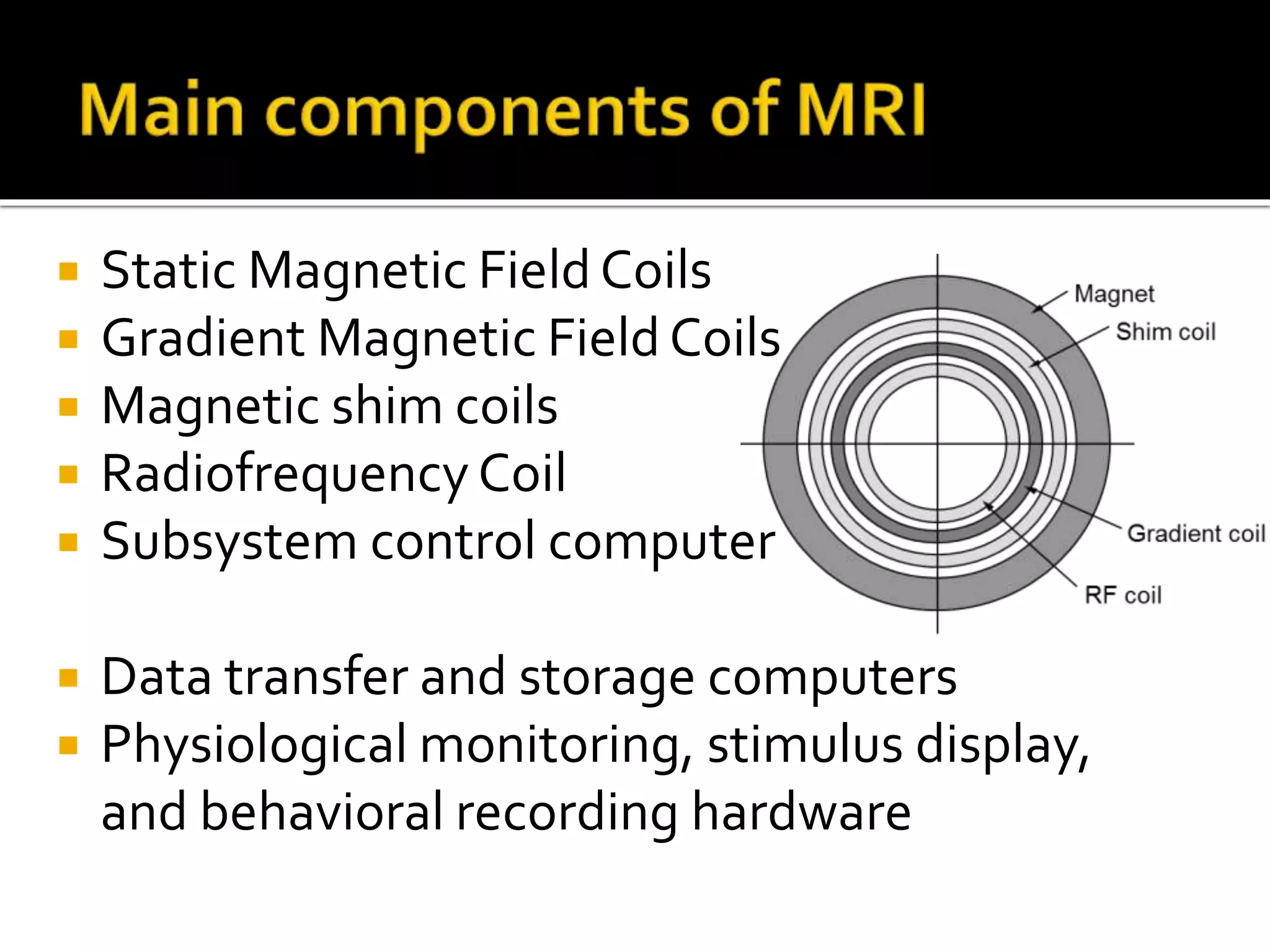
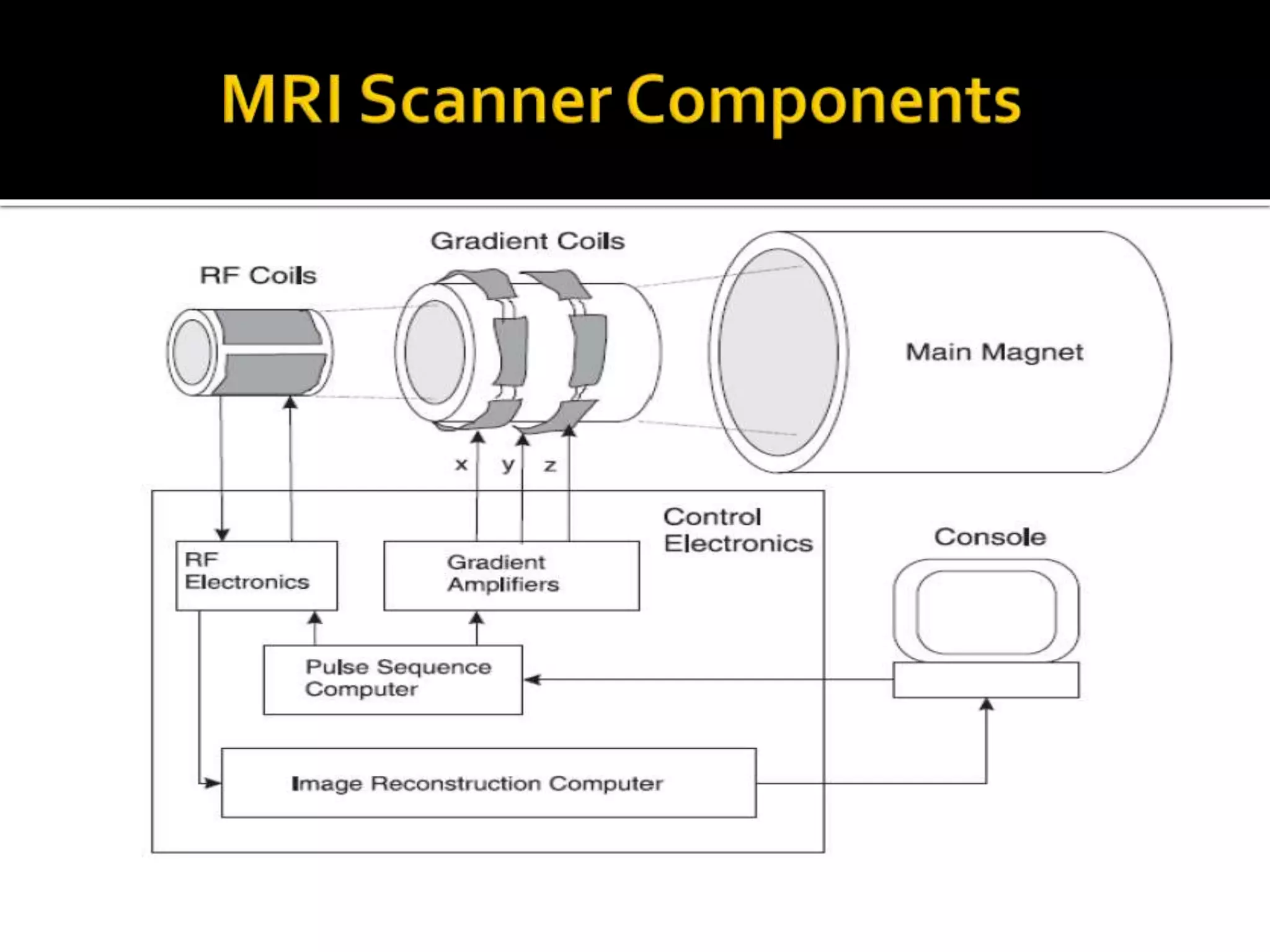
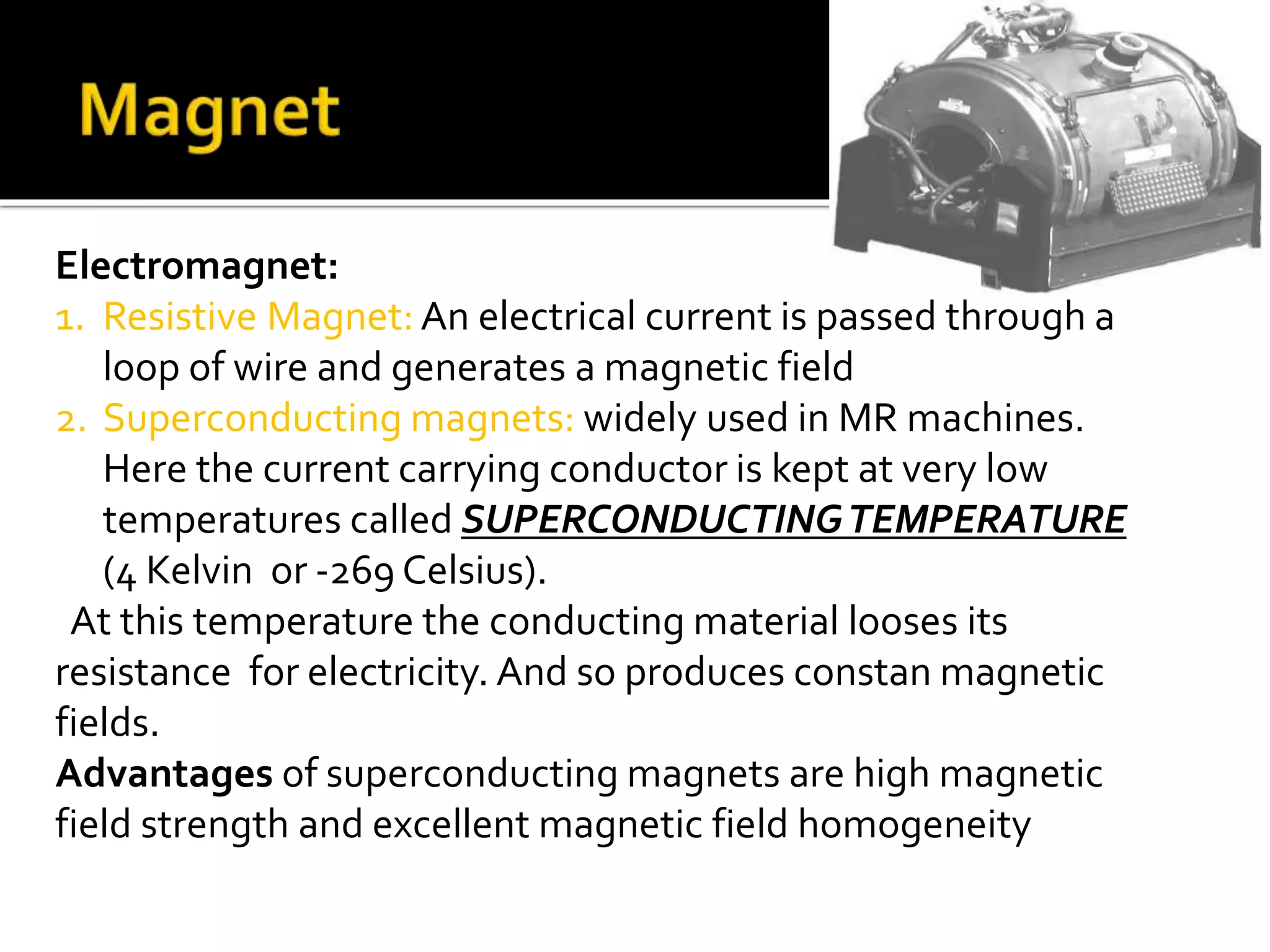
This document introduces the key components of an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) system. It describes the static magnetic field coils, gradient magnetic field coils, magnetic shim coils, radiofrequency coil, subsystem control computer, data transfer and storage computers, and physiological monitoring equipment that make up an MRI system. It then provides details on static magnetic fields, including that those used in medical imaging are typically between 0.5 and 1.5 Tesla. It discusses permanent and electromagnets, focusing on superconducting magnets which are widely used due to their ability to produce high, homogeneous magnetic fields when kept at very low temperatures. Finally, it describes the purpose of radiofrequency coils and magnetic shim coils in MRI systems.