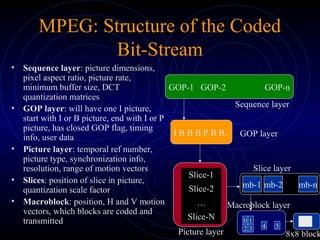
MPEG defines standards for compressing audio and video for digital media. This document discusses some key aspects of MPEG video encoding standards:
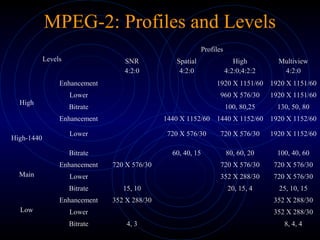
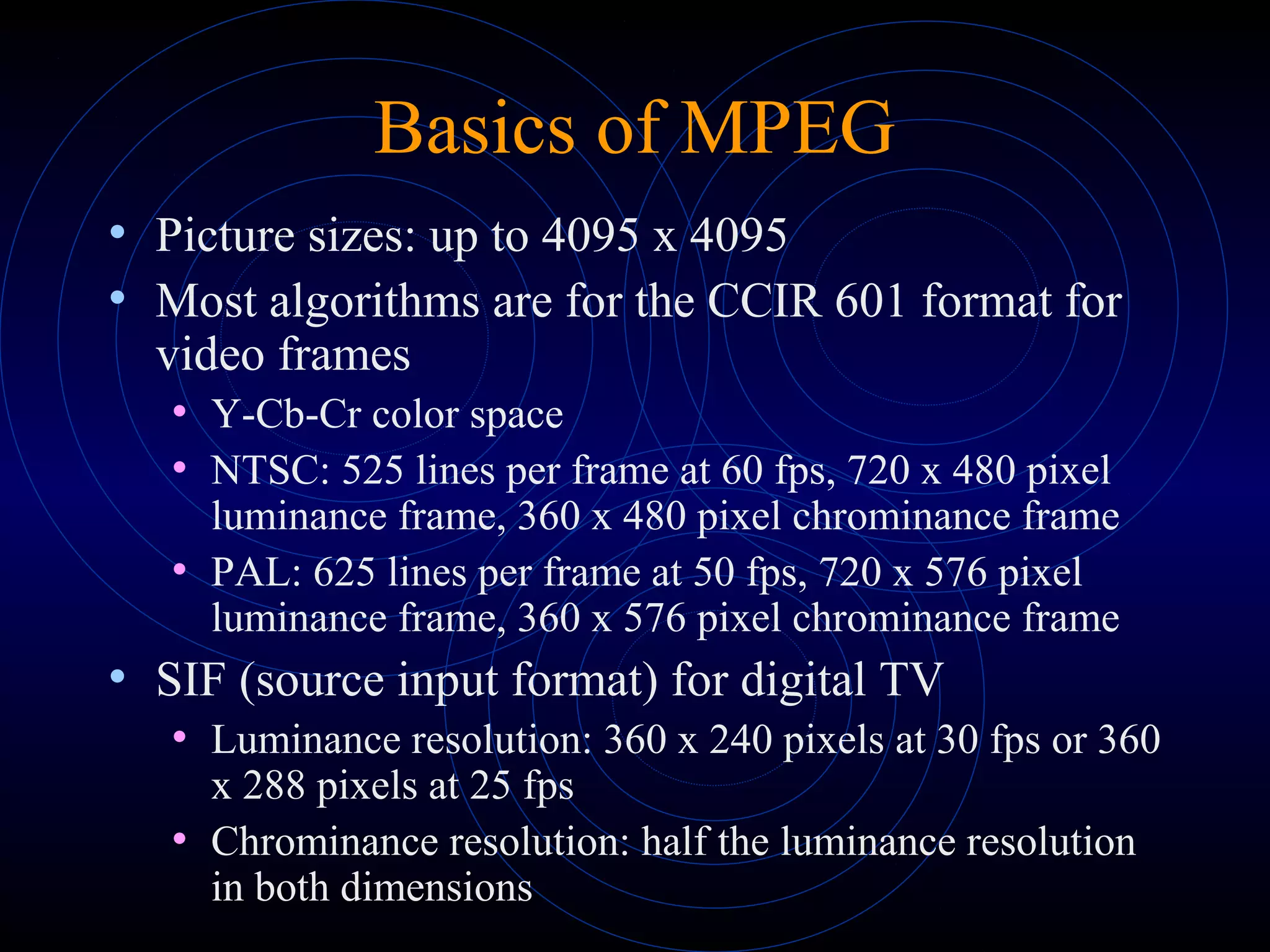
- MPEG supports a variety of picture sizes and frame rates for different video formats like NTSC and PAL. It uses YCbCr color space and different resolutions for luminance and chrominance frames.
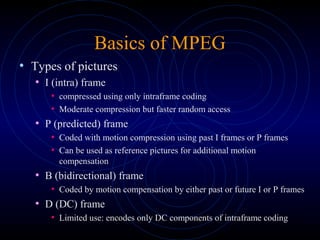
- MPEG uses I, P, and B frames coded with intra-frame and inter-frame compression. P frames use motion vectors from past reference frames while B frames use past and/or future reference frames.
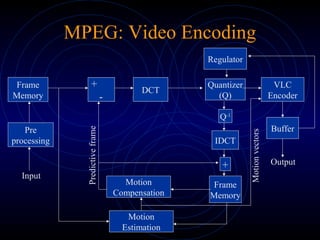
- The MPEG standard defines syntax for the coded bitstream but not the encoding process. Encoding involves motion estimation, compensation, DCT, quant



![MPEG: Macroblock Coding
c h a n g e
M Q U A N T
n o c h a n g e t o
M Q U A N T
I p ic t u r e
c h a n g e
M Q U A N T
n o c h a n g e t o
M Q U A N T
c o d e d n o t c o d e d
in t e r fr a m e
c h a n g e
M Q U A N T
n o c h a n g e t o
M Q U A N T
in t r a fr a m e
m o t io n c o m p .
A
m o t io n v e c t o r
s e t t o 0
P p ic t u r e
A
F w d m o t io n
c o m p e n s a t io n
A
B w d m o t io n
c o m p e n s a t io n
A
in t e r p o la t e d
c o m p e n s a t io n
B p ic t u r e
P ic t u r e T y p e
A
MQUANT= scale factor q
],[
],[8
],[
jiqQ
jiDCT
jiQDCT =
Quantization
matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mmclass5b-140513064004-phpapp01/85/Mmclass5b-8-320.jpg)