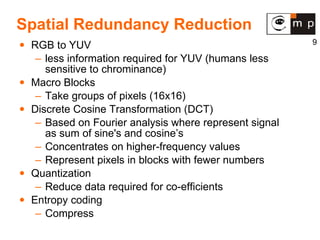
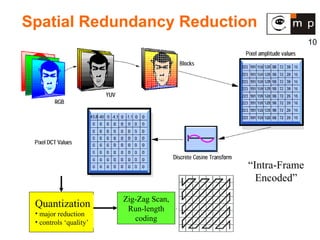
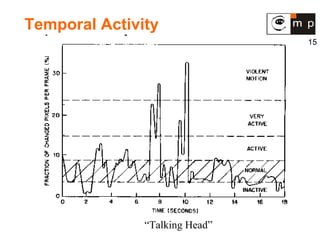
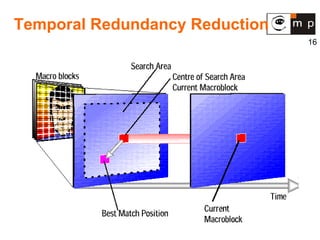
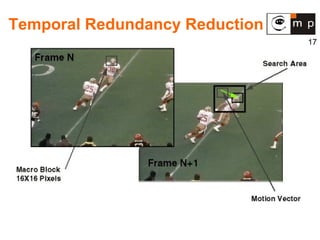
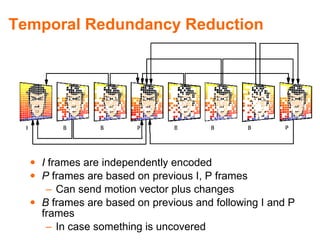
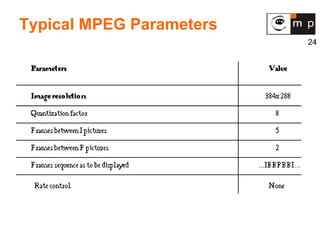
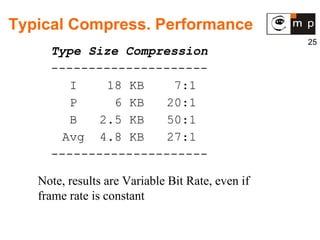
MPEG is a video compression standard developed in the late 1980s to enable full-motion video over networks and storage mediums. It was created by the Motion Picture Experts Group to address the need for high compression ratios to transmit video given bandwidth limitations of the time. MPEG uses spatial and temporal redundancy reduction techniques like discrete cosine transformation, quantization, and entropy coding to compress video frames and take advantage of similarities between neighboring pixels and successive frames. It defines a group of pictures structure and different frame types like I, P, and B frames to enable features like random access while maintaining synchronization and error robustness. MPEG became widely adopted and evolved through standards like MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG
![MPEG: A Video Compression Standard for Multimedia Applications V áclav Hlaváč CTU Prague, [email_address] Initial material were slides of Didier Le Gall, Worcherster Polytechnic Institute.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/85videocompress-110602060809-phpapp01/85/85-videocompress-1-320.jpg)