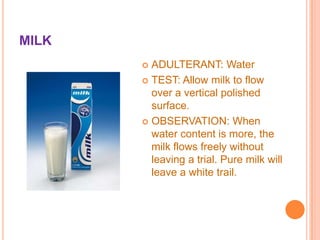
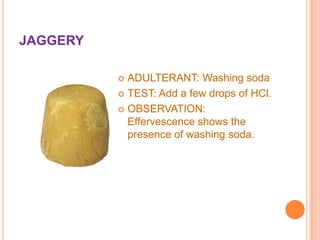
This document summarizes consumer rights and protections in India related to unfair trade practices and food adulteration. It outlines the Consumer Protection Act of 1986, which was enacted to protect consumer interests and establish councils to settle disputes. The objectives of the Central and State Councils are described, including the rights to protection from hazardous products, access to product information, and redress against unfair practices. Common types and methods of detecting adulteration in foods like rice, wheat, pulses, milk, ghee, and spices are then explained. The document concludes by describing where to lodge complaints about adulteration.