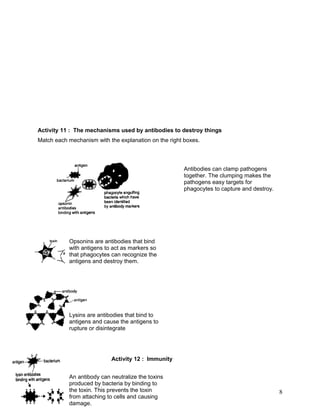
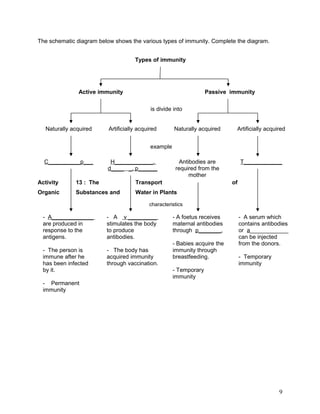
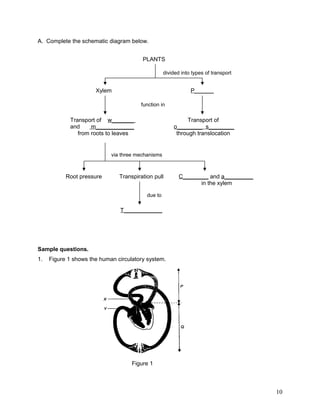
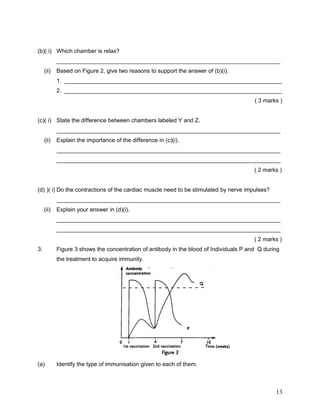
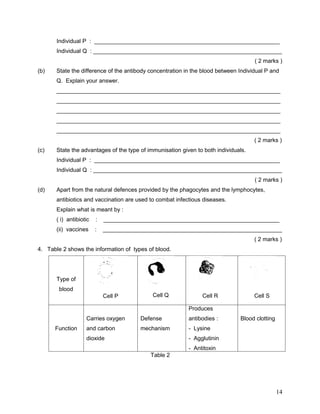
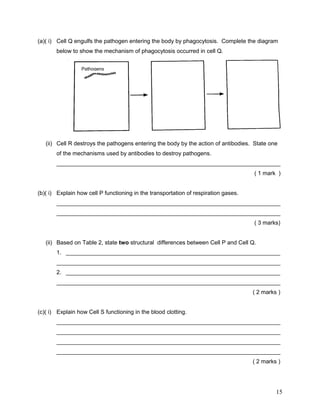
The document summarizes the circulatory system. It discusses that humans have a closed, double circulatory system consisting of blood, blood vessels, and the heart. The heart pumps blood through the arteries, capillaries, and veins, carrying oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and removing waste. Various activities describe the cellular components of blood and their functions, compare the structures and functions of different blood vessels, label the structures of the heart, and explain the flow of blood and pumping action of the heart.