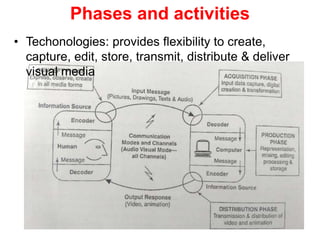
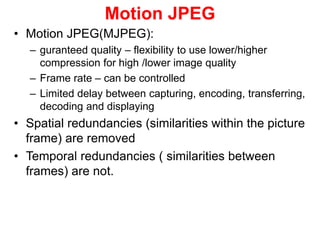
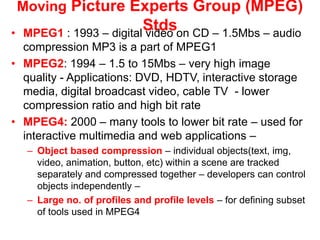
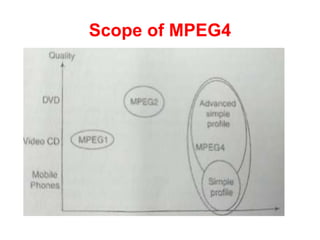
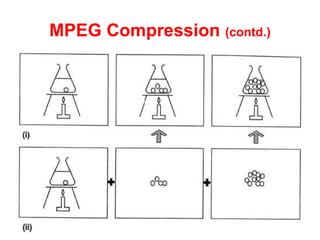
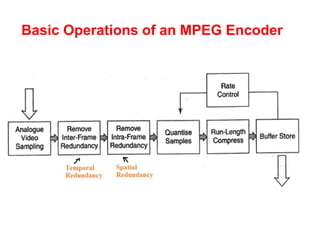
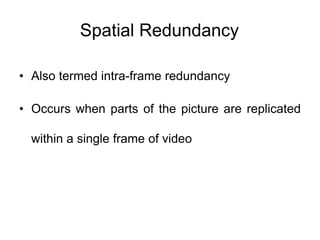
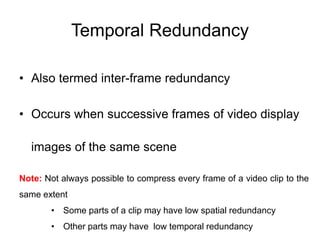
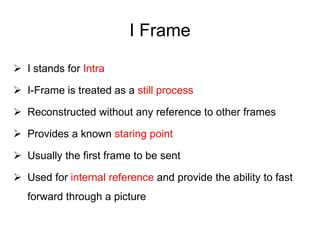
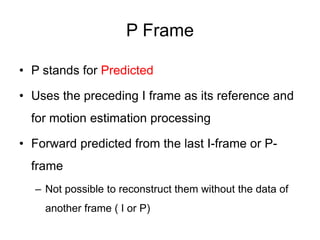
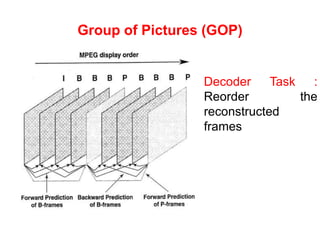
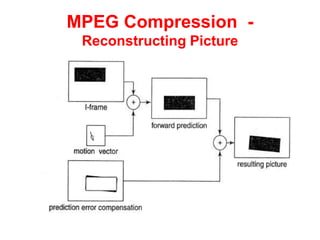
Video and animation involve capturing and displaying sequences of images to depict motion. Video uses real-world images while animation uses drawn or computer-generated images. MPEG standards like MPEG-1, 2, and 4 are used to compress digital video for storage and transmission by removing spatial and temporal redundancies between frames. MPEG compression involves three frame types - I, P, and B frames. I-frames are independent while P and B frames use motion prediction from previous and following frames. Grouping frames into GOPs allows efficient compression. The MPEG encoding and decoding process reconstructs frames using motion vectors and compensating for prediction errors.