The document discusses several theories of mental development and memory:
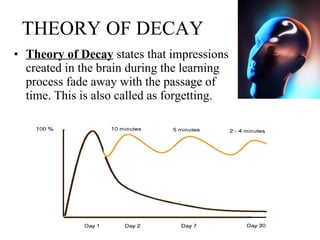
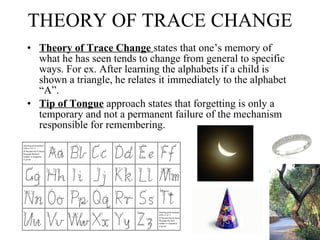
1. There are three main theories of memory and forgetting - the theory of decay, interference, and trace change.
2. The theory of decay states that memories fade over time. The theory of interference says memories can be disrupted by other memories. The trace change theory is that memories become more specific over time.
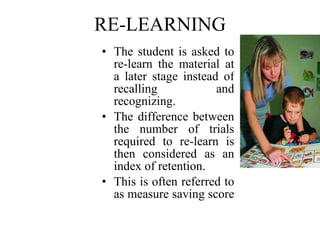
3. Psychologists use recall, recognition, and re-learning to measure memory retention. Recall tests free recollection, recognition identifies previously seen items, and re-learning measures saved effort.