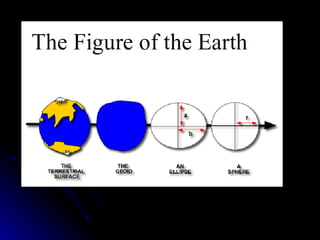
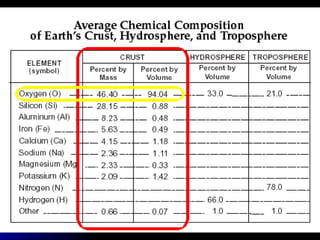
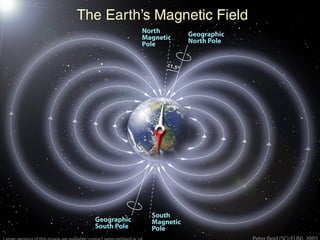
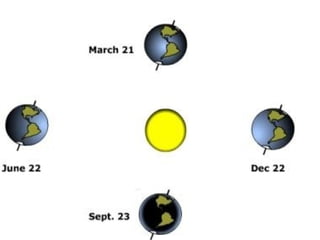
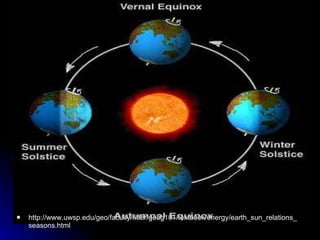
The document summarizes key properties and dynamics of the Earth, sun, and moon systems. It describes the Earth as an oblate spheroid that rotates daily on its axis, causing night and day. It also revolves yearly around the sun, resulting in seasons due to the tilt of the Earth's axis. The summer and winter solstices occur when the sun is at its maximum distance from the equator in each hemisphere, while equinoxes occur when the sun is directly above the equator.