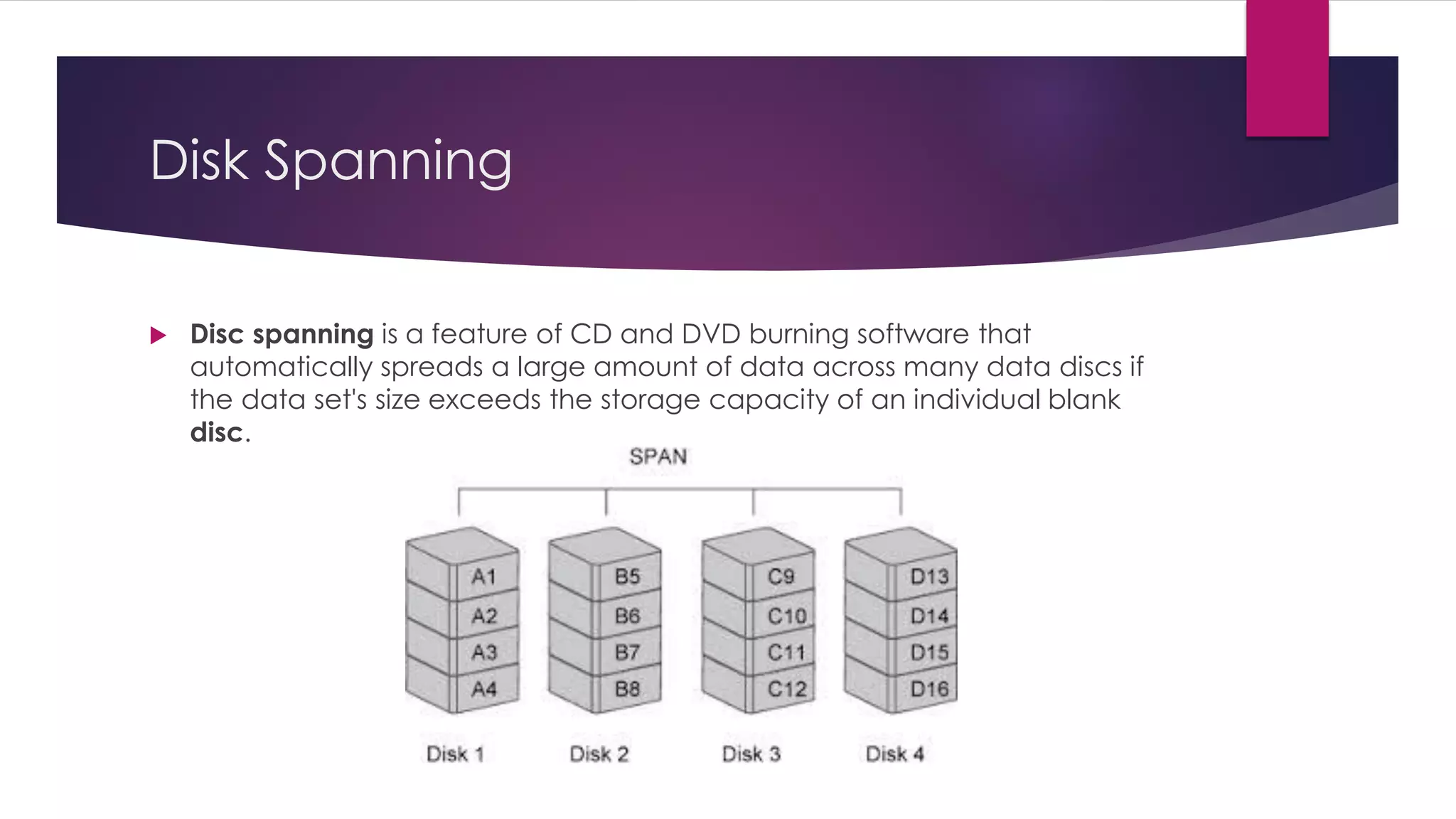
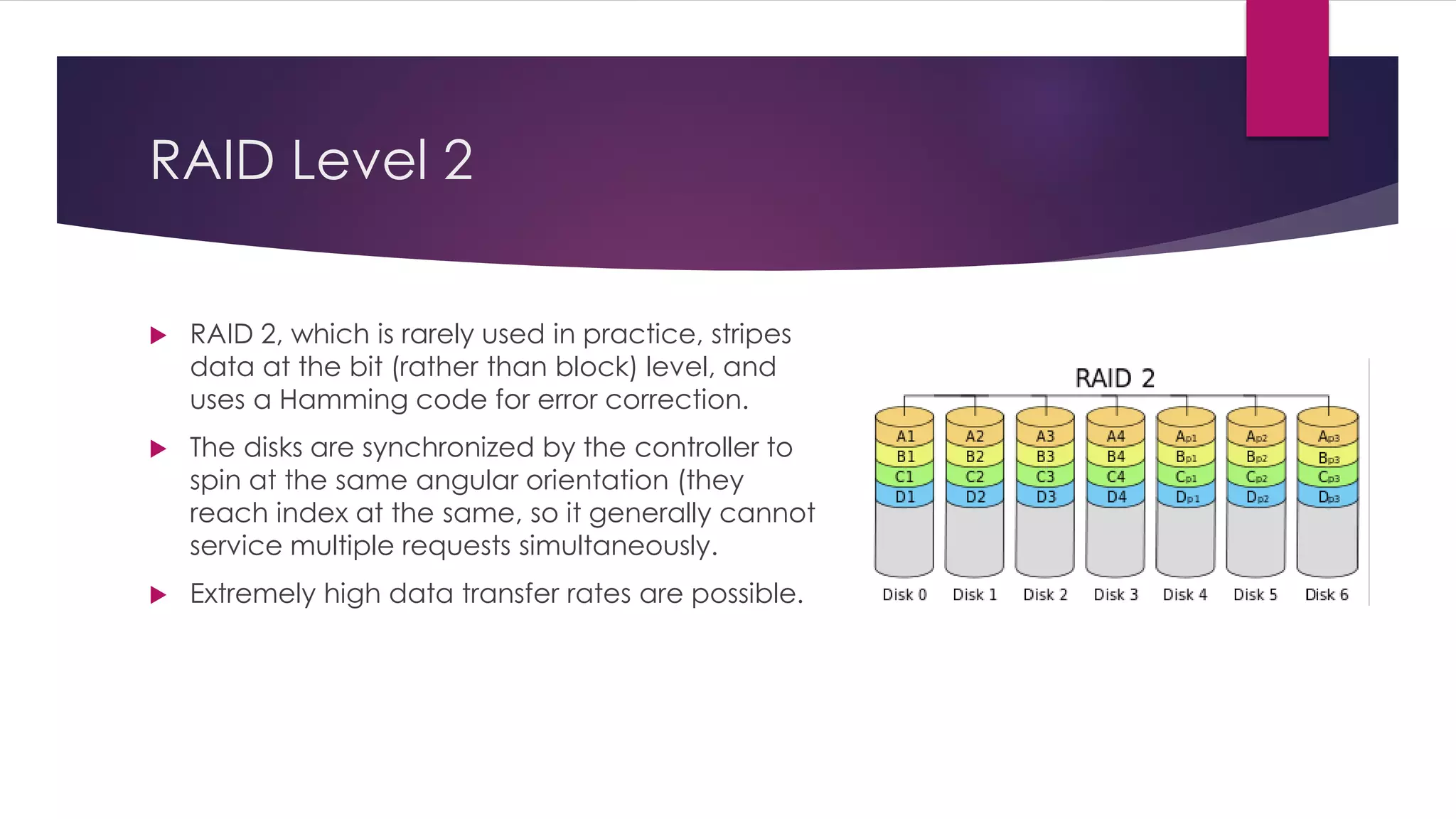
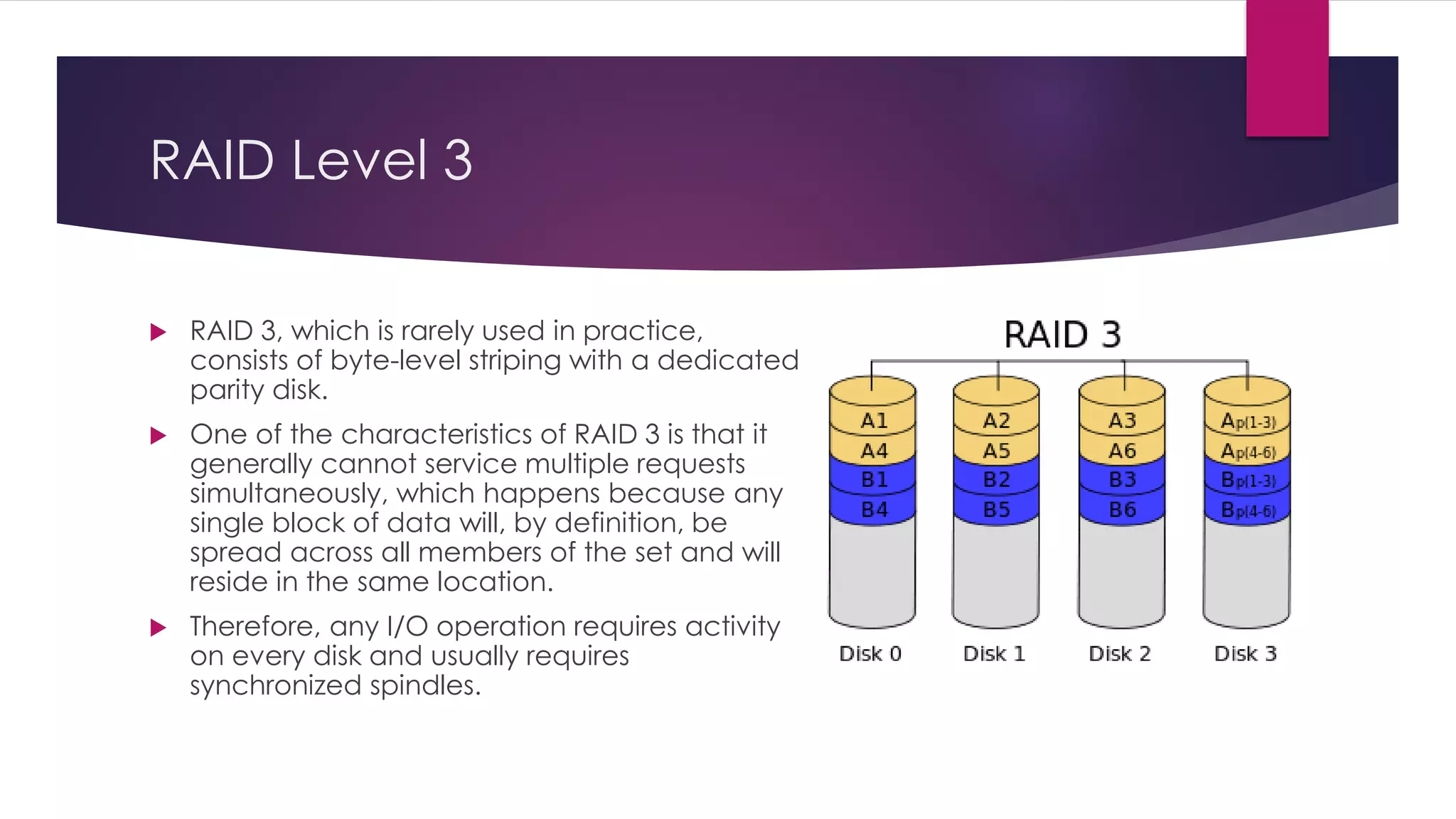
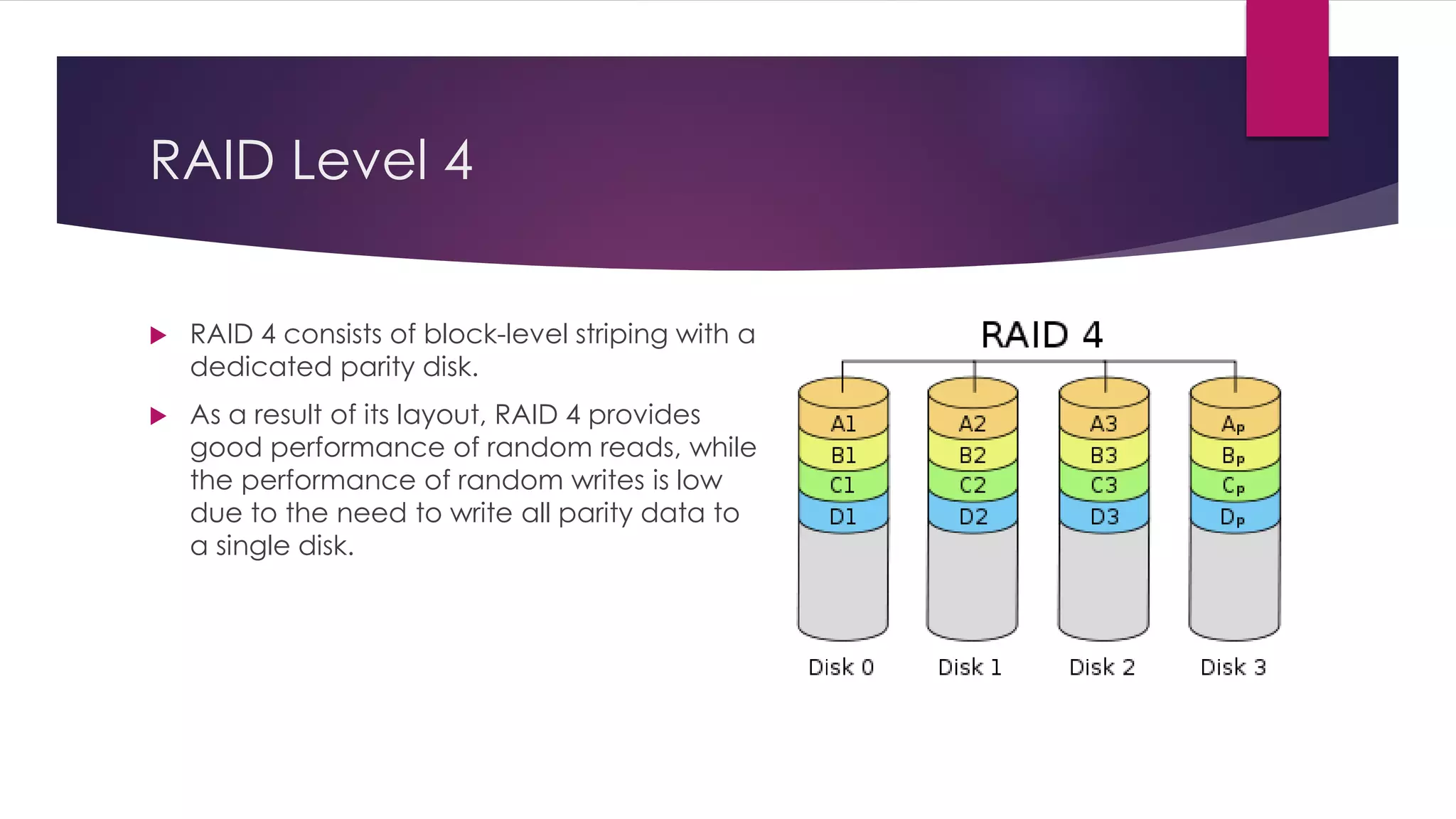
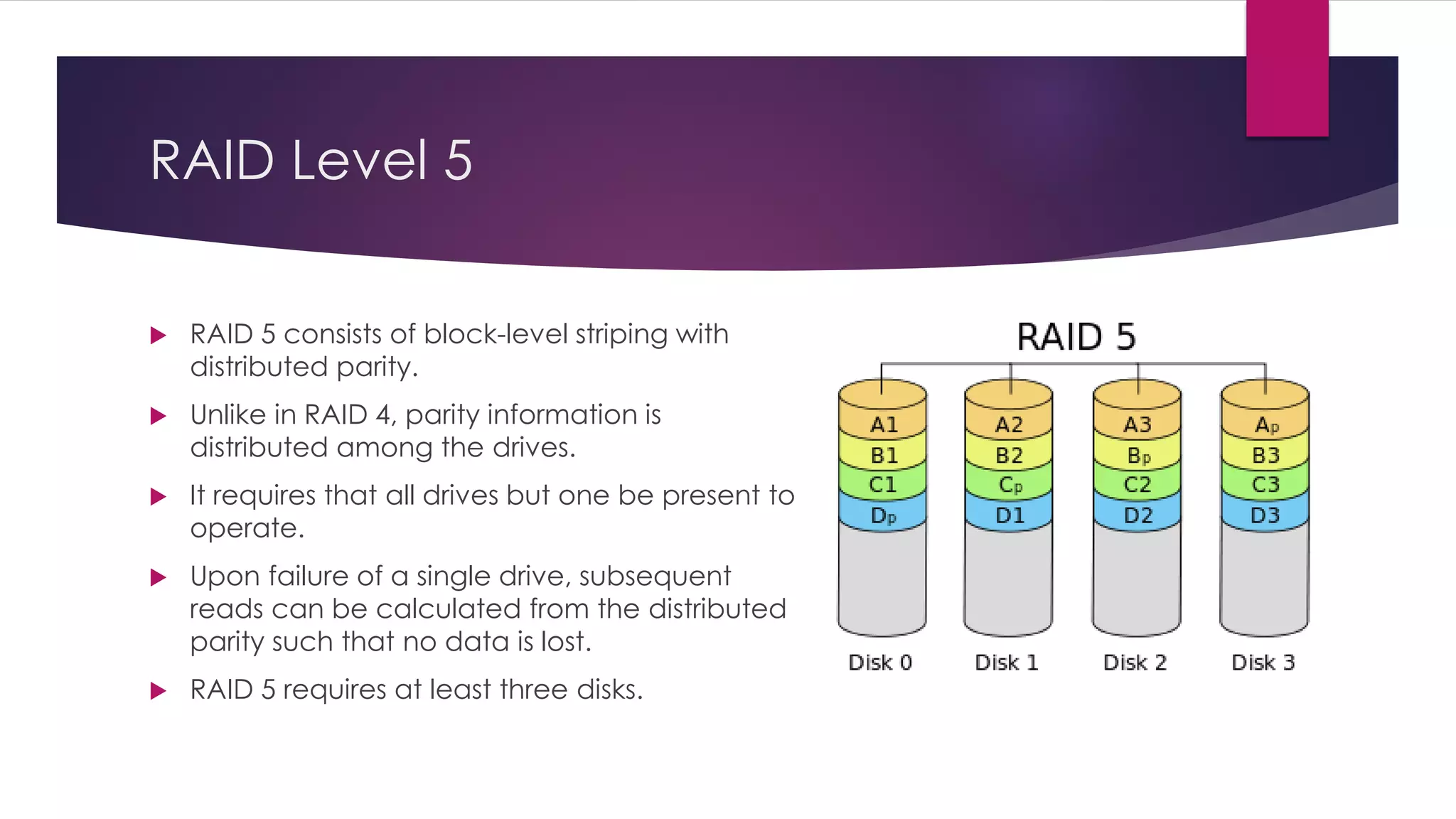
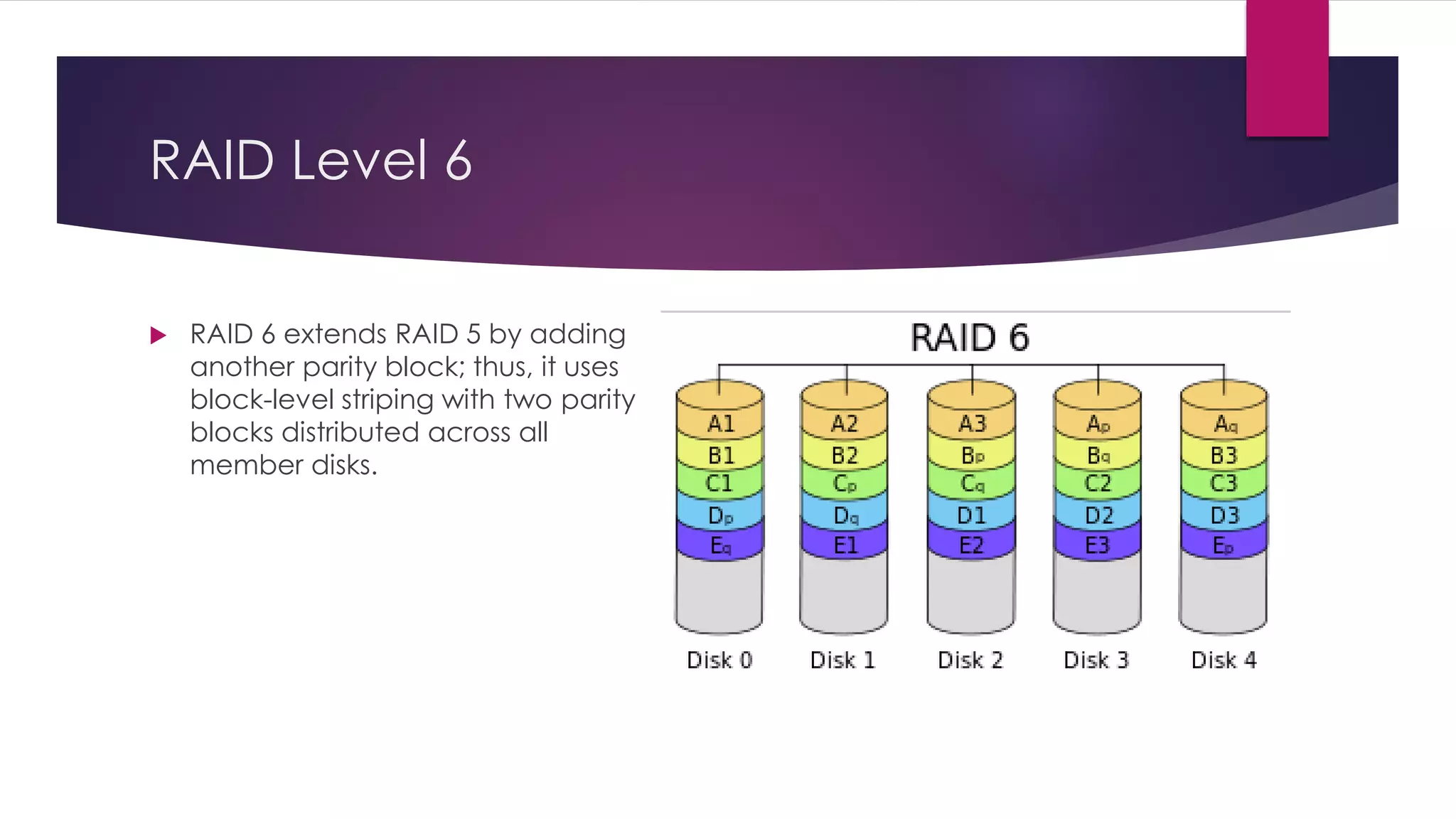
Chapter 8 discusses multimedia storage and retrieval, defining data storage devices and various methods of recording information. It explains multimedia storage mediums, types of media (continuous vs discrete), and RAID technology, including various RAID levels (0 to 6) with their characteristics and uses. RAID systems enhance performance and reliability, with detailed descriptions of each level's operational principles and fault tolerance features.