Embed presentation
Downloaded 78 times




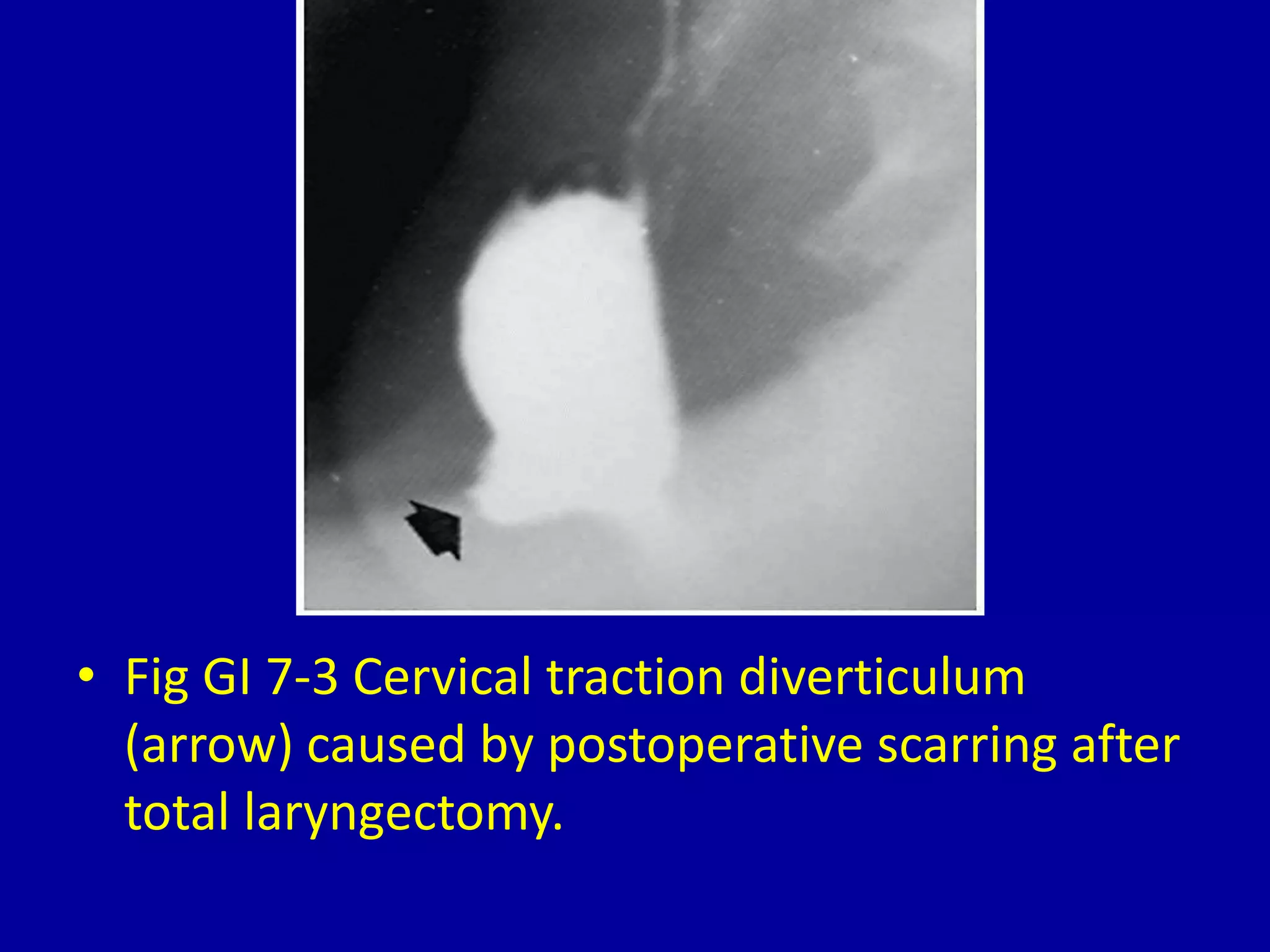

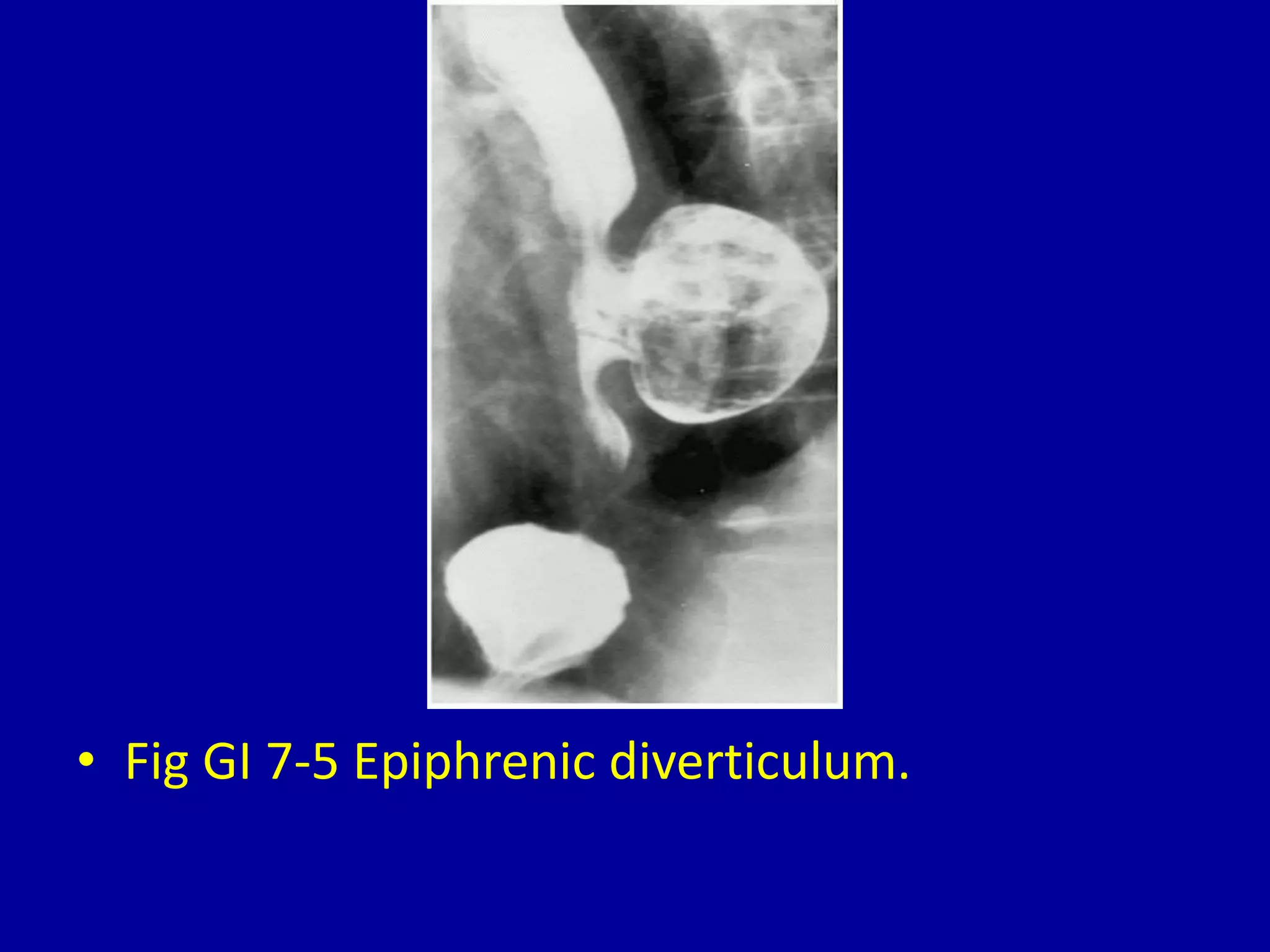

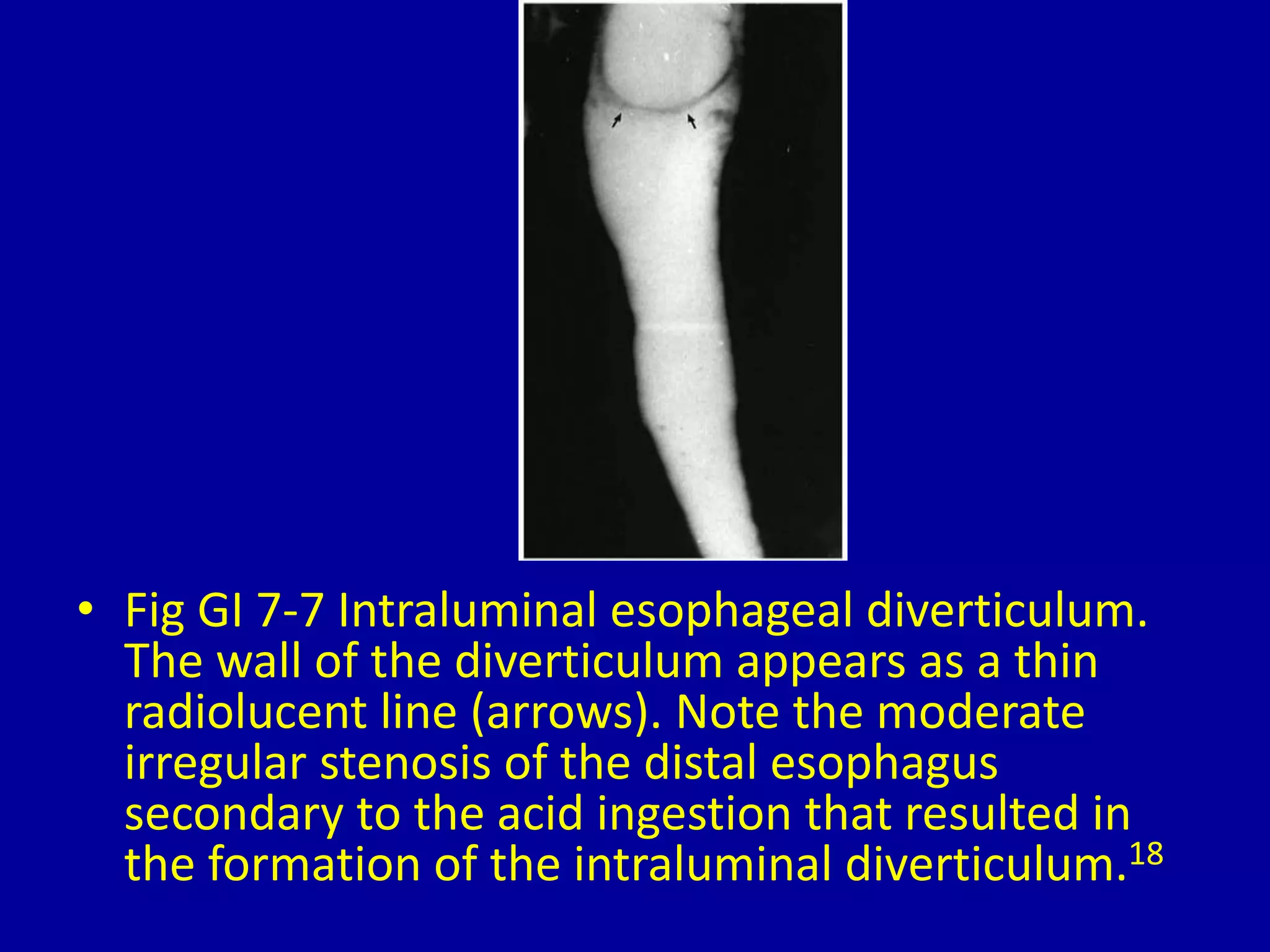



This document discusses and provides images of different types of esophageal diverticula. It defines and shows examples of Zenker's diverticulum, cervical traction diverticulum caused by post-operative scarring after laryngectomy, thoracic diverticulum, epiphrenic diverticulum, intramural esophageal pseudodiverticulosis, and intraluminal esophageal diverticulum. The final image shows an intraluminal diverticulum caused by acid ingestion resulting in moderate stenosis of the distal esophagus.
Introduction to esophageal diverticula and imaging techniques for diagnosis.
Visual representations of small and large Zenker's diverticulum affecting the esophagus.
Illustration of cervical traction diverticulum due to scarring post-laryngectomy.
Images depicting thoracic diverticulum and epiphrenic diverticulum in the esophageal region.
Illustrations of intramural pseudodiverticulosis and intraluminal diverticulum with related complications.










