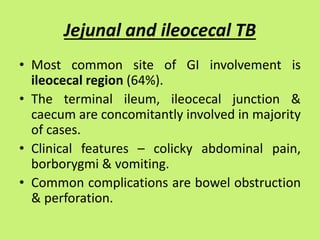
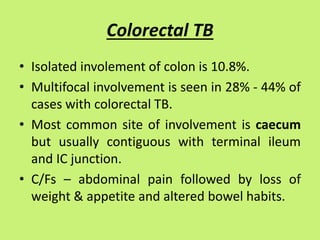
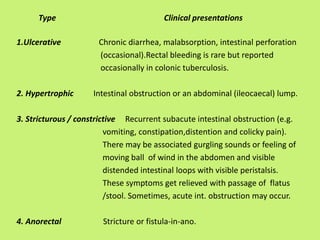
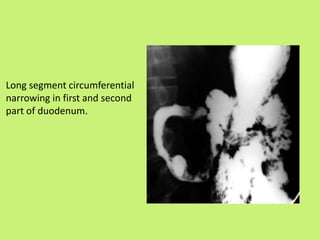
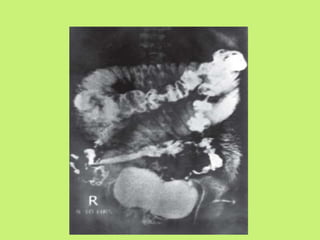
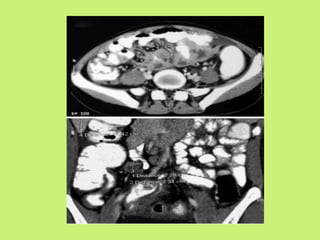
1. Abdominal tuberculosis poses a diagnostic challenge due to its non-specific symptoms which can lead to delays in diagnosis and complications. It commonly involves the lymph nodes, peritoneum, and gastrointestinal tract like the ileocecal region.
2. Imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scan, barium studies and laparoscopy are important for diagnosis as they can show features like lymphadenopathy, bowel wall thickening, strictures, and ascites. Histopathological examination of biopsy samples typically shows non-caseating granulomas.
3. Treatment involves a 6-month course of anti-tuberculosis drugs which is effective in resolving lesions. Surgery is only indicated for complications like obstruction or perfor