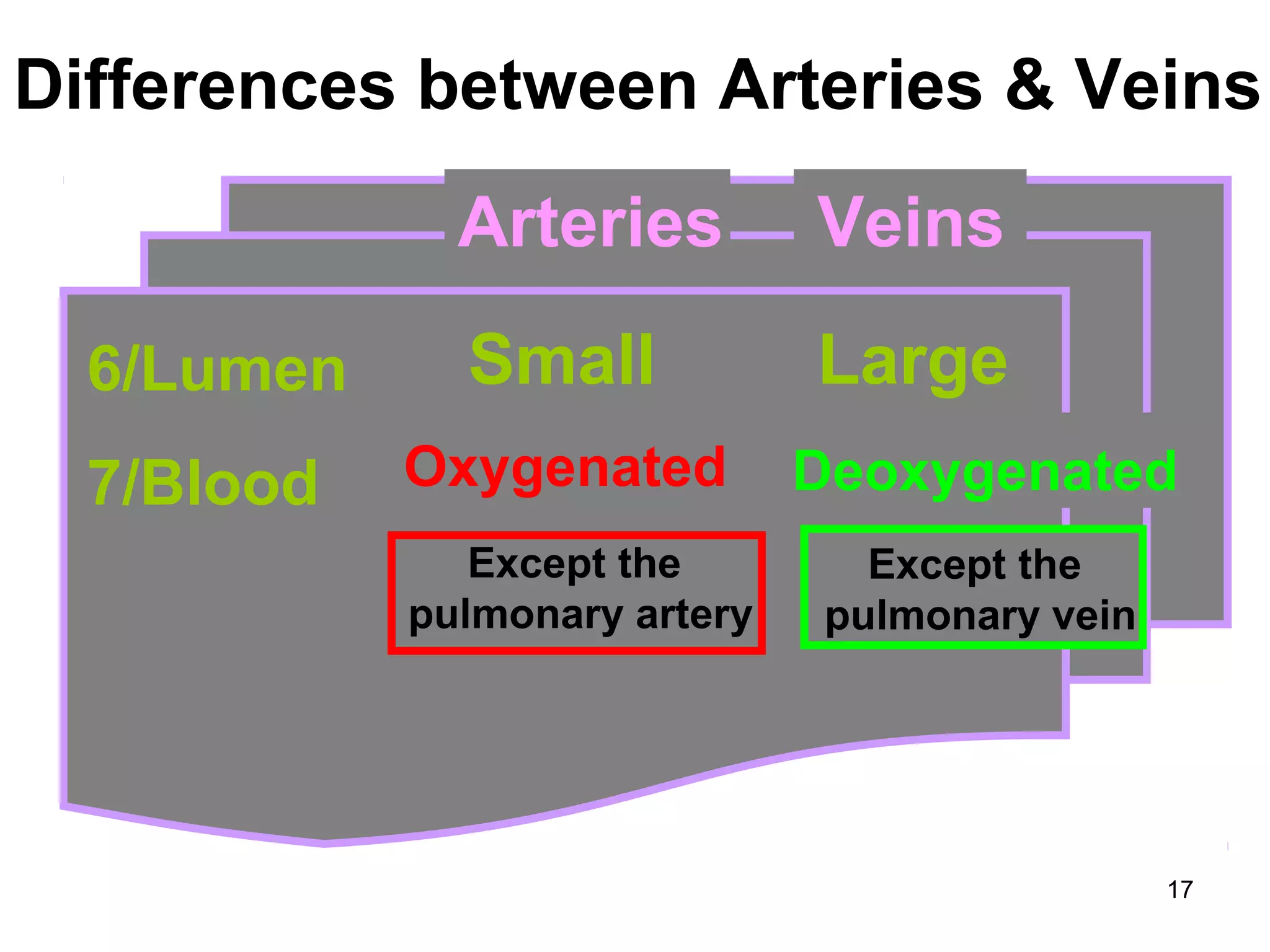
The document discusses transport systems in animals and plants. It describes how circulatory systems transport oxygen, nutrients, wastes, and other materials throughout animal bodies using blood, blood vessels and the heart. The circulatory system consists of arteries, veins and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Transport of water and nutrients in plants occurs through xylem tissue while transport of food occurs through phloem tissue. Transpiration through leaves generates suction that transports water through xylem vessels in plants.