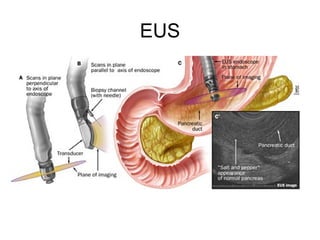
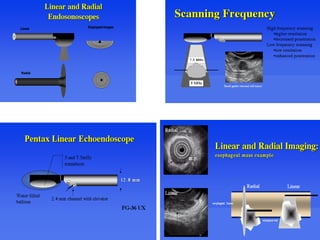
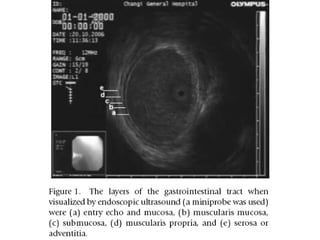
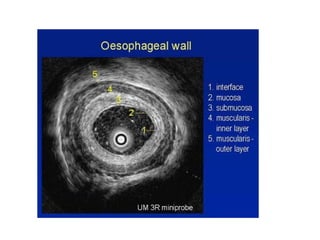
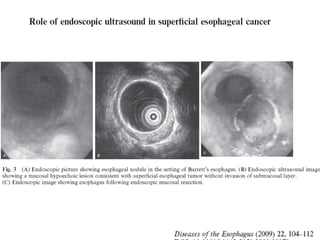
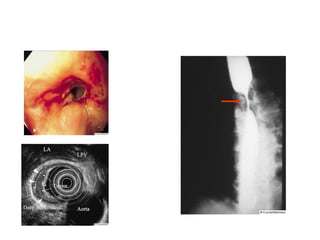
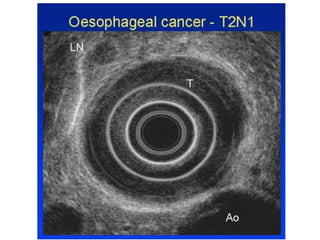
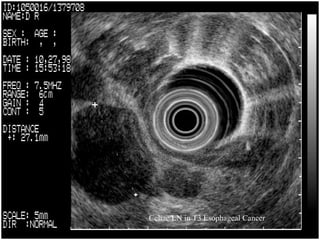
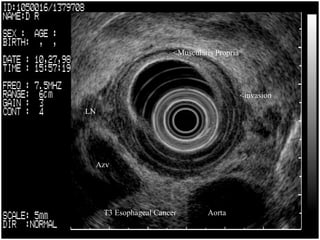
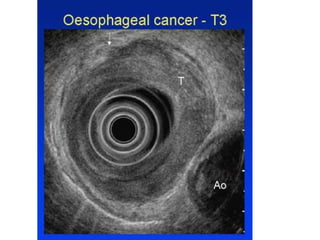
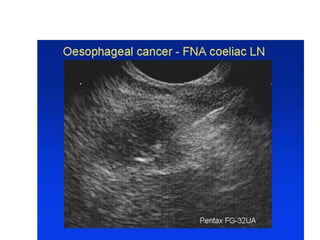
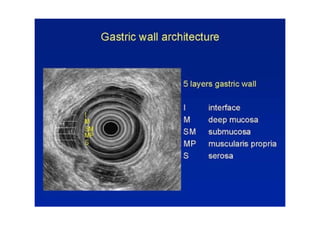
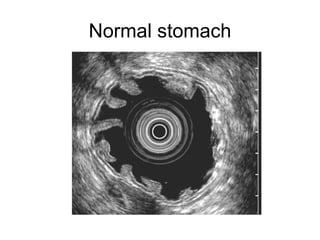
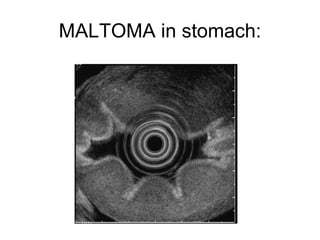
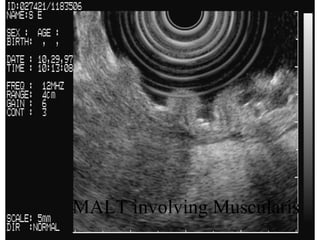
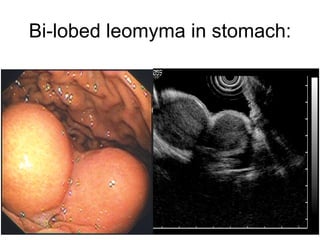
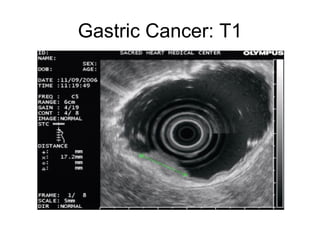
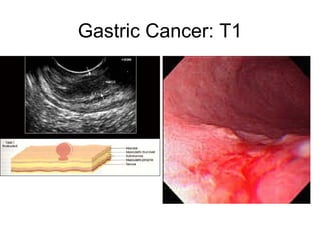
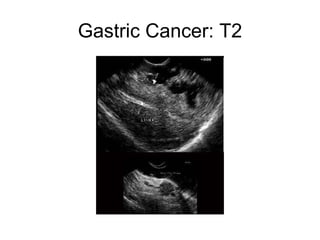
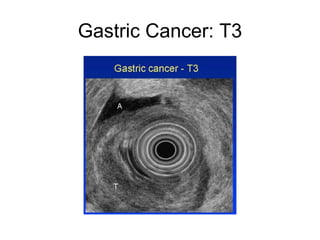
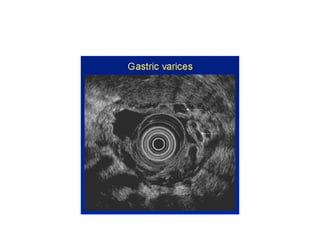
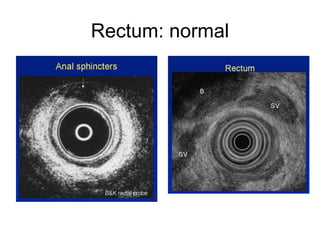
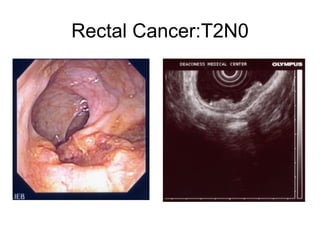
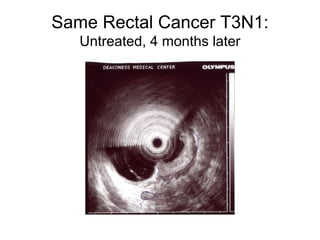
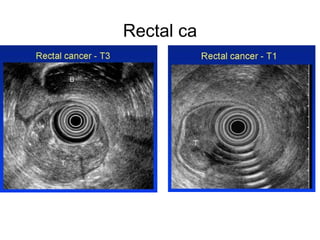
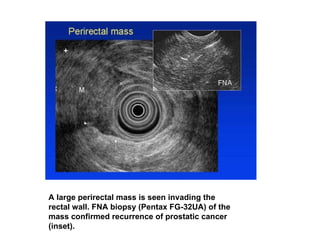
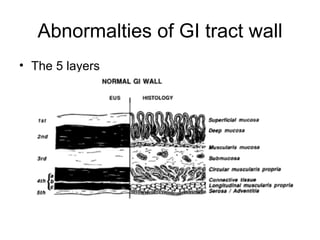
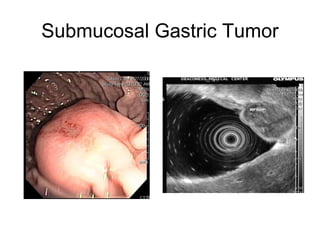
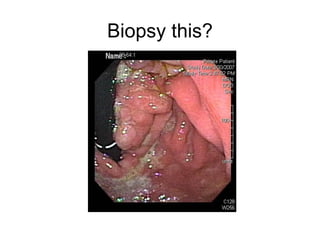
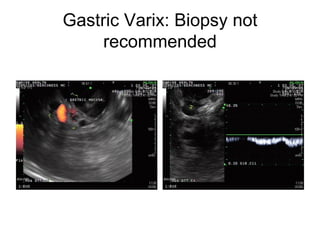
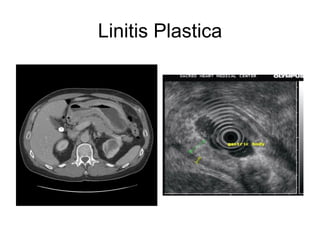
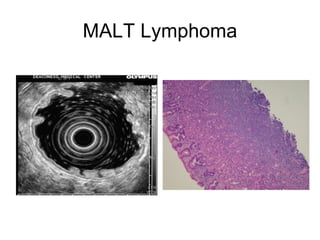
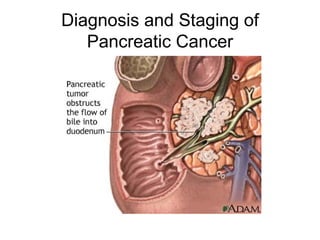
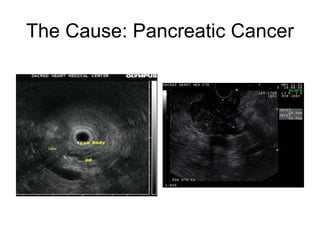
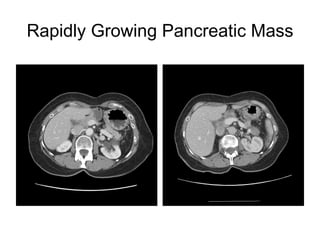
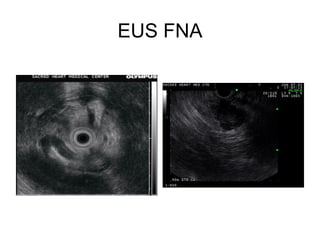
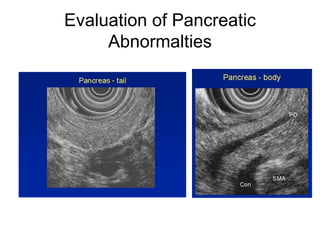
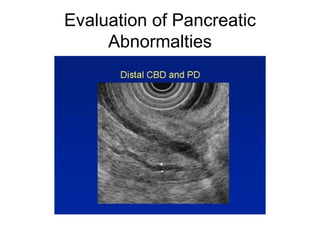
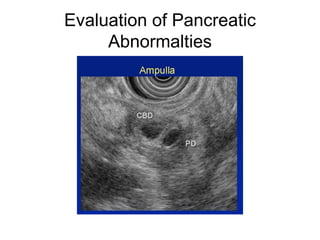
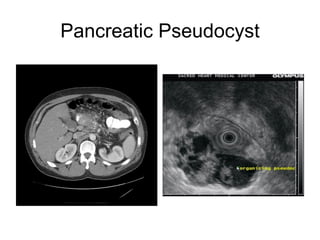
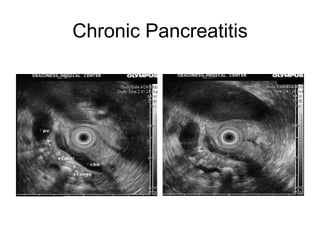
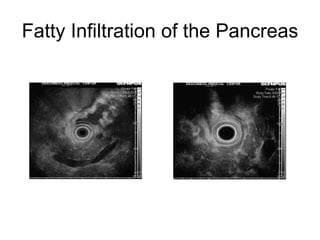
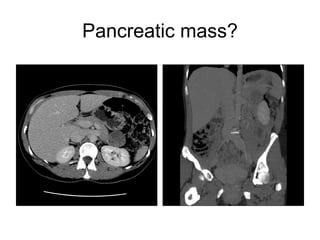
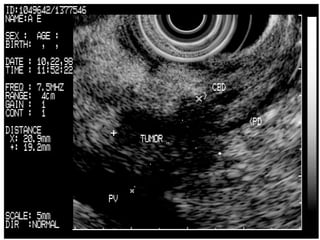
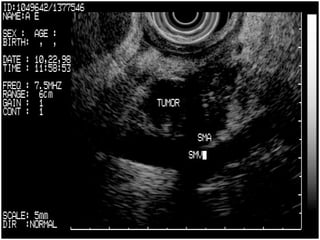
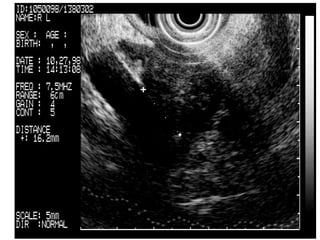
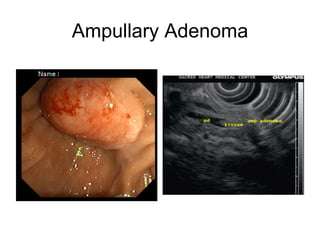
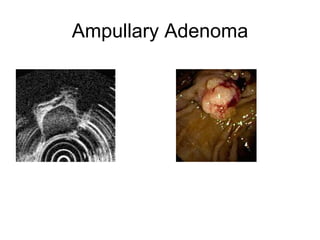
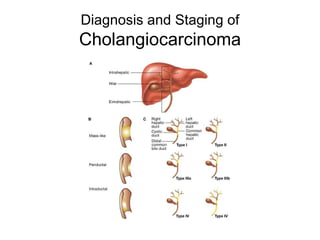
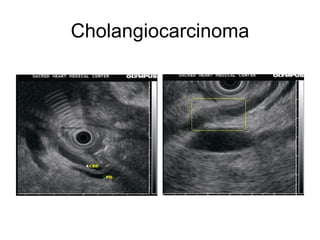
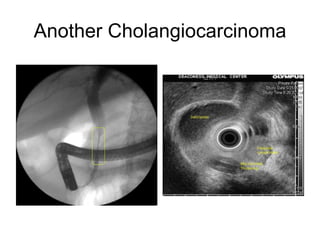
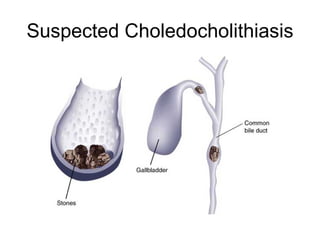
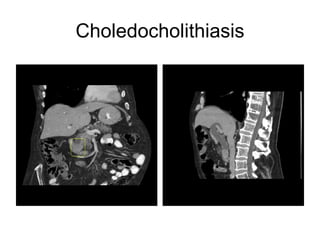
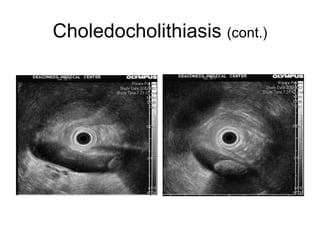
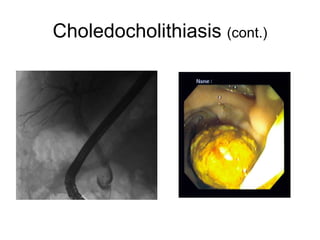
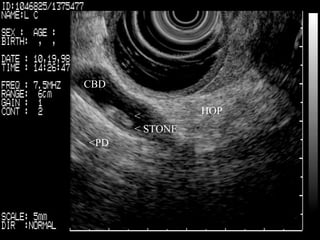
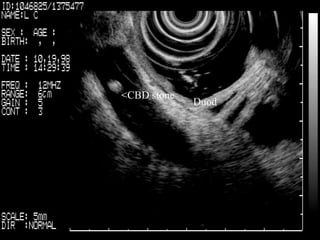
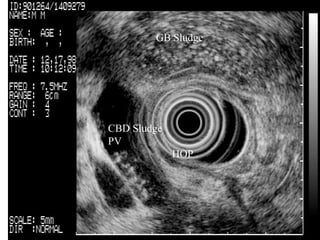
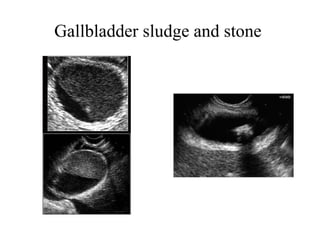
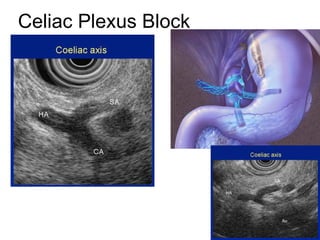
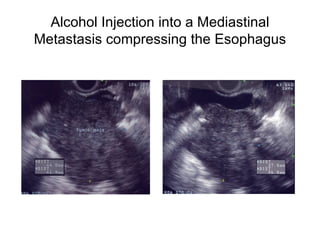
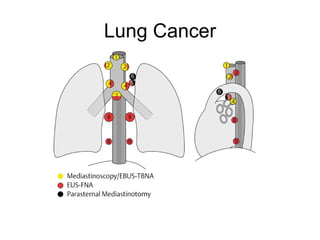
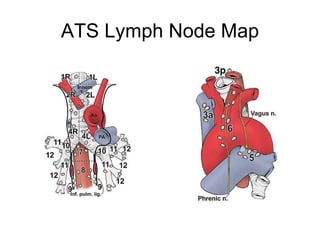
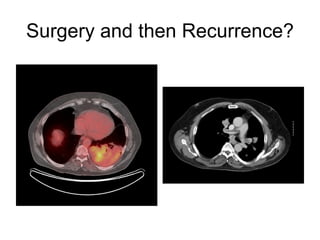
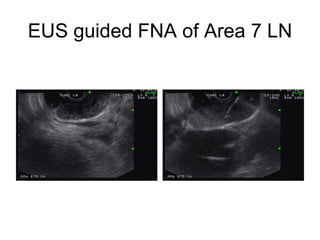
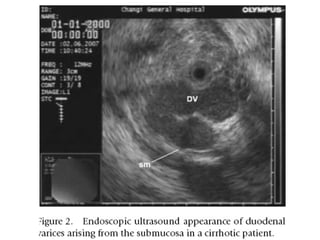
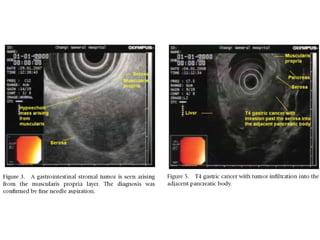
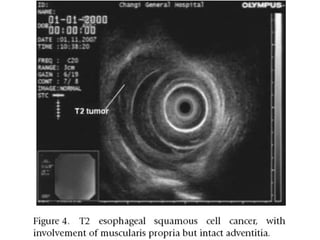
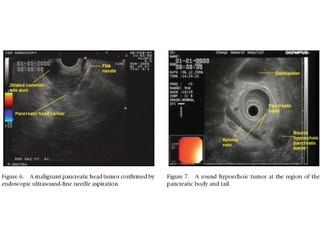
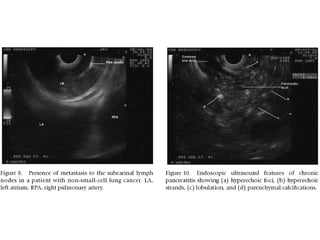
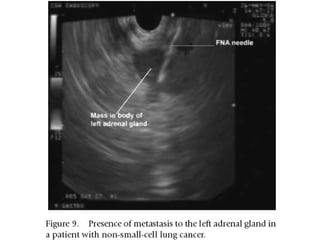
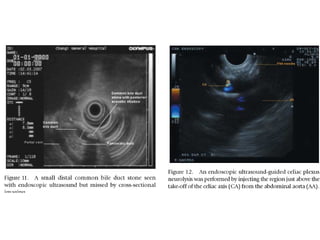
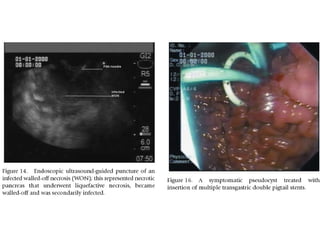
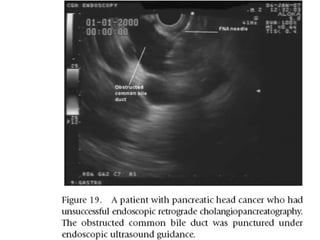
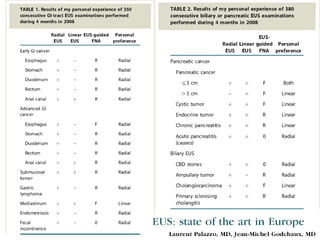
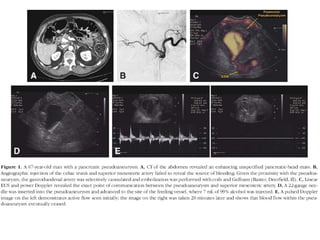
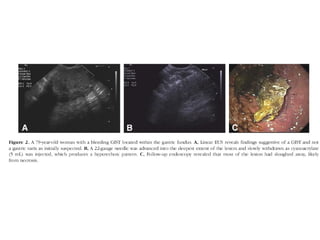
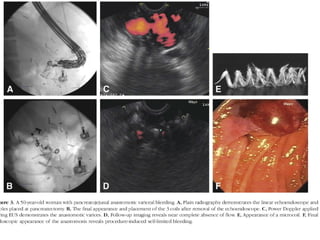
EUS can be used to stage cancers of the esophagus, stomach, rectum, lung and diagnose pancreatic cancer. It allows evaluation of abnormalities in the GI tract wall and adjacent structures. EUS guided FNA biopsy enables cytopathological diagnosis of cancers and nodal metastases. EUS is well-suited for TNM tumor staging as it can assess depth of tumor penetration, locoregional nodal spread and vascular invasion. It also has applications in diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, evaluation of pancreatic cysts and masses, and celiac plexus neurolysis for pain relief.